Analysis of Foreign Exchange Business of Rupali Bank Limited
This report shows an analysis of import, export and foreign exchange remittance business of RBL. To complete the study two types of data were gathered – primary data and secondary data. All the managers, FE officers of Authorized Dealer Branches and responsible person for international division of Rupali bank ltd. are related with the foreign exchange business. The data collection sources are 27 AD branches. The total sample size is 55. Primary data collected through structured questionnaire with easily understandable open ended form.
Going through different document and papers, annual report, brochures, manuals of RBL, web sites the secondary data is collected. It is found that the volume of foreign remittance is better than import and export business. All the branch of RBL are engaged for foreign remittance transactions that’s why volume of foreign remittance is highest. Compared with the export, import volume is higher. From the above study it can be said that if RBL takes proper steps to for arranging easier way for inflow of foreign remittance and skilled manpower are placed for providing better service, then the inflow of foreign remittance will be increased significantly. For export, invention of new product, diversification of traditional goods like jute, searching new destinations providing incentives to exporters etc. are obvious for increasing export-remittance. On the other hand new customer needs to be finding out solving the existing problem to strengthen the FE business of RBL.
Statement of the Problem
Rupali Bank ltd. is providing service with its 535 branches. All the branches are doing general banking but only 27 branches are engaged for doing foreign exchange business along with general banking. These 27 branches are Authorized Dealers branches. Though the number of the AD branches is very small but it plays significant role in the international trade of RBL. Import, export and foreign remittance are three sections of foreign exchange business. Foreign exchange business of RBL is not satisfactory compared with the expectation. Foreign exchange transactions depends on some issues among them enough skilled manpower, technological advancement, foreign correspondence, marketing policy, working environment are important. The entire essential sector was stable without developing due to the improper decision of management. All the AD branches are not doing foreign exchange business. Volume of import, export and foreign remittance are not equal in every year. This report will mainly focus on finding out the issues that has to be solved to increase the overall foreign exchange business of Rupali Bank Limited.
Objectives of the Study
The broad objective of the study is to examine the foreign exchange performance of Rupali Bank Ltd. However, the specific objectives are the following:
(1) To investigate the present pattern of import, export and foreign remittance of RBL.
(2) To compare year wise import, export and foreign remittance business of RBL.
(3) To identify whether there is any problem in import, export and foreign remittance of RBL.
(4) To suggest the better ways for increasing the foreign exchange performance of RBL.
METHODOLOGY
Target population involved in FE business of RBL
All the managers, officers and responsible person for international division of Rupali bank ltd are related with the foreign exchange business. These foreign exchange officers are selected for the focus group for this research.
Managers —————————-27
Branch Officers———————32
ID Officers—————————16
Total———————————-75
Methods of collecting data
For conducting a survey accurate data and information should be collected from the right sources. For the present study two sources were used for collecting data. They are as follows:
- Primary data
- Secondary data
(a) Primary Data:
Primary data collected through structured questionnaire with easily understandable openended form. By face to face conversation with related officers and high officials of RBL primary data have been gathered. Data were collected from managers, officers and responsible person of international division of Rupali Bank ltd by face-to-face interview also.
(b) Secondary Data:
Going through different documents and papers, annual report, brochures, manuals of RBL, web sites the secondary data were collected. Official records related to foreign exchange kept in International Division of RBL were also consulted. Over the last few years, a few studies have been done on migrants’ remittance. Along with these studies and reports of Central Bank, Rupali Bank Ltd., and various websites related to foreign exchange constituted secondary information.
Sampling Plan
Study Population:
All the employees responsible for the foreign exchange department of twenty seven AD branches of RBL are the targeted population of this study. The managers, Department in charges, officers and responsible officers of international division are includes under population.
Sampling Frame:
As the number of officers responsible for the foreign exchange department is fixed and enlisted. The researcher has collected list of all the officers responsible for the foreign exchange business. Then the researcher has arranged the name according to alphabetical way. The samplings were taken randomly. The data collection sources are 27 AD branches. The total sample size is 55. Similarly customer list was collected from the Authorized Dealers branches. Total sample size for the customer was 30.
Analysis of Data
The researcher conducted primary data analysis through questionnaire review and studied additional data from secondary sources. All the collected data have been analyzed with MS Excel Spread sheet and MS Excel graphical presentation.
Variables covered
To evaluate the foreign exchange performance of RBL the following variables are covered:
- Foreign exchange policy
- Import & export transactions
- Foreign remittance transactions
- Inflow & out flow of remittance
Software used
In processing the data, MS Word and MS Excel was used. Tables and Graphs were prepared using respective facilities provided by MS Excel.
Foreign Exchange
Foreign exchange means – foreign currency and includes any instrument drawn, accepted, made or issued under clause (13) of Article 16 of the Bangladesh Bank Order 1972.
– all deposits, credits and balances payable in any foreign currency.
– any draft, travelers cheque, letter of credit and bill of exchange expressed and drawn in Bangladesh currency but payable in any foreign currency.
Foreign exchange is money denominated in the currency of another nation or group of nations. Foreign exchange can be in the form of cash, funds available on credit and debit cards, travelers cheque, bank deposits, or other short-term claims. When a company sells goods or services to a foreign customer and receives foreign currency, it needs to convert domestic currency. When importing, the company needs to convert domestic to foreign currency to pay the foreign supplier. This conversion usually takes place between the company and its bank.
Foreign Exchange Transactions is transactions that have any one of the following features-
- Involves any currency other than local currency i.e. cross currency transactions.
- Involves at least one country other than own country i.e. cross border transactions.
Identification of Foreign exchange Transactions
- Rupali Bank sell USD to a customer on account of import
- Rupali Bank issues FDD to a student who goes for abroad for study
- Rupali Bank sells USD to someone for travel abroad
- Rupali Bank Sanctions a USD loan to M/s. Bengal leather complex ltd., a local company.
- X (a resident) wants to pay Mr. Y (a non-resident)
Authorized Foreign Exchange Dealers
The act provisions authorized dealers in foreign exchange. It restricts foreign exchange dealings like buying, borrowing, selling, lending, conversion etc. by any person other than an authorized dealer. The authorized dealers have to comply with general and/or specific directions and instructions issued by Bangladesh Bank from time to time. The authorized dealers shall, before undertaking any transaction in foreign exchange on behalf of any person, require that person to declare that the transaction will not involve any violation of the act.
Regulatory Authority
There are two regulatory authorities for the foreign exchange business. Local rules and international customs. Among the local rules BB guide lines, rules from MoF, rules from MoC, Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, 1947 Chief controller of import and export. International regulatory authority is ICC publications like UCPDC-600, URC, and URR.
IMPORT
Import means to purchase goods from outside of the country and bring the goods inside the country. From the very beginning RBL has embarked on extensive foreign exchange business with a view to facilitating international trade transactions of the country. The bank has established credit of import financed included electronic equipment’s, sports goods, rice, wheat, seeds, soybean, polyolefin, dyes, chemicals, accessories etc.
For the import processing in RBL, an importer has to take import registration certificate from the chief controller of import & export. The following papers are taken at the time of issuing letter of credit in RBL
(i) Application
(ii) Pro-forma invoice/ indent order
(iii) Insurance cover note
(iv) Letter of credit authorization form
(v) IMP form
(vi) Charge form
(vii) Trade license
(viii) IRC
(ix) Income tax certificate
(x) Member ship certificate
(xi) VAT registration certificate
Types of Importer
Commercial importer
It means an importer is registered under the imports, exporters and indentors registration order, 1981 who import goods for sale. When issued to a commercial importer, gives the category held by him with ITC classification and public notice against which they are admitted into import trade.
Industrial importer
When issued to an industrial consumer, gives the items of import as raw materials and packing materials and spare parts etc.
Import Procedures of RBL
- Registration of importer
- Furnish the relevant papers/documents through the nominated bank one can demand notice from CCI&E
- The nominated bank of the applicant will scrutinize the papers/documents and verify the signature of the applicant
- L/C authorization form
- Opening of L/C
- Task of Banks- The issuing bank opens/issues the L/C in accordance with the instruction/request of the importer and request another bank located in the seller’s/exporters country to advise the L/C to the beneficiary. The issuing bank may also request the advising bank to confirm the credit, if necessary.
- The advising bank advises/informs the seller that the L/C has been issued.
- As soon as the exporter/ seller receives the L/C and is satisfied that he can meet the L/C’s terms and conditions, he is in a position to make shipment of the goods.
- The negotiating bank examines the documents and if found O. K negotiates the documents and sends the said documents to the L/C issuing bank.
- After receiving the documents the L/C issuing bank also scrutinizes the documents and if found o.k. makes the payment to the negotiating bank.
- The L/C opening bank then requests the importer to receive the documents on payments.
- The importer after paying all dues receives the documents from the L/C issuing bank and then releases the imported goods from the port authority.
- Import against LCA form without opening L/C.
Documentary Credit/Letter of Credit
Documentary credit is an assurance of payment by the bank. It is an arrangement under which the bank at the request of the buyer or on its own undertakes to make payment to the seller provide specified documents are submitted. Documentary credit is an arrangement whereby a bank acting at the request and on the instruction of a customer or on its own behalf undertakes to make payment to or to the order of a third party or accept and pay bills of exchange drawn by the beneficiary, or authorize another bank to negotiate against stipulated documents provided the terms and conditions to the credit are complied. Thus, Documentary credits are a kind of bank guarantees. In popular language, they are known as letter of Credit. Bank guarantees are, however, issued to cover situation of non- performance whereas documentary credits are issued on behalf of the buyer to cover situation of performance i.e. the issuing bank agrees to make payment to the beneficiary once he surrenders the requisite complying documents.
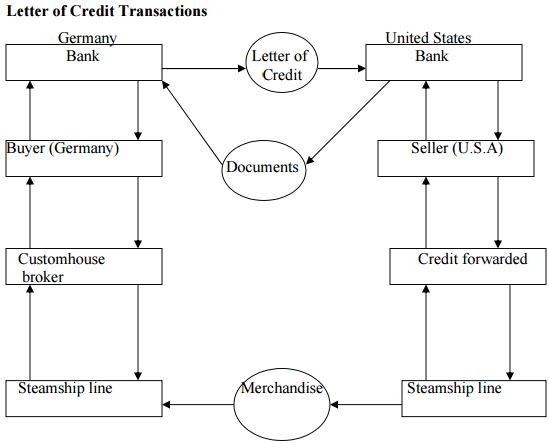
Figure illustrates the routes taken by the merchandise, letter of credit, and documents in a letter of credit transaction between a U.S seller and a German buyer. When the German buyer accepts the terms of sale that provide for confirmed and irrevocable letter of credit, she goes to her bank to arrange for opening the required letter. The buyer will furnish the bank with the information contained in the pro-forma invoice, specify the documents that the exporter must present to obtain payment, and set the expiration date for the credit. The German bank then instructs its correspondent bank in the United States to confirm the credit and inform the seller that it has been established. The seller prepares the merchandise for shipment and notifies the freight forwarder, which books space on a ship prepares the export documents and arranges to have the merchandise delivered to the port. The documents together with a sight or time draft drawn by the seller are presented to the U.S bank, which pays the seller and forwards the documents for collection to the German bank. To obtain the documents that give title to the shipment, the buyer in Germany must either pay the sight draft or accept a time draft. Having done, so the buyer receives the documents, which are the given to the customhouse broker. The customhouse broker acts as the buyer’s agent in receiving the goods form the steamship line and clearing them through German customs.
Parties to a Letter of Credit
- The issuing Bank
- The Confirming Bank, if any and
- The Beneficiary
Other parties, which facilitate the Documentary Credit
- The applicant
- The advising bank
- The nominated paying /Negotiating/ Accepting Bank
- The Transferring Bank.
Opening /issuing bank
Opening or Issuing bank is the bank which opens/issues a L/C on behalf of the importer. It is also called the importer’s/buyer’s bank.
Confirming Bank
Confirming bank is a Bank which adds its confirmation to the credit and it is done at the request of the issuing bank. The confirming bank may or may not be the advising bank.
Exporter’s /Seller/ Beneficiary
Exporter/Seller/Beneficiary is the party in whose favor the L/C is established.
Importer/Buyer
Applicant is the person who requests the opening bank to open a L/C. He is also known as importer/buyer/Consignee.
Advising/Notifying Bank
Advising bank is the bank through which the L/C is advised to the exporter. It is a bank situated usually in the exporting country and it may be a branch of the opening g bank or a correspondent bank. It may also assume the role of confirming and/or negotiating bank depending upon the conditions of the credit.
Negotiating Bank
Negotiating bank is the bank, which negotiates the bill and pays the amount to the beneficiary. It has to carefully scrutinize the documentary credit before negotiation in order to see whether the documents apparently are in order or not. The advising bank and the negotiating bank may or may not be one and the same. Sometimes it can also be the confirming bank.
Paying/Accepting Bank
Paying bank is the bank on whom the bill will be drawn. It is nominated in the credit to make payments against stipulated documents complying with the terms of the credit. It may or may not be the issuing bank.
Reimbursing Bank
Reimbursing bank is the bank, which would reimburse the negotiating bank. It is to be nominated by the issuing bank.
Transferring bank
Transferring bank is the bank which will transfer the L/C, being instructed by the original beneficiary.
Special Documentary Credit
Revolving Credit
The revolving credit is one that provides for restoring the credit to the original amount after it has been utilized. How many times it will be taking place must be specially mentioned in the credit. The revolving credit may be either cumulative or noncumulative.
Transferable Credit
A transferable credit is one that can be transferred by the original beneficiary in full or in part to one or more subsequent beneficiaries. Such credit can be transferred once only, unless otherwise specified. Fractions of a transferable credit can be transferred separately, provided partial shipments are not prohibited.
Back to Back Credit
The Back to Back Credit is a new type of credit opened on the basis of an original credit in favor of another beneficiary. Under the back to back concept, the seller as the beneficiary of the first credit offers it as security to the advising bank for the issuance of the second credit. The beneficiary of the back to back credit may be located inside or outside the original beneficiary country.
Red Clause Credit
A red clause credit is a credit with a special condition incorporate into it that authorities the confirming Bank or any other Nominated Bank to make advances to the Beneficiary before presentation of the documents. Under the above credit, the opening bank is liable for the pre-shipment advances made by the negotiated bank, in case the beneficiary fails to repay or deliver the documents for negotiation.
Standby Credits
The Standby Credit is a documentary credit or similar arrangement, however named or described, which represents an obligation to the Beneficiary on the part of the issuing bank to – repay money borrowed by the applicant, or advanced to or for the account of the applicant, make the payment on account of any indebtedness undertaken by the applicant, or make payment on account of any default by the applicant in the performance of an obligation.
Shipping Documents Required Under Documentary Credit
Following types of shipping documents are used in L/C operation –
- Transport Documents
- Commercial Invoice
- Insurance Documents
- Other Documents
(A) Transport Documents
The following transport documents are being used at present in the international trade –
i. Bill of Lading
ii. Airway bill/ Air Consignment Note
iii. Roadway Bill/ Truck Receipt
iv. Railway Receipt
v. Postal Receipt
vi. Courier Receipt
Bill of Lading
The bill of lading is the most important documents in international trade. It is signed by the master of the ship or shipping company or its agents acknowledging receipt of specified goods on board of the vessel for carriage which are deliverable to the consignee named in the bill, or to his order or his assignees in the same condition as they were received at an agreed destination on payment of a remuneration called freight.
A bill of lading is not a negotiable instrument though it has some features of negotiability. It can be transferred buy endorsement. The bill of lading serves three main purposes,
– As document of title of goods.
– As a receipt from the shipping company
– As a contract for transportation of the goods
Airway Bill/Air consignment Note
Airway bills / Air consignment notes are receipts evidencing the delivery of goods to an airline or its agent for transportation by air to a named consignee according to the defined and agreed terms. Airway bills /Air Consignment Notes are not negotiable instruments but still in most of the cases the airway bills are made out in favor of banks where the goods are consigned and so the financial interest of the exporter are well looked after.
Roadway Bill/ Truck Receipt
It is an internationally approved document of transportation when goods are sent by roads.
Railway Receipt
The Railway receipt/Railway consignment note is a receipt which is issued by the railway authorities when the exporter or his agent delivers a consignment to them for its onward carriage to a named destination indicating the details of the consignment and destination to which they would carry it.
Postal Receipt
It is receipt issued by the Post Office for the parcel they have received for direct delivery to the addressee.
Courier Receipt
It is a receipt issued by the courier service for the goods they have received/picked up for direct delivery to the addressee.
Contents of Transport Documents
In order to examine or recognize a transport documents it is very important to know its contents. A full-fledged transport document should contain the following information-
- Name of the carrier and be signed
- Description of goods
- Identifying marks and number
- The name of the carrying vessel or the intended vessel
- An indication of dispatch or taking in charge or loading on board and the place of final destination.
- Whether the freight has been paid or to be paid
- Terms and conditions of the carriage
- Date of issuance
(B) Commercial invoice
A commercial invoice is the seller’s bill for the merchandise. It is drawn up by the seller on his business letter-head and contains full details of the goods shipped or dispatched.
As such it is also termed as the description of goods dispatched. It contains full name and address of the consignee, quantity, quality, unit price and total price of the goods.
Commercial invoice does not have any standard form. Each exporter designs his own commercial invoice according to his requirement.
Types of commercial invoice-
- Consular Invoice
- Pro-forma Invoice
- Customs Invoice
- Certified Invoice
Consular Invoice
It is a special type of invoice which is required by some countries. It is an invoice made out in a specially printed form of the shipper and is shown as being correct in all respect before the consul of importing country stationed in the exporter’s country. The consul of the importing country may certify the invoice. It can also contain the declaration of the origin of goods. A consular invoice enables the importing country to have all accurate record of the merchandise shipped.
Pro-forma Invoice
Pro-forma invoice is a memorandum of the terms of contract of sale wherein the seller gives the quotation to the buyer. If the buyer approves the terms he sends a definite order for supply. Such invoice is marked with the words “Pro-forma Invoice”.
Customs Invoice
It is also a special type of invoice which can be certified by the custom authority as directed in the letter of credit. It depends on the demand of the importer or his country.
Certified Invoice
It is also a special type of invoice, which can be certified by the person or authority in the importers country who has inspected the goods and found in accordance with the letter of credit. It is also certified as the goods are of specific country of origin.
Contents of Invoice
The commercial invoice usually contents quality, quantity, unit price, total value etc. of the goods. It also contains complete reference of the letter of credit number, the related import license number and date, particulars of packages and identification mark on the packages and goods. The name of the carrying vessel and date, port of discharge are also recorded on the commercial invoice.
(C) Insurance Documents
Insurance policies are subject to average. The term average is used in marine insurance in a special sense. It means damage or loss.
General Average
A general average is a loss which is incurred for the common safety of all interest connected with the marine adventure. In order to protect the whole property or the ship or the cargo or to enable the ship to proceed safety to destination the results of the voluntary sacrifice are made.
Particular average
Particular average is a partial loss not the general loss, loss suffered by the insured goods and is caused by the particular peril for which the subject matter is insured against.
Contents of Insurance Documents
An insurance document generally contains the following information-
- The name of the insurer or his agent
- The name of the ship/Carrier
- The name of the assured
- The subject matter of insurance
- The time or the voyage insured
- The peril insured against
- The date and subscription
- The valuation
- The stamp
(D) Other Documents
- Weight list/Certificate
- Packing list
- Certificate of Origin
- Inspection Certificate
- Health, Veterinary and Sanitary certificate
- Phyto Sanitary Certificate
- Certificate of Analysis
Weight Certificate
It is a certificate which indicates the weight of the goods and the weight should show in all the documents.
Packing list
This list is prepared by the exporter showing item by item, the contents of the containers or cases to enable the importer to check the shipment. It should contain the description of goods, net weight and gross weight, measurement etc.
Certificate of Origin
A certificate of origin is statement evidencing the origin of the goods and it is required in compliance with exchange control regulation in the importing country. This certificate form is a part of the shipping documents.
Inspection Certificate
This is a certificate declaring that the goods have been examined and found to be in accordance with the letter of credit. This is signed by the manufactured or supplier.
Health, Veterinary and Sanitary Certificate
This certificate is an evidence of quality in order to meet health requirements in the country of destination or to satisfy the importer about the precise strength or chemical composition of the goods.
Phyto Sanitary Certificate
Phyto sanitary certificate is required for perishable items, such as, vegetables.
Certificate of Analysis
Certificate of analysis is a certificate issued by an independent authority accepted by the buyers and sellers who undertakes a sample checking of some particular type of goods concerning the strength of metal of chemical content and its quality.
EXPORT
Chowdhury, L. (2011), says, by the export we mean out earring of anything from one country to another. Export as sending of visible things outside the country for sale. Export trade plays a vital role in the development process of an economy. Import payment is settled with the export earnings.
Export Procedure of RBL
In the export processing various functions are done by the bank among them L/C advising and negotiations are very important. When a L/C comes to the bank for advising then exporter is informed by the bank. After getting the L/C exporter goes to prepare the goods as per L/C terms and conditions. After making the shipment exporter comes to the bank for negotiation. If bank finds all documents comply with the terms and conditions of the letter of credit then the bill is negotiated. Party finds the bill value and bank send the documents to the letter of credit issuing bank claiming the L/C value as per terms and conditions.
Preparation of export documents
These documents are prepared before the export shipment –
- Bill of exchange /draft
- Commercial invoice
- Bill of lading
- Inspection certificate
- Packing list
- Shipment advice
- Certificate of origin
- Weight certificate
- Certificate of analysis
- DHL courier Receipt
Export documents checking
These Export documents are checked very carefully before shipment –
- L/C restricted or not.
- Exporter has to submit documents before expiry date of the credit.
- Shortage of documents.
- Each and every point is verified with the L/C.
Flow chart for export
- Goods ready for shipment
- Inspection of the goods from the competent authority as per L/C terms
- Preparation of invoice and packing list and vessel booking particulars
- Papers to be sent to the C&F agent for shipment
- C&F will conduct the custom formalities. Checking the goods as per invoice & packing list inspection report.
- C&F wil take the permission for shipment/handover the goods to shipping co.
- After completion of all custom formalities, the nominating shipping co. received the goods for sail/load in the ship and issued a receipt which is known as mates receipt.
- Handing over the shipping receipt to the exporter by the C&F agent, original B/L may also be taken in payment of freight and other expenditure.
- Exporter may dispatch the shipment advice to the importer directly as per L/C terms.
- C&F agent receives the original B/L from the relative shipping co. and dispatches the same to the bank for negotiation or receives from the shipping co. directly.
- Exporter submits all original and duplicate sets of documents to the opening bank for negotiation.
- After negotiation bank should dispatch the documents to the opening bank for delivery of the goods from the port.
- Opening bank lodges the documents and make payment to the negotiating bank A/C as per L/C terms.
Export Financing
Pre-shipment finance is an advance granted by a bank to an exporter to meet the cost up to the packing of goods for export to overseas buyer. This is done in the pre-shipment stage. So it is also called pre-shipment advance. The purpose of the investment is for purchase of raw materials for finished goods or manufacturing processing, packing transporting up to warehoused /port of shipment etc. for export. Pre shipment is an advance for procurement of finished goods.
Issuance of Proceeds Realization Certificate (PRC)
Sometimes exporters require proceeds realization certificate to submit to the Govt. Agencies for refund of Duty draw back. After realization of the proceeds branch is issue PRC.
FOREIGN REMITTANCE
According to Chowdhury, L. (2011), remittance means transfer of Money/Fund from one place to another place/country through banking channel. Money send by wage earners’ through abroad is called Foreign Remittance. In a broad sense, Foreign Remittance includes purchase and sales of all Foreign Bills and currency on account of Import & Export transaction/payment and other purposes. Remittance means transfer of Money/Fund from one place to another place/country through banking channel. Inward Foreign Remittance (Incoming Foreign Remittance): Private Remittance, Indenting Commission, Recruiting Agents Commission, Export Bills, Importers Claim, Gift, Donation, Foreign Loan, Service Charges, FC Notes etc. (Inward Remittance by different Exchange House or Company through the NRTK account: Demand Draft, TT, Instant cash payment etc.)
Outward Foreign Remittance (Outgoing Foreign Remittance): Travel Expenses (Cash FC, TC), Medical Expenses, Education Expenses, Examination/Tuition Fees, Membership Fees, profit/dividend of Foreign Investment, Service Charges, Insurance Premium, Hajj Travel Expense, Foreign Loan Repayment, Consultation fees, Import Payment etc.
Parties of Foreign Remittance
The four major parties of remittances are:
- Remitter
- Remitting Bank
- Receiving Bank
- Beneficiary.
Remitter
Remitter is the people or organization who is sending foreign currency from one country to another country. Bangladeshi workers who are living in various parts of the world and send foreign currency to Bangladesh such as commissions, salary etc. are remitters.
Remitting Bank
Bank of foreign country by which foreign currency are sending is called remitting bank. Foreign currency has to be sent by through banking channel.
Receiving Bank
Receiving bank is the bank to which foreign currency are sent. Remitting bank use the SWIFT communication with the receiving bank and transfer the currency to the bank where remitter wants to deposit the currency.
Beneficiary
Remitter selects the name to which the currency will be sent. This people or organization is the beneficiary.
Modes of Foreign Remittance
There are various types of remitting money, such as:
Pay Order: Payment Order is used for making a remittance to the local beneficiary. Pay Order gives the payee the right to claim payment from the issuing bank. It can be enchased from issuing bank only. Unlike cheque, there is no possibility of dishonoring pay order because before issuing pay order bank takes out the money of the Pay Order in advance. Pay Order cannot be endorsed or crossed and so it is not negotiable instrument.
Local Demand Draft: Demand Draft (DD) is an order of issuing bank on another branch of the same bank to pay specified sum of money to the payee on demand that is the named person or order of the demand. It is generally issued when customer wants to remit money in any place, which is outside of the clearing house area of issuing branch. Payee can be a purchaser himself or another mentioned in the DD. It is a negotiable instrument and it can be crossed or not crossed.
Foreign Demand Draft: Foreign Demand Draft (FDD) is an order of issuing Foreign Bank/Exchange Company on a branch of a bank to pay specified sum of money to the payee on demand. It is generally issued when customer wants to remit money in any place, which is outside of the country of issuing bank. Payee can be purchaser himself or another mentioned in the FDD. It is a negotiable instrument and it can be crossed or not crossed.
Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
This Method transfers money from one place to another place by telegraphic message. The sender branch will request another branch to pay required money to the stipulated payee on demand. Generally for such kind of transfer payee should have account with the paying bank. Otherwise it is very difficult for the paying bank to recognize the exact payee. When sending money is urgent then the bank uses telephone for remittance. This service is only provided for valued customers, who is very reliable and with which banks have long standing relationship.
Foreign Telegraphic Transfer (FTT)
Foreign Telegraphic Transfer (FTT) is an order of issuing Foreign Bank/Exchange Company on a bank to pay specified sum of money to the payee. It is generally issued when customer wants to remit money in any place, which is outside of the country of issuing bank. After receiving the FTT’s order local bank can issue TT/TTPO like its local TT operation for remitting the fund to stipulated beneficiary.
Mail Transfer (MT)
When the remitter desires the banker to remit the funds to the payee instead of purchasing a draft himself the banker does it through a mail transfer advice. The payee must have an account with the paying office as the amount remitted in such a manner is meant for credit to the payee’s account and not for cash payment. It is the least used technique for transferring fund. Where there is no telex machine or telephone line then this method is used.
Foreign Remittance Trade Mechanism of Rupali Bank Ltd.
Rupali Bank Ltd acquires foreign remittance by purchasing foreign currency through exchange rate and its export business. Foreign currency sells through import business and also sells in local market.
The remittance trade mechanism of RBL includes –
(i) Purchasing of foreign currencies
(ii) Selling of foreign currencies
(iii) Selling of foreign currencies in local market
(iv) Front office activities
(v) Back office activities
Purchasing of Foreign Currencies
Rupali Bank purchases foreign currencies i.e. US Dollar (USD), British Pound Sterling (GBP), and other currencies by giving exchange rate. At present, Rupali Bank has established Taka Drawing Arrangement for purchasing Foreign Currencies with 21(twenty one) Exchange Companies in different countries like UK, USA, Canada, UAE, Oman, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait etc.
Selling of Foreign Currencies
Every day Rupali Bank sells foreign currencies i.e. US Dollar, British Pound Sterling, and any other currencies through competitive rate in local market and invests in its import business. To purchase any kinds of goods/products from abroad it is required to make Letter of Credit (L/C), which requires foreign currency. Rupali Bank invests foreign currencies in its import business while making L/Cs through its 27 Authorised Dealer (A/D) Branches. The surplus amount of foreign currencies sells in local market.
Selling of Foreign Currencies in local market
The Bank maintains two offices in selling foreign currencies i.e. Front Office and Back Office.
Dealing Room activities i.e. Front Office’s Activities
Front Office sells the surplus amount of foreign currencies in local foreign currencies market (i.e. sells foreign currencies to other local banks/financial institutes) in a specific competitive rate. Dealer makes the deal confirmation to other bank over telephone in a specific rate/period from front office and then they sent deal ticket to back office. The Back Office does other documentary work. The Dealer maintains three rates while selling and purchasing foreign currencies i.e. Spot Rate, Forward Rate and Cross Rate in Rupali Bank.
Spot Rate is used in buying and selling of currencies in the same day. In this system, purchasing or selling of currencies in the prevailing rate of the purchasing date.
Forward Rate is used in buying and selling of currencies in a specific forward day. In this system, purchasing or selling of currencies in the date of contact in a fixed rate after certain date.
Cross Rate is used in buying and selling of currencies through cross rate for third currency i.e. dividing/multiplying one currency by another currency other than local currency.
Back Office’s Activities
Back Office maintains all the required registers for proper handling currency market. Back Office provides all the documentary support of deal confirmation. After completion of deal by the Dealers, Back Office makes all necessary papers in respect of deal send it to respective bank to effect payment.
Facilities allowed in connection with foreign remittance
i. No commission is collected for collection of draft money from branches of the same bank.
ii. Payment of remittance money within three days.
iii. Customers can make any complain regarding the payment of money through compliance cell.
Major Problems of FE Business of RBL
The trend of foreign remittance over the period from 2004 to 2014 is in increasing trend. Whereas import and export business has downward trend in some years. The gradual increase of total amount of foreign remittance during the last nine years indicates that the foreign remittance business of Rupali Bank limited is stronger compared with the import and export business. The following are the major findings of the analysis
(i. Rupali Bank Ltd. has no foreign exchange marketing policy to develop the foreign exchange business.
(ii. Rupali Bank Ltd. is lagging behind its counterparts in remittance business as regards automation/computerization of transactions. RBL has not yet gone for fully online banking that is very much required for quick delivery of remittance instructions. Some payment messages require Branch, identification under the present system, which cause delay in settlement.
(iii. No. of AD branches are not enough to increase the business volume and all existing AD branches are not doing both import and export business.
(iv. Manpower shortage is one of the notable weak points of Rupali Bank Limited that creates serious problem in handling foreign exchange business. Skilled foreign exchange employees are going on retirement. Expert employees are not replaced in the vacant positions.
(v. Most of the AD branches are doing business with the existing customers.
(vi. Ensuring timely delivery and quality services relating to foreign exchange business depends on the availability of logistic support. Major branches are not equipped with sufficient support instruments like phone, Fax, e-mail compared with other competitor banks.
(vii. Branch decoration is one of the important issues to attract the customer that is very poor situation in RBL.
(viii. Decision making power in branch level is not enough to take prompt decision regarding FE business in RBL.
(ix. RBL has not yet introduced any deposit & investment scheme exclusively for expatriates/wage earners that will increase the foreign remittance.
(x. Foreign exchange training is not enough for the newly recruited employees than required.
(xi. RBL has got unique advantage of largest network with 535 branches located at different places of the country. This advantage can be utilized for capturing remittance of rural Expatriates.
(xii. As a nationalized bank, RBL has good reputation and mass people trust it to do (any kind of transactions.
(xiii. Correspondence bank are not enough to increase the inflow of foreign remittance.
(xiv. RBL has made SWIFT arrangement with different banks. As some of the AD branches have SWIFT connectivity, it has competitive advantage over other commercial banks in handling remittance business and various messages of import and export.
(xv. Rupali Bank Ltd. has do not have strong research department to launch the new product, which would get competitive advantage over its competitors.
(xvi. Unstable situation of RBL regarding selling the bank has lost the image and some important clients have left the bank.
Conclusion
Foreign exchange business has a great impact on banks overall business development. To accomplish foreign exchange business it needs foreign currency. Foreign remittance send by expatriates is one of the sources of foreign currency. Banks needs huge amount of foreign currency to make the import payments. Banks can buy foreign currency from the inter-bank market that will reduce the profit. Export business is another source of foreign remittance. So, it is clear that import, export and foreign remittance are interrelated among each other. Our government gives more emphasize in collecting foreign remittance from abroad as it increases our foreign currency reserve. Rupali Bank Ltd. should increase its AD branches to increase foreign exchange business.
Some of the AD branches are not doing both importing and exporting business. So, these AD branches should start all type of business. It is found that the volume of foreign remittance is better than import and export business. All the branch of RBL are engaged for foreign remittance transactions that’s why volume of foreign remittance is highest. Compared with the export, import volume is higher. From the above study it can be said that if RBL takes proper steps for arranging easier way for inflow of foreign remittance and skilled manpower are placed for providing better service, then the inflow of foreign remittance will be increased significantly. For export, invention of new product, diversification of traditional goods like jute, searching new destinations, build up backward-linkage industries, providing incentives to exporters etc. are obvious for increasing export-remittance.
To flourish the foreign exchange business all three types of business have to be increased. Maximum clients of RBL are doing one type of business import or export. Most of the clients are importer. Few clients are doing export business. RBL have to encourage all clients to do all types of business. Bank should provide special types of service to the clients and give information for prospective opportunity for the import or export.
















