Executive Summery:
During my internship period in Habib Bank Ltd I have tried my best to go deep in daily operation and describe precisely. I highlight the following areas:
- Introduction
- General banking
- Foreign trade
In introduction I discuss about overall identity of Habib Bank Ltd Ltd. Here I highlight Introduction. Slogan, values, mission of Habib Bank, Product mix of Habib Bank. Performance of Habib Bank. Organogram of Habib Bank Motijheel branch-At a glance.
In general banking operation I discuss about customer service operation and other daily operations. I highlight Introduction, Account opening, rules and regulation regarding Cheque issue and cancel, Remittance, Telegraphic transfer (TT), Clearing, Collection.
In Foreign trade is the most important section in any bank. I have completed my internship with emphasizing on Foreign Trade. Here I highlight: Habib bank-Foreign Trade.
At last I go through SWOT (Strength, weakness, opportunities, threats) analysis of Habib Bank Ltd and recommended against SWOT analysis.
OBJECTIVES OF THE INTERNSHIP WORK AND THE REPORT:
The world is changing specially business world. New technologies are invented continuously and introduce in banking sector. The policies, strategies are also changing. So business world is become more competitive and globalize. The Internship is as a part of our education. So that, we can know the present situation of our Banks are available around us. And we can adopt ourselves with changing .Its another objectives is to establish permanent relation with Banking operations. The third objective is to increase over all skill so that we can be more modern and challenging to manage our future business.
The main objective of this study is to compare my Banking knowledge from CSE courses with the actual Banking activities and also get some experience. Moreover there are some other objectives. All objectives could be pointed out as follows:
- To be apprehended about real banking operations.
- To find out deviations from theories and reasons of deviation.
- To understand Foreign Trade process with its prospects and problems.
- The rules and regulations of private commercial Banks
- To know the background of the HBL
- To know the Overall Banking system of HBL
- To have the idea about the communication between the branch office and Head office.
- To better understand about the foreign exchange activities.
- To learn the Banking Laws.
- To make SWOT analysis and recommend if necessary.
- To be apprehended in organizational environment, behaviors, cultures and intra-relationship
RESEARCH OF METHODOLOGY
Internship report preparing is not so easy task. It is the comparative study between theoretical knowledge and practical knowledge. After getting permission from the Habib Bank I have completed my internship for three months. I asked questions to officers about their respective areas and get materials for report.
Methods used are:
- Analysis of Secondary data (Books, Annual reports, forms, files & documents)
- Personal observations & Practical experience.
- Sample Survey.
Scope of Internship:
The key functional area of any Bank company is Corporate Banking, Personal Banking, International Trade & Foreign Exchange, Lease Finance, Capital Market Services, marketing, and personnel. There are also various operations, which have to be performed to run a Bank successfully. It will over view of all sectors in a resize form. In my report I like to touch all area of General Banking operations in Habib Bank-An emphasis on Foreign Trade.
CHAPTER-01
Introduction:
Bangladesh economy has been experiencing a rapid growth since the ’90s. Industrial and agricultural development, international trade, inflow of expatriate Bangladeshi workers’ remittance, local and foreign investments in construction, communication, power, food processing and service enterprises ushered in an era of economic activities. Urbanization and lifestyle changes concurrent with the economic development created a demand for Banking products and services to support the new initiatives as well as to channel’s consumer investments in a profitable manner. A group of highly acclaimed businessmen of the country grouped together to responded to this need.
The Bank was incorporated as a public limited company under the Companies Act. 1994. The Bank started its commercial operation on July 05, 1995 with an authorized capital of Tk. 1,000 million and paid up capital of Tk. 100 million. The paid up capital of the Bank stood at Tk. 303.46 million as on 31 December 2001. The total equity (capital and reserves) of the Bank as on 31 December 2001 stood at Taka 771.53 million including the sponsor’s capital of Tk.1.43 million. .
The Bank has 19 branches across the country and a wide network of correspondents all over the world. The Bank has plans to open more branches in the current fiscal year to expand the network.
The Bank offers the full range of Banking and investment services for personal and corporate customers, backed by the latest technology and a team of highly motivate office and staff.
In our effort to provide Excellence in Banking services, the Bank has launched fully automated Phone Banking service, joined a countrywide-shared ATM network and has introduced a co-branded credit card. A process is also underway to provide e-business facility to the Bank’s clientele through Online and Home Banking solutions.
Habib Bank Ltd. is the preferred choice in Banking for friendly and personalized services, cutting edge technology, tailored solutions for business needs, global reach in trade and commerce and high yield on Backed by the latest technology and a team of highly motivated officers and staff, the Bank offers full range of Banking and investment services for personal and corporate customers.
Some of the corporate Banking products of the Bank include Letter of credit, guarantee Import and Export Finance Syndicated loan, Project Financing Leasing, working capital financing.
Under its capital market service, Habib Bank provides undertaking of initial public offering, advising & safe custody of share for the investors etc.
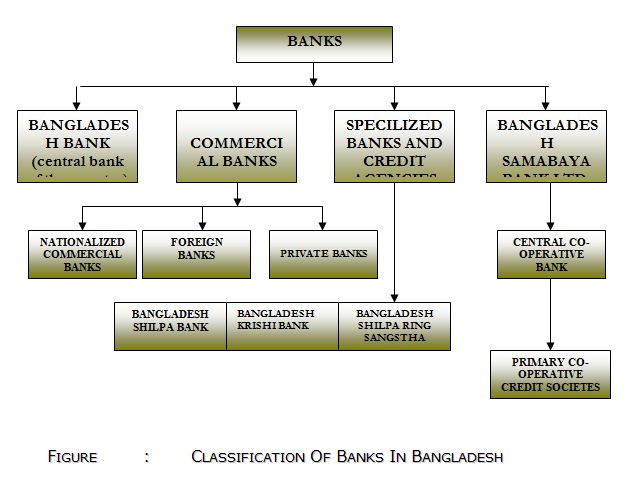
Banks in Bangladesh can be classified into the following categories.
Slogan of Habib Bank Limited:
Excellence in Banking
Values of Habib Bank Limited:
- Customer focus
- Integrity
- Team work
- Respect for the individual
- Quality
- Responsible citizen
Mission of Habib Bank:
To be the premier financial institution in the country providing high quality products & services backed by latest technology & a team of highly motivated personnel to deliver Excellence in Banking.
Products mix of Habib Bank Ltd.
Deposit product line:
Current account
Saving account
FDR
STD
Special note deposit
Education saving scheme
Pension saving scheme
Marriage saving scheme
Savers benefit deposit
Loan product line:
Credit card
House building loan
Commercial loan
Loan against import
Working capital
Large / medium scale loan
Bank overdraft
Agricultural loan
Other product line:
On line Banking system
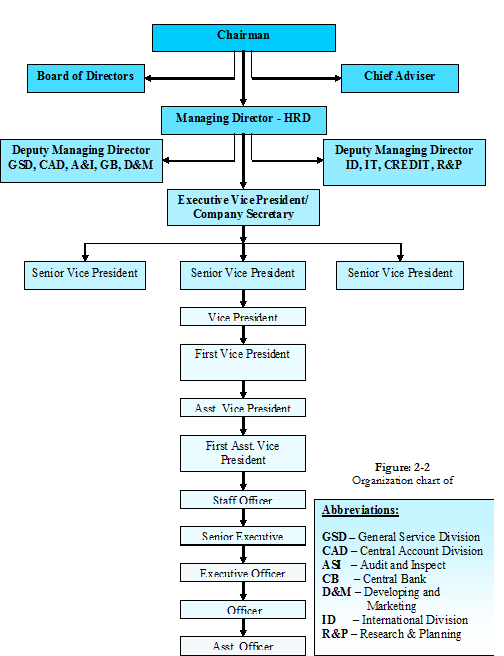
Management of HABIB BANK Ltd.
Organization Chart of Habib Bank Limited

Motijheel Branch
At A Glance
Chapter-02
General Banking operations
In
Habib Bank Ltd.
Introduction:
General banking creates a vital link between customer and bank. It’s really crucial department for the progression of the bank. It is the introductory department of the bank to its customer. The Habib bank Motijheel branch has all the required section of general banking. Every day it receives deposits from customer and meets their demand for cash by honoring instruments. General banking department is that department which is mostly exposed to the maximum number of bank customer.
Habib bank Motijheel branch has the full-fledged arrangement for providing general banking facilities and has the major following section:
- Account opening section
- Cash (receive and disbursement) section
- Clearing and collection section
- Remittance section
Outlook of general banking:
General banking:
——————————————–
Account cash clearing and Remittance
Opening collection
Account opening:
A person is treated as a client when he/ she opens an account on the bank. Then it becomes a contractual relationship between bank and client. The account opening section of Dhaka bank ltd Agrabad branch is very important section. This section takes care of all the relevant duties related to the opening of account. There are different types of account facilities provided by this branch. These are:
Account opening process:
| 01 | Current deposit (CD) |
| 02 | Saving deposit (SB) |
| 03 | Fixed deposit (FDR) |
| 04 | Short term deposit (STD) |
| 05 | Pension Saving Scheme (PSS) |
| 06 | Education Saving Scheme (ESS) |
| 07 | Marriage Saving Scheme (MSS) |
| 08 | Bearer certificate deposit (BCD) |
| Step 1 | Receiving filled up app. Form in bank’s prescribed form monitoring what type of a/c is desired to open. |
| Step 2 | App. form is filled up by the applicant himself /herself. Two copies of passport size photograph from individual are taken, in case of firm photo of all partners are taken. |
Application must submit with required document.
Introducer must sign application.
Card must bear specimen signature.Step 3Authorized officer accepts the application.Step 4Minimum balance is deposited-only cash is accepted.Step 5Account is opened and a cheque book and pay-in-slip book is given.
General condition of governing accounts:
- The law rules and regulation of Bangladesh usual custom and procedures common to Banks in Bangladesh will apply to and govern the conduct of account opened with the Bank.
- Any person opening an account will be deemed to have read, understood and accepted the rules governing the account. Minimum balance to be maintained in current A/C.Tk. 10,000/-and in savings A/C Tk. 5,000/-
- A suitable introduction by an introducer acceptable to the Bank is required prior to opening of any account. Recent photographs of the account openers duly attested by the introducer must be produced.
- Each account will be given one account number. This number is to be properly quoted on all letters and/or documents addressed to the Bank and on all deposit slips. The Bank will not responsible for any loss or damage occurring as a result of wrong quotation of account number.
- Interest / commission / service or maintenance of account charge will be levied by the Bank as determined by the Bank from time to time and as per Bangladesh Bank regulation.
- The funds available in any of the account holders account (the customer) with the Bank will be considered by the Bank to be a security for any commitment(s) and / or obligation(s) present and / or future of the customer to the Bank. In the event of dishonor or unfulfilment of such obligation(s) and / or commitment, the Bank is entitled without giving prior notice to the customer to utilize such funds against the obligation(s) and / or commitment of the customer to the Bank.
- Any statement of account dispatched to the customer will be considered as approved unless discrepancy (ies) is notified in writing to the Bank within 15 days from the date of dispatch. The Bank is not responsible for the delays or non-delivery due to mail problems. Statement of accounts to be picked- up will be considered as approved even if not pick-up 15 days after the date they are produced. Statements of accounts are not produced when there is no operation during the Month. Those can be obtained on special request.
- Account holders must provide maximum security to the cheque books in there permission and the Bank is not responsible for any loss or misuse must be immediately reported to the Bank and confirmed in writing without delay.
- When cheques deposited are payable by other Banks or outstation they are available after clearing or collection only. Service charge will be charged @ Tk. 100/- in current account and Tk.50/-in savings account yearly or as charge by the Bank from tome to time as and when required.
- The Bank reserves the right to close the any account without giving prior notice if the conduct of the account is unsatisfactory in the pinion of the Bank or for any other reason(s) whatsoever.
- The balance in the account(s) is payable solely at Dhaka Bank Ltd and shall be govern by and subject to laws in effect in Bangladesh. As used herein “Laws” will includes Bank circulars, Modification, regulation and order of the government and Bangladesh Bank including practice in Banking.
- The Bank reserve the right to amend the present rules at any time in any manner with or without giving prior notice to the account holder(s) separately of to the public. The cheque book will not be issued unless and until all the required formalities are completes.
- Current Account:
Business people for their convenience generally open a current account. This Account Facilitates to deposit and withdrawn money at any time. Usually no banks allow any interest against this account. People prefer to deposit money on current account mainly for the following reason….
- Overdraft Facility and
- Other facilities like collection of cheque transfer of money and rendering agency and general utility services.
General Characteristics;
- CD Accounts are unproductive in nature as banks loan able fund is concerned. Sufficient fund has to be kept in liquid form, as current deposits are demand liability.
- This huge portion of this fund becomes non-performing. For this reason banks do not pay any interest to CD account holders.
- There is no restriction on the number and the amount of withdraws from a current account.
- Service charge and incidental charge are recovered from the depositors since the bank make payment and collect the bills, drafts, cheques, for any number of times daily.
- Businessman and companies are the main customers of these products.
- The Banks through current accounts grant the loans and advances.
Initial deposit:
It requires a minimum amount of TK. 10,000/- to open a current account in the local office but under special cases it could be to taka. 5,000/-. Here we can see some essential requirement for different type of CD A/C (Current Account).
Individual CD A/C:
Introducer who is having CD A/C with the same branch. SB A/C holder Cannot be the introducer of a CD A/C.
Signature card with three-specimen signature.
Full address.
Account must be opened only in cash
Two Copy Color passport size Photographs attested by the introducer.
Sole proprietorship:
Introducer (current account holder)
Two Copy Color passport size Photographs.
Account agreement form.
Trade license.
Rubber stamp impression.
Specimen Signature card.
III. Partnership firm:
Introducer.
Registered partnership deed.
Memorandum.
Photographs attested by other partners.
Specimen signature card.
- Club Society & Association:
Registration certificate.
Copy of the rules and constitutions.
vAuthentic copy of the resolution.
List of the executive committee.
Passport Size photographs attested by the introducer.
Specimen signature card.
Account agreement form.
- Public/ Private limited company:
Introducer.
Certificate true copy of the memorandum and articles of association of the company.
Certificate true copy of the resolution of the board of directors.
Certificate list containing names and signatures of the directors.
Certificate of commencement of business (public limited)
Acts/ Ordinance / resolution circulars.
Specimen signature card.
Passport size photographs attested by introducer.
Short-term deposit account (STD):
The deposit held in STD A/C are payable on short notice for 7 days of 30 days. The interest rate of STD in is 4.5% Different big organization; companies and other Govt. departments maintain STD A/C.
General Characteristics:
- Customers deposit money for a shorter period of time.
- STD account can be treated as semi-term deposit.
- STD should be kept for at least seven days to get interest.
- The interest offered for STD is less than that of savings deposit.
- Volume of STD A/C is generally high. In HBL various big accounts.
- Frequent withdrawal is discouraged and requires prior notice.
Requirements:
Account opening agreement form is used for CDA
- Account opening agreement form is used for CDA.
- Specimen Signature card.
- The Approval of the manager.
Saving Bank Accounts (SB):
This Type of deposit is intended for primarily small-scale saver. It carries an interest of 6%. A depositor is allowed to withdraw up to 25% of the balance per week. In case of 25% of the balance withdrawal in a week 7 or 10 days notice to be given to the bank. Saving account may be opened either individually or jointly.
SAVINGS DEPOST ACCOUNT:
General Characteristics:
As per BB instruction 90% of SB deposits are treated as liability and 10% of it’s as demand liability.
- Interest is paid on this account. HBL offers a reasonable rate of interest for SB A/C.
- Generally, banks require a 7-day prior notice of the total amount of one or more withdrawals on any date exceeds 25% of the balance of the account unless is given.
- But in DBL there is no restriction about drawing money form savings account. Any time Account holders may draw money of any amount without prior notice.
- The number of withdrawals over period of time is limited. Only two withdrawals are made in a week. No interest will be paid on rest amount for that month.
- Generally householders, individuals and other small-scale savers are the clients of this account.
- Minimum Balance of TK.5000/- is to be maintained.
- Interest will be counted on the minimum balance form the date 1-6 of a month.
- HBL gives no interest if the balance is below TK 2000.
- No service charge as it is and interest bearing account.
Fixed deposit account (FDR):
Fixed deposit is that kind of account that is repayable after the expiry of a predetermined period fixed by the customer himself. It is popularly known as time deposit. Offers different size of period varies from 3 months to 3 years or above. Interests on fixed deposit accounts are paid at rates fixed by the head office from time to timer depending on their period of maturity.
Different FD rates:
Table: Showing different FD rates:
| Periods | 3 Month | 6 Month | 12 Month & Above |
| Interest rates | 8.5% | 8.75% | 9% |
Requirements:
- Account agreement form
- Amount and period of deposit must be mentioned clearly.
- The approval of manager.
- Photograph.
- Introducing is not required.
- Specimen signature.
Encashment of FDR:
In case of pre-matured FDR, is not bound to accept surrender of the deposit before its maturity date. In order to deter such tendency, the interest on such as fixed deposit is being cut on a certain percentage less than agreed rate.
Loss of FDR:
Incase of a lost FDR the customer is asked to record a general diary in the nearest police station. After that the customer has to furnish and indemnity bond to the branch. A duplicate FDR is than issued top the customer by the bank.
Bearer certificate of deposit (BCD):
The bearer certificate deposit is a document of title similar to tome deposit received issued by the bank. The document is bearer documents hence readily negotiable, whoever present it to the bank has the right to get the money. To open bearer certificate of deposit the following processes are maintained….
i. No ‘Account Opening Form’ on specimen signature card is required to open BCD
ii. A credit voucher crediting BCD with the full amount shall be prepared.
iii. Serial Number of BCD, date of issue, date of Encashment, rate of interest, will be recorded in the BCD register.
Closing of an account:
A customer may close out his/her account at any time by submitting an application to the branch. The customer should be asked to draw the final cheque for the amount standing to the credit of his account less the amount of closing (Tk.-50/- in DBL) and other incidental charges and surrender the unused leaves of the chequebook. In case of joint account all the joint account holders should signed in the application for closing the account. On receipt of the application the following steps are taken:
a) The signature of the account is verified.
b) The number unused leaves of the chequebook shall be noted thereon.
c) The manager will approve the application.
d) Incidental charge should be debited the account.
e) The account holder is advised to draw the remaining balance from the a/c
Cheque:
A cheque is treated as an important document in the branch. Cheque is an instrument in printed from containing an unconditional order signed by the a/c holder directing a certain person to pay a certain amount of money only to or to the order of a certain person or to the b bearer of the instant.
Issue of a cheque book:
The in charge of the department stock of the chequebook will get to know and to allow entering the DCBIR (Department cheque book issued register)
Separate folios of the register are allotted for CD A/C of cheque book of 100 leaves and 10,15,25.50 for SB A/c
At the time of opening an A/C the customer is required to sign a cheque book requisition slip (No.S.F. -73) if the A/c opening form is found complete in all respect a cheque book is issued to the client.
The account number is written in each page of the cheque book and its requisition slip.
The name and account number of the client is also entered in the CBIR
The requisition slip should be preserved as voucher.
Loose cheque:
Loose cheque is the customer in that situation requires an instrument that is delivery by the banker when he might on be having his original cheque book with him. Loose cheques are issued to the customer form a new full cheque book reserved by the department for this purpose. Before issuing the loose cheques entries are made in the CBR (Cheque book requisition) and in the computer as well with the concerned officer’s initial.
Loose cheque is issued if…
The party requires a loose cheque has the loose check requisition slip supplied to him by the bank.
An officer who personally knows him attests the requisition slip.
The officer in charge deposit department verifies the signature of the account holder.
The approval of the manager has been obtained to issue that loose cheque.
The name of the account holder, his account number, date of the loose cheque issued and the amount to be drawn is written of the cheque and its counterfoil.
A stamp bearing the bearing the title LOOSE CHEQUE is affixed on the face of the cheque at top under authorized signature.
Remittance section:
Remittance means transfer of money from one place to another. In banks it is done in the form of DD (Demand Draft), TT (Telegraphic Transfer) or pay order. The details are as Follows…
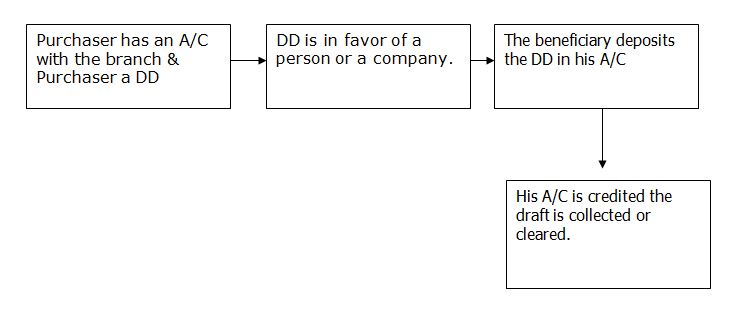
Demand Draft (D.D.)
Demand draft is that kind of instrument which is payable on demand. A branch issues it to another branch containing and order to pay a certain amount of money to ascertain person. To issue a D.D. the sender of the D.D should have and A/C With that Issuing Branch. D.D. can be send from one branch to another by cash or cheque. Every bank charges a certain amount as commission for issuing a D.D. the commission is 15% of the worth of DD+VAT (commission*15%) +Telex-Taka 40
The Flow chart of the total procedure of issuing Demand Draft is as follows: –
Against Cash:
The Customer is asked to complete a form (No. Sf-18) which is treated as an application as well as credit voucher for H.O. Account (Br. Concern).
Commission Charges are calculated and inserted in the form.
The voucher than given to the customer to deposit the amount.
The cashier receives the cash and delivered the voucher to the remittance department against initial in his book.
Then the draft is prepared and entered in the D.D. issue register. The amount of the draft is protected by the ‘protect to graph’. Then the draft No. is written of the voucher.
Draft book and the voucher along with register are sent to officer in charge of the remittance department for parth-11 test, verification and signature.
The draft and the voucher are sent to general section head for part-1 test and signature.
Then a memorandum is issued to the customer if be desires so.
Payment of D.D.:
The followings should be checked before payment of D.D.:
D.D. is drawn on the branch.
Issuing branch’s rubber stamp is fixed.
Amount in word & the amount in figure should be same.
Verify the test number is tested.
If D.D is placed before arrival of ‘IBA’ then make the payment by debiting.
Suspense A/C. D.D paid without advice, Advice will come than.
Particulars of D.D payable & D.D. Paid without advice is entered in the respective register.
Charges taken for the draft:
Tk. 50.00 as postage charge is taken and 0.15% commission on the draft value. The amount is separately credited to the concern income account.
Cancellation of Demand Draft:
To cancel an issued D.D. the client has to submit an application. Issuing branch then sends an I.B.D.A (inter branch debit advice to the drawn branch against previously issued I.B.C.A (inter branch credit advice).
Pay Order:
If any person wants to transfer money within the local areas where the bank located then the transfer be made by ‘Pay Order’ Deference between ‘Pay Order’ and ‘Demand Draft’ is in terms of place only. Pay order is issued for remitting money within the city whereas D.D. is issued for within the country.
Issue of pay-Order:
To issue a ‘Pay-Order’ the party should maintain and A/C. with the bank. The bank also allows special customers without A/C for Pay-Order in special circumstances. The main feature of pay-Order is that in where (That is in which branch) the P.O. is issued the party should encash the money form the same branch.
Table: charges of issuing pay order:
| Amount up to (Tk.) | Charge rate (Tk.) | VAT |
(Tk)1,00,0002545,00,000609Above 5,00,0007511
The procedure for selling P.O. is as follows: –
- Purchaser must be an account holder of DBL Agrabad Branch.
- Depositing money with P.O. application form.
- Giving necessary entry in the bills payable (PO) register.
- Payees name, date, P.O. no. Etc.
- Preparing instrument.
- After it has been scrutinized & approval by higher authority, the instrument is delivered to customer. Signature of customer is taken in the counterpart.
Practice and operation of pay order:
Type of P.O.:
Account payee only : only can encash it by depositing it in his Account.
Blank crossed : Any one can encash it by depositing in their account.
Cash payment : Identification regarding payee.
Settlement of a P.O.
When P.O. submitted by collecting bank through clearinghouse, the issuing bank gives payment.
Thus bank’s liability is settled by debiting bills payable. But before giving payment it should be examined whether endorsement was given by the collecting bank or not. If not hen the instrument is dishonored marking ‘Endorsement required’.
Collection of PO:
A customer of HBL who is the payee of a P.O. Will deposits it for collection. The instrument is given to the clearing that will place it to the issuing bank in the clearing house. Before placement, HBL as a collection bank gives necessary endorsement.
¨ Telegraphic Transfer (T.T)
This is the most usable instrument in remittance section. In local office, T.T. Is generally done by telex, telephone is also used necessary.
Issue of T.T:
To issue a T.T the party should maintain an A/C with that issuing Bank.
Then….
- The customer is asked to complete an application that is also treated as credit voucher for head office account (Branch concern)
- Telegram charges are also recovered from the customer and are credited to income account telegram charges covered a credit voucher is prepared for the customer.
- Text of telegram is written and handed over.
- Then the massage is typed on the from.
- The original telegram & confirmation is sent to the dispatch departmet.
- IBCA is prepared in duplicated. A Separated register is maintained for T.T. Issue.
Telegraphic transfer is one of the fastest means of transferring money form one branch to another or from one place to another. The TT issuing bank instrument is given for T.T Both parties should have account, as money is transferred.
Outgoing T.T.-Its Procedure:
- Application by customer along with money given.
- In receipt of money a cost memo is given to the customer containing TT serial number. The customer informs this number to the awaiting party in the other branch.
- Tested fax message is prepared, where TT serial and the of the concern party to whom the money will be credited is mentioned.
- Activity report is received form the telex department confirming transmission of message.
Incoming TT- Practice:
- After receiving the fax message it is sent for test agree.
- TT serial number is scrutinized in the “TT in -concern branch” register.
Payment of TT:
The payment of TT requires a lot of paper works. Vouchers are made. At first H.O. concern bank is debited with TT payable credited. Then the TT payable is debited with party’s A/C credited. The receiving party can also take the cash after his A/C is credited. For the payment of TT caution must be taken because various fraud and forgery. So test no. is required for security.
Clearing:
Clearing is one of the most important functions of general banking. Mainly clearing is an arrangement held in Bangladesh bank where daily representative of the member bank gather to clear their cheques and instruments. The bank receives many such instruments during the from the A/C holders. May of these instruments are draw payable at other banks.
When the bill is within the range of the clearinghouse it is sent for collection through clearing section. As far as safety is concerned customers get crossed cheque for the transaction crossed check can’t be encashed form the counter, rather it has to be collected through banking channel i.e., clearing. If a client of HBL received a check of another bank which is located within the clearing range and deposit the instrument in his account at HBL then HBL will collect the money through clearing house. After received the check HBL will credit client account. However, the amount is credited in the customer A/C but he will no get the money until the check is honored.
Procedures for clearing:
- Received seal is stamped on the cheque.
- Crossing of the cheques are don.
- “Payee’s A/C Credited” endorsement is given.
- Entries are given in the Outward clearing Register.
- Clearing seal is given.
- Cheques are sorted bank wise and entries are given to the computer (NIASH2)
- Entries age given in the clearing House Register before dispatching to the clearing house.
After that, a debit voucher is prepared.
Instruments of other branches:
However, the principal branch clears its checks as well as the checks of other branches because, no other branch is allowed to represent directly. The other branches send the instruments along with IBDA principal Branch acts as an agent in this case.
Dishonor of Cheuqe:
If the cheque is dishonored, HBL sends a memorandum (cheque return memo) to the customer stating the reason.
Outward clearing:
Outward clearing refers to the instruments drawn on other banks and deposited in HBL for collection. The following steps are taken for outward clearing…
The duly signed instruments are received.
The instruments are checked for any kind of discrepancy.
Received for Clearing” seal is stamped on the counterfoil of the deposit slip.
Instrument is stapled with Deposit Slip.
Special crossing in favor of “Habib Bank Ltd” is given on the instrument there of.
Entry is given in NIKASH.
Payee’s A/C Credited” endorsement is given.
The instruments are sorted bank wise as well as branch-wise.
Entries are given in the Clearing House Register before dispatching to the clearinghouse.
All the instruments are sent to the First Clearing House to deliver them to the respective banks.
Function in the Clearing House:
- The clearinghouse is an assembly of the locally operating scheduled banks for exchange of checks, drafts, and other demand instruments drawn on each other and received form their respective customers for collection.
- The house meets at the appointed hour on all working days under the chairmanship of the central bank. The clearing house ists twice ina working day.
- The Member submits the claimable checks in the respective desks of the banks and vice-versa.
- Consequently, the debit and credit entries are given.
- At the end, the debit summation and the credit summation are calculated. Then the banks clear the balances through the check of Bangladesh Bank.
- The dishonored checks are sorted and returned with return memo.
- If the instruments are dishonored then they are sorted again and sent back to the returning house along with their return memo.
- Later on all the instruments of HBL which were claimed by other banks are sorted and delivered to respective branches.
- If the instruments are honored the treatment is:
Inward clearing:
Inward clearing refers the instruments drawn on the Agrabad branch, which are received from other banks in the clearinghouse by the representative of other banks. The followings steps are taken for inward clearing………..
- The instruments drawn on the bank, which are received form other banks through clearing house.
- The amounts of number of instruments are entered in the house form the main schedule of respective banks.
- The instruments with schedule are arranged branch wise.
- The instruments send to branches concerned for clearance and IBCA’s are collected form them for honored cheque.
- The instruments are sent to the respective departments and the schedules are filled.
- These sorts of instruments are cleared form the second house of the central bank.
Collection:
When the bills are supposed to be drawn on any bank, which is out of range of clearing house of Bangladesh bank this instrument are sent for collection not clearing. These bills are of two types. They are inward bill for collection and outward bills for collection. We can see a brief scenario about these two types of bill as below:
Inward bills for collection:
When instruments received form other branches or other banks, they are treatment as inward bills for collection. In practices instruments of other banks or branches are cleared through clearinghouse. For those instruments form other branches of and other banks outside clearinghouse come under the bill collection procedure.
When the OBC is received form the other bank’s branches, which are treated as outward bills for collection. This collection procedure occurs in two different situations.
CHAPTER-03
FOREIGN TRADE
In
HABIB BANK LTD.
Introduction:
Foreign trade can be easily defined as a business activity, which transcends national boundaries. These may be between parties or government ones. Trades among nations are a common occurrence and normally benefit both the exporter and importer. In many countries, international trade accounts for more than 20% of their national incomes.
Foreign trade can usually be justified on the principle of comparative advantage. According to this economic principle, it is economical profitable for a country to specialize in the production of that commodity in which the producer country has the greater comparative advantage and to allow the other country to produce that commodity in which it has the lesser comparative advantage. It includes the spectrum of goods, services, investment, technology transfer etc.
This trade among various countries causes for close linkage between the parties dealing in trade. The bank which provides such transactions is referred to as rendering international banking operations. International trade demands a flow of goods from seller to buyer and of payment from buyer to seller. And this flow of goods and payment are done through letter of credit (L/C).
As more than one currency are involved in foreign trade, it gives rise to exchange of currencies which is known as foreign exchange. The term “Foreign Exchange” has three principal meanings Firstly it is a term used referring to the currencies of the other countries in terms of any single one currency. To a Bangladeshi, Dollar, Pound sterling etc. are foreign currencies and as such foreign exchange. Secondly, the term also commonly refer to some interments used in international trade, such as bill of exchange, Drafts, Travel cheque and other means of international remittance thirdly, the terms foreign exchange is also quite of ten referred to the balance in foreign currencies held by a country.
In terms of section 2(d) of the foreign exchange regulations 1947, as adopted in Bangladesh, Foreign Exchange means foreign currency and includes any instrument drawn, accepted made or issued under clause (13) of article 16 of the Bangladesh Bank order, 1972, all the deposits, credits and balances payable in any foreign currency and draft cheque, letter of credit and bill of exchange expressed or drawn in Bangladesh currency but payable in any foreign country.
In exercise of the power conferred by section 3 of the foreign exchange regulation, 1947, Bangladesh Bank issues license to schedule bank to deal with exchange. These banks are known an Authorized Dealers. Licensees are also issued by Bangladesh Bank to persons or firms to exchange foreign currency instruments such as T.C, currency notes and coins. They are known as Authorized money changers.
Functions of Foreign Exchange Department:
Exports:
- Pre-shipment advances.
- Purchase of foreign bills.
- Negotiating of foreign bills.
- Export guarantees.
- Advising/Confirming letters – letter of credit.
- Advance for deferred payments exports.
- Advance against bills for collection.
Imports:
Opening of letter of credit (L/C)
Advance bills.
Bills for collection.
Import loan and guarantees.
Remittances:
- Issue of DD, MT, TT etc.
- Payment of DD, MT, TT etc.
- Issue and enhancement of traveler’s cheque.
- Sale and enhancement of foreign currency notes.
- Non-resident accounts.
- FOREIGN TRADE
- THREE BROAD CATEGORY
- International Trade Business
- International Remittance
- Foreign Currency Dealings
REGULATORY FRAMEWORK:
- Domestic
- International
DOMESTIC:
- Foreign Exchange Regulatory Act 1997
- Export Import Act 1950
- Guide Line for Foreign Exchange Transaction
- Foreign Exchange Circular by Bangladesh bank
- Regulation of Ministry of Commerce
INTERNATIONAL:
- UCPDC-Uniform customs & practices for documentary credit
- ICC Publications
- URC-Uniform Rules for Collection
- URR-Uniform Rules for reimbursement
- INCOTERMS
MODE OF PAYMENTS IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE:
- Cash in advance
- Open Account
- Collection Method
- Documentary Credit

Documentary Credit:
- Letter Of Credit – Undertaking of the bank to the exporter on behalf of importer for payment certain amount of money if he fulfills certain terms and conditions.
- Documents – Papers that support the terms & condition of the letter of credit.
DOCUMENTARY CREDIT:
EXCHANGE RATE:
- Price of one currency in terms of other currency.
- 1 US Dollar = Tk. 60.00
EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM
- Fixed
- Floating
- EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM: BUYING:
- TT Clean
- TT OD & Doc
- OD Sight
FLOATING EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM:
- INDEPENDENT FLOATING
-Determine by supply and demand of the market
- MANAGED FLOATING
– Central bank will intervene if exchange rate becomes unstable.
– Managing by supplying dollar in the market.
– Managing by reducing the supply of taka in the market.
- PEGGING
– Exchange rate of one currency is tagged/pegged with another
Currency.
– With single currency or basket.
EXCHANGE RATE SYSTEM: SELLING:
- TT & OD
- BC Selling
TRAVELERS CHEQUE:
- What you need to buy TC?
-Valid Passport
-Valid Air Ticket
-Visa
TRAVELERS CHEQUE:
- How much can you get?
-SAARC Countries
- Maximum $1000(for air) $500(for road)
-Other Countries
- Maximum $3000
- How much for a year?
- How much for a minor?
- What about cash?
The Most commonly used documents in Foreign Exchange:
- Documentary Letter of Credit.
- Bill of exchange.
- Bill of Lading.
- Commercial Invoice.
- Certificate of origin of goods.
- Inspection certificate.
- Packing List.
- Insurance Policy.
- Proforma Invoice / Indent.
- Master receipt.
- GSP Certificate.
Documentary Credit:
In simple terms a documentary credit is a conditional bank undertaking a payment. Expressed more fully, it is a written undertaking by a bank (issuing bank) given to seller (beneficiary) at the request, and in accordance with the instructions of the buyer (applicant) to effect payment (that is, by making a payment, or accepting or negotiating bill of exchange) up to a stated sum of money, with in a prescribed time limit and against stipulated documents. The customary clauses contain in a L/C are the followings:
- A clause authorizing the beneficiary to draw bills of exchange up to certain on the opener.
- List of shipping documents, which are to accompany the bills.
- Description of the goods to be shipped.
- An undertaking by the opening bank that bills drawn in accordance with the conditions will be dully honored.
- Instructs to the negotiating banks for obtaining reimbursement of payments under the credit.
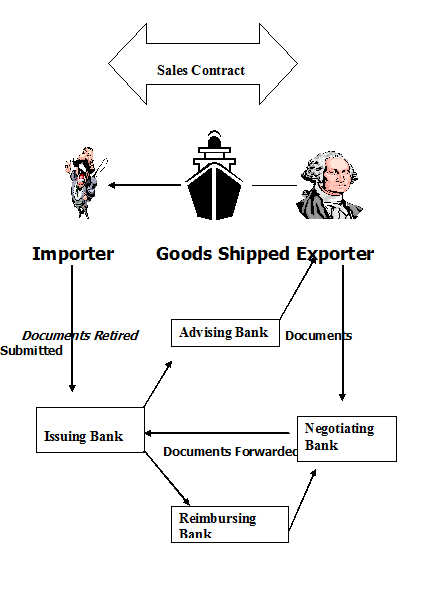
Parties to a Letter of credit (L/C):
The parties to a Letter of Credit are:
Importer / Buyer.
Opening Bank/Issuing Bank.
Exporter/Seller/Beneficiary.
Advising Bank/Notifying Bank.
Negotiating Bank.
Confirming Bank.
Paying / Reimbursing Bank.
Bill of Lading:
A bill of leading is a document that is usually stipulated in a credit when the goods are dispatched by sea. It is evidence of a contract of carriage, is a receipt for the goods, and is a document of title to the goods. It also constituted a document that is, or may be, needed to support an insurance claim.
The Details on the bill of Leading should include:
- A description of the goods in general terms not inconsistent with in the credit.
- Identify marks and numbers, if any.
- The name of the carrying vessel.
- Evidence that the goods have been loaded on board.
- The ports of shipment and discharge.
- The names of shipper, consignee, and name and address of the notifying party.
- Whether freight has been [paid or is payable at destination.
- The number of original bills of lading issued.
- The date of issuance.
A bill of lading specifically states that goods are loaded for ultimate destination specifically mentioned in the credit.
Commercial Invoice:
A Commercial Document is the accounting document by which the sellers change the goods to the buyer. A commercial invoice normally includes the following information:
Date.
Name and address of the buyer and seller.
Order of contract number, quantity and description of the goods, unit price and the total price.
Weight of the goods, number of the package, shipping marks and numbers.
Terms of delivery and payment.
Shipment details.
Certificate of Origin:
A certificate of origin is a signed statement providing evidence of the origin of the goods.
Inspection Certificate:
This is usually issued by an independent inspection company located in the exporting country certifying or describing the quality, specification or other aspects of the goods, as called for in the contract and the L/C. the inspection company is usually nominated by the buyer who also indicates the types of inspection he wishes the company to undertake.
Insurance Certificate:
The Insurance Certificate documents must –
- Be that specified in the credit.
- Cover the risks specified in the credit.
- Be consistent with the other documents in its identification of the voyage and description of the goods.
- Unless otherwise specified in the credit.
- Be a document issued and / or signed by an insurance company or its agent, or by underwriters.
- Be dated on or before the date of the date of shipment as evidenced by the shipping documents.
- Be for an amount at least equal to the CIF value of the goods and in the currency of credit.
Import:
Importation is foreign goods and services purchased by customer, firms and Governments in Bangladesh.
An importer must have import registration certificate (IRC) given by chief controller of import and exports (CCI & E) to import any thing from other country. To obtain import registration certificate (IRC) the following certificates are required:
Trade License.
Income Tax clearance certificate.
Nationality certificate.
Banks solvency certificate.
Asset certificate.
Registration partnership deed (if any).
Memorandum and Article of association.
Certificate of incorporation (if any)
Rent receipt of the business premises.
Import Procedure:
To import through United Commercial Bank Limited (UCBL), a customer/client requires –
- Bank Account.
- Import registration certificate.
- Tax paying identification number.
- Proforma Invoice/Indent.
- Membership Certificate.
- L/C application form duly attested.
- One set of IMP Form.
- Insurance Cover Note with money receipt.
- Others.
Import Mechanism:
To import, a person should be competent to be an importer. According to import and Export control Act, 1950, the office of chief controller of Import and Export provides the registration certificate (IRC) to the importer. After obtaining this person has to secure a letter of credit authorization (LCA) from Bangladesh Bank and then a person becomes a qualified importer.
He is the person who requests or instructs the opening bank to open an L/C. He is also called opener or applicant or the credit.
Importer’s application for L/C limit / margin:
To have an import L/C limit, an importer submits an application to the department of (UCBL) furnishing the following importation:
Full particulars of bank account.
Nature of business.
Required amount of limit.
Payment terms and conditions.
Goods to be imported.
Offered security.
Repayment schedule.
A credit officer scrutinizes this application and accordingly prepares a proposal (CLP) and forwards it to the head office credit committee (HOCC). The committee, if satisfied, sanctions the limit and returns back to the branch. Thus the importer is entitled for the limit.
Opening of Letter of Credit (L/C) by Bank:
Opening of L/C means, at the request of the applicant (importer) issuance of a L/C in favor of the beneficiary (Exporter) by a bank. The bank, which open or issue L/C is called L/C opening bank or issuing bank.
On receipt of the importer’s L/C application supported by the firm contract (Indent / Proforma Invoice) and Insurance Cover Note the bank scrutinize the same thoroughly and fix up a margin on the basic of banker – customer relationship.
Before opening a L/C, the issuing bank must check the following:
- L/C application properly stamped, signature verified and margin approved and properly retained.
- Indent / Proforma Invoice signed by the importer and Indenter / supplier.
- Ensure that the relevant particulars of L/C application correspond with those stipulated in Indenter / Proforma Invoice.
- Validity of LCA entitlement of goods, amount etc. conforms to the L/C application.
- Conversion and rate of exchange correctly applied.
- Charges like commission, FCC, Postage, Telex charge, SWIFT charge, if any recovered.
- Insurance Cover Note – in the name of issuing bank – A/c importer covering required risks and voyage route.
- Incorporation of instruction for Negotiating Bank as per banks existing arrangement.
- Reimbursement instructions for reimbursing bank.
- If foreign bank confirmation is required, necessary permission should be obtained and accordingly advising bank is advised as per banks existing arrangement.
- If add confirmation is required on account of the applicant charges should be recovered from the applicant.
- In case of usance L/C, mention rate of interest clearly in the letter of credit.
Liability of Issuing Bank:
As per Article 9(a) of UCPDC 500, An Irrevocable Credit constitute a definite undertaking of the issuing Bank, provided that the stipulated documents ——— comply with the terms and conditions of the credit.
Advising of Letter of Credit:
Advising means forwarding of a Documentary Letter of Credit received from the issuing bank to the beneficiary (Exporter).
Before advising a L/C the advising Bank must see the following:
- Signature of Issuing Bank officials on the L/C verified with the specimen signatures book of the said bank when L/C received.
- If the export L/C is intended to be an operative cable L/C Test Code on the L/C invariably be agreed and authenticated by two authorised officers.
- L/C scrutinized thoroughly complying with the requisites of concerned UCPDC provisions.
- Entry made in the L/C Advising Register.
- L/C advised to the Beneficiary (Exporter) promptly and advising charges recovered.
Advising Bank’s Liability:
Advising bank’s liability is fixed up in uniform customs and practice for documentary credits, publication 500.
Article 7(a): A credit may be advised to a beneficiary through another bank (the “Advising Bank”) without engagement on the part of the advising bank, but that bank, if it elects to advise the credit shall take reasonable care to check the apparent authenticity of the credit which it advises. If the bank elects not to advise the credit, it must inform the issuing bank without delay.
Article 7(b): If the advising bank cannot establish such apparent authenticity it must inform, without delay, the bank from which the instructions appear to have been received that it has been unable to establish the authenticity of the credit and if it elects nonetheless to advise the credit it must inform the beneficiary that it has not been able to establish the authenticity of the credit.
Adding Confirmation:
Adding Confirmation is done by the confirming bank confirming bank is a bank which adds its confirmation to the credit and it is done at the request of the issuing bank the advising usually does not do it if there is not a prior arrangement with the issuing bank. By being involved as a confirming agent the advising bank undertakes to negotiate beneficiary’s bill without recourse to him.
- Issue L/C and request to add confirmation.
- Review the L/C terms.
- Provide reimbursement.
- Drafts to be drawn on L/C opening bank.
- Availability of credit facilities.
- Line allocation from the business and ownership units in the importer’s country.
- Confirm and advise L/C.
Amendments to Letter of Credit:
After issuance and advising of a L/C, it may be felt necessary to delete, add or alter some of the clauses of the credit. All these modifications are communicated to the beneficiary through the same advising bank of the credit. Such modifications to a credit are termed as amendment to a letter of credit.
There may be some of the conditions in a credit are not acceptable by the beneficiary. In that cases beneficiary contact applicant and request for amendment of the clauses. On receipt of such request applicant approaches his bank that is issuing bank with a written request for amendment to the credit. The issuing bank scrutinizes the proposal for the amendment and if the same is not in contravention with the exchange control regulation and bank’s interest, the bank may then process for amendment there can be more than one amendment to a credit. All the amendment forms an integral part of the original credit.
L/C amendments are to be communicated by SWIFT or mail. If there is more than one amendment to a credit, all the amendment must bear the consecutive serial number so that the missing the any amendment can be identified by the advising bank or by the beneficiary.
What is to be done by the issuing bank before advising amendments?
The issuing bank has to –
- Obtain written application from the applicant of the credit duly signed and verified by the bank.
- In case of increase of value, applications for amendment are to be supported by revised Indent/Proforma Invoice evidencing consent of the beneficiary.
- In case of extension of shipment period, it should be ensured that relative LCA is valid/revalidated/increased up to the period of proposed extension.
- Amendments an increase of credit amount and extension of shipment period both the cases amendment of Insurance Cover Note also be submitted.
- Proper recording and filing of amendment is to be maintained.
- Amendment charges (if an account of applicant) will be recovered and necessary voucher is to be passed.
The following clauses of L/C are generally amended:
- Increase/decrease value of L/C and increase/decrease of quality of goods.
- Extension of shipment/negotiated period.
- Terms of delivery i.e. FOB, CFR, CIF etc.
- Mode of shipment.
- Inspection clause.
- Name and address of the supplier.
- Name of the reimbursing bank.
- Name of the shipping line etc.
Settlement of Letter of Credit :
Settlement means fulfillment of issuing bank in regard to affecting payment subject to satisfying the credit terms. Settlement to may be done under three separate arrangements as stipulated in the credit.
- Settlement by Payment:
Here the seller presents the documents to the nominated bank and the bank scrutinizes the documents. If satisfied, the nominated bank makes payment to the beneficiary and in case this bank is other than the issuing bank, then sends the documents to the issuing bank and claim reimbursement as per arrangement.
- Settlement by Acceptance :
Under this arrangement, the seller submits the documents evidencing the shipment to the accepting bank (nominated by the issuing bank for acceptance) accompanied by draft down on the bank at the specified tenor. After being satisfied with the documents, the bank accepts the documents and the draft and if it is a bank other than issuing bank, then sends the documents to the issuing bank stating that it has accepted the draft and at maturity the reimbursement will be obtained in the pre-agreed manner.
- Settlement by Negotiation:
This settlement procedure starts with the submission of documents by the seller to the negotiating bank. in a freely negotiate documents and if negotiation restricted by the issuing bank, only nominated bank can negotiate the documents. After scrutinizing that the documents meet the credit requirement, the bank may negotiate the documents and give value to the beneficiary. The negotiating bank then sends the documents to the issuing bank as usual; reimbursement will be obtained in the pre-agreed manner.
Accounting Treatment:
Sundry Deposit L/C Margin A/C Dr.
PAD A/C Cr.
(Margin amount transferred to PAD A/C)
Customer A/C Dr.
PAD A/C Cr.
(Customer A/c debited for the remaining Amount)
PAD A/C Dr.
Head Office A/C + Exchange Trading A/C Cr.
Income A/c interests on PAD Cr.
(Amount given to Head Office ID and interest credit)
Reversal Entries:
Banker’s Liability Dr.
Customer’s Liability Cr.
(When lodgment is given)
After realizing the telex charge, service charge, interest (if any), and the shipping documents is then stamped with PAD number & entered in the PAD Register. Intimation is given to the customer calling on the bank’s counter requesting retirement of the shipping documents. After passing the necessary vouchers, endorsements is made on the back of the bill of Exchange as “Receipt Payment” and the Bill of Lading is endorsed to the effect “Please deliver to the order of M/s………………………. under two authorized signatures bank’s officer’s (P.A. holder). Then the documents are delivered to importer.
Payment procedure of the Import Documents:
This is the most sensitive task of the import department. The officials have to be very much careful while making payment.
- Date of Payment: Usually payment is made within 7 days after the documents have been received. If the payment is become deferred, the negotiating bank may claim interest for making delay.
- Preparing Sale Memo: A sale memo is made at BC rate to the customer. As the TT & DD rate is paid to the ID, the difference between these two rates is exchange trading. Finally, an Inter Branch Exchange Trading Credit Advice is sent to ID.
- Requisition for the foreign Currency: For arranging necessary fund for payment, a requisition is sent to the International Department.
- Transmission of Telex: A telex is transmitted to the correspondent bank ensuring that payment is being made.
Export:
Practically by the term Export we mean out carrying of anything from one country to another. As banker we define export as sending of visible things outside the country for sale. Export Trade plays a vital note in the development process of an economy. With the caring we meet out import bills.
Although export trade is always encouraged, any body cannot export anything to any place. Like importer the exporters are also required to get them registered before entering into export trade. Export registration certificate (ERC) given by CCI & E is required for this purpose. The required documents to obtain ERC are also same as IRC.
When a bank (Authorized dealer) receives a L/C (cable or original) it ascertains the correctness of the test number and the authorized signature. Then the bank sends the original copy of the L/C to the beneficiary.
The exporter presents the relative documents to the negotiating bank after the shipment of the goods. The L/C issuing bank undertakes to honor is obligation only if the beneficiary fulfills the conditions stipulated in the L/C, may namely, the submission of stipulated documents with in the stipulated time.
Even a slide deviation of the documents from these specified in the L/C may give an excuse to the negating bank. So the negotiating bank must be careful, promote, systematic and bias-free while scrutinizing the tender documents after careful and through examination of the documents, the banker has to
List out the discrepancies, which may be classified as major or minor, irremovable or removable. The removable discrepancies can be corrected by the tendered or future losses, which may arise due to non-repatriation of proceeds.
The following types of discrepancies may be noted while the negotiating bank examines the documents:
- L/C expired.
- Late shipment.
- Amount drawn in excess of the L/C.
- Bill of exchange not properly drawn.
- Descriptions of goods differ.
- Bill of Lading or Airway Bill state.
- Bill of Lading classed.
- Insurance Cover Note as per terms L/C.
- Insurance Cover obtained after the Bill of Lading or Airway Bill date.
10. Enough number of copies not submitted as required by L/C.
11. Negotiation under L/C restricted.
12. Packing List and certificate of analysis not as per the L/C.
13. Documents not properly endorsed in favor of the bank.
14. Full shipment not effective and part shipment prohibited.
15. Gross Weight and Net Weight shown in different documents differ.
16. Same of the documents required by L/C not submitted and
17. Documents inadequately stamped.
Documents with major discrepancies, which could not be negotiated, should be sent on collection basis with the permission of the exporter.
Export Procedure:
The Export and Importer trade in our country are regulated by imports and exports (control) Act, 1950. Under the Export Policy of Bangladesh the exporter has to get the valid Export Registration Certificate (ERC) from chief controller of Import & Export (CCI & E). The ERC is required to renew every year. The ERC number is to be incorporated on EXP Forms and other papers connected with exports.
Registration of Exporters:
For obtaining ERC indenting Bangladeshi exporters are required to apply to the Controller / Joint Controller / Deputy Controller / Assistant Controller of Imports and Exports, Dhaka / Chittagong / Khulna / Mymensing / Sylhet / Comilla in the prescribed Form along with the following documents:
- Nationality and assets certificate.
- Memorandum and Articles of Association and certificate of Incorporation in case of limited company.
- Bank certificate.
- Income tax certificate.
- Trade license etc.
Securing the Order:
After getting the ERC (Export Registration Certificate) the exporter may proceed to secure the export order. He/she can do this by containing the buyers directly or through agent. In this purpose exporter can get help from:
Liaison Office.
Buyer’s local agent.
Export Promotion organization.
Bangladesh mission abroad.
Chamber of Commerce (Local & Foreign)
Trade fair etc.
Signing the contract:
After communicating with buyer exporter has to get contracted (writing or oral) for exporting exportable item(s) from Bangladesh detailing commodity, quantity, price, shipment, insurance and marks, inspection, arbitration etc.
Receiving the Letter of Credit:
After getting contract for sale, exporter should ask the buyer for letter of credit clearly stating terms and conditions of export and payment.
The following are the main points to be looked into for receiving (collecting export proceeds by means of documentary credit:
- The terms of the L/C are in conformity with those of the contract;
- The L/C is an irrevocable one, preferable confirmed by the advising bank;
- The L/C allows sufficient time for shipment and negotiation;
Terms and conditions should be stated in contract clearly in case of other modes of payment:
- Cash in advance;
- Open A/C
- Collection basis (documentary / clean).
(Here the regulatory frame work is URC-525, ICC Publication).
Procuring the Materials :
After making the deal and on the L/C opened in his favor, the next step for the exporter is to set about the task of procuring or manufacturing the contracted materials/merchandise.
Shipment of goods:
Then the exporter should take the preparation for export arrange for delivery of goods as per L/C and INCO-terms, prepare and submit shipping documents for Payment/ Acceptance/ Negotiation in due time. Documents for shipments –
- EXP Form,
- ERC (Valid),
- L/C Copy,
- Customer Duty Certificate,
- Shipping Instruction,’
- Transport Documents,
- Insurance Documents,
- Invoice,
- Other documents,
- Bill of Exchange (if required),
- Certificate of Origin,
- Inspection Certificate,
- Quality Control Certificate,
- G.S.P. Certificate,
- Phyto-sanitary certificate,
Final Step:
After those, exporter submits all these documents along with a letter of Indemnity to NCCBL for negotiation. An officer scrutinizes all the documents. If the document is a clean one, NCCBL purchases the documents on the bank’s of banker – customer relationship. This is known as Foreign Documentary Bill purchases (FDBP).
Procedure for FDBP:
After purchasing the documents, NCCBL gives the following entries:
FDBP A/c Dr.
Customer A/c Cr.
(Before realization of proceeds)
Head Office A/c Dr.
FDBP A/c Cr.
(Adjustment after realization of proceeds).
A FDBP Registered is maintained for recording all the particulars.
Foreign documentary Bills for Collection:
United Commercial Bank Limited forwards the documents for collection due to the following reasons –
- If the documents have discrepancies.
- If the exporter is a new client.
- The banker is in doubt.
Foreign documentary bills for collection signify that the exporter will receive payment only when the issuing bank gives payment. The exporter submits duplicate EXP Form & Commercial Invoice. Subsequently, the value of the bill is calculated and the following accounting entries are given:
Head Office A/C Dr. @ TT Clean.
Client’s A/c Cr.(@ OD sight)
Govt. Tax A/c Cr.(@ of Invoice Value)
Postage A/C Cr.
Income A/c profit on Exchange Cr.
After passing the above vouchers, an Inter Branch Exchange Trading Debit Advice is sent for debiting the NOSTRO account. United Commercial Bank Limited has NOSTRO account with its reimbursing bank. an FDBP register is maintained, where first entry is given when the documents are forwarded to the issuing bank for collection and the second one is done after realization of the proceeds.
Export Bill Scrutiny Sheet :
Bank scrutinizes the export bill on they following points –
- General:
- Late shipment.
- Late presentation.
- L/C expired.
- L/C overdrawn.
- Partial shipment or Trans shipment beyond L/C terms.
- Bill of Exchange:
- Amount of bill differs with invoice.
- Not drawn on L/C issuing bank.
- Not signed.
- Tenor or B/E not identical with L/C.
- Full set not submitted.
- Invoice.
- Not issued by the beneficiary.
- Not signed by the beneficiary.
- Not made out 1 name of the applicant.
10. Description, price, quantity, sales terms of the goods not correspond to the credit.
11. Not marked one fold as original.
12. Shipping marks differs will B/A & Packing List.
Packing List :
- Gross weight, Net weight & Measurement, number of cartoons / packages differs with B/L.
- Not marked one fold as original.
- Not signed by the beneficiary.
- Shipping marks differs with B/L.
- Bill of Lading / Airway Bill :
- Full set of bill not submitted.
- B/L is not drawn or endorsed.
- “B/L shipping on Board” “Freight Prepaid” or “Freight Collect” etc. notations are not marked on the B/L.
- B/L not indicate the name and capacity of the party i.e. carrier or master, on whose behalf the agent is signing the B/L.
- Shipped on Board notation not showing name of pre-carriage vessel/intended vessel.
- Shipping on Board notation not showing port of loading and vessel name (Incase B/L indicates a place of receipt or taking in charge different from the port of loading).
- Short form B/L.
- Charter party B/L.
- Description of goods in B/L not agree with that of Invoice/E & P/L.
10. Alternations in B/L not authenticated.
11. Loaded on deck
12. B/L bearing clauses or notations expressly declaring defective condition of the goods and/or the packages.
- Others :
- Non-negotiable documents not forwarded to buyers or forwarded beyond L/C terms.
- Inadequate number of Invoice, Packing List & others submitted.
- Short shipment certificate not submitted.
Settlement of Local Bill :
The settlement of Local Bill is done in the following ways:
- The customer submits the L/C to United Commercial Bank Limited along with the documents to negotiate.
- United Commercial Bank Limited official scrutinize the documents to ensure the conformity with the terms and conditions.
- The documents are then forwarded.
- The L/c issuing bank gives the acceptance and forward an acceptance letter.
- Payment is given the customer on either by collection basis or by purchasing the documents.
Accounting treatment of or purchase of Local Bill :
Local Bill purchase documentary Dr.
Party A/c Cr.
Commission Cr.
Interest A/c Cr.
A LBPD (Local Bill purchase documentary) register is maintained to record the acceptance of the issuing bank until the acceptance is obtained, the record is kept in a collection register.
Mode of payment of export bills under L/C :
The most common methods of payment under a L/C are as follows:
- Sight Payment Credit: In a Sigh payment credit, the bank pays the stipulated sum immediately against the exporter’s presentation of the documents.
- Negotiation Credit : In negotiation Credit, the exporter has to present a bill of exchange payable to him in addition to other documents that the bank negotiation.
- Deferred Payment Credit: In deferred payment, the bank agrees to pay on a specified future date or event, after presentation of the export document. No bill of exchange is involved. In UCBL, payment is given to the party at the rate of D.A 60-90-120-180 as the case may be. But the Head Office is paid at T.T clean rate. The difference between the two rates is the exchange trading for the branch.
- Acceptance Credit: In acceptance credit, the exporter presents a bill of exchange payable to himself and drawn at the agreed tenor (that is, on a specified future date event) on the bank that is to accept it. The bank signs its acceptance on the bill returns it to the exporter. The exporter can then represent it for payment on maturity. Alternatively he can discount it in order to obtain immediate payment.
Advising L/C :
When exporter L/C is transmitted to the bank for advising, the bank sends an advising letter to the beneficiary depicting that L/C has been issued.
Test Key Arrangement :
Test Key arrangement is a secret code maintained by the banks for the authentication for their telex message. It is a systematic procedure by which a test number is given and the person to when this number is given can easily authenticate the same test number by maintaining that same procedure. United Commercial Bank Limited has test key arrangements with so many banks for the authentication of L/C messages and for making payment.
Back to Back Letter of Credit :
A Back to Back letter of credit is a new credit. It is different from the original credit based on which the bank undertakes the risk under the back to back credit. In this case, the bank’s main security is original credit. The original credit (selling credit) are separate instruments independent of each other and in no way legally connected – although they both from part of the same business operation.
The supplier (beneficiary of the back to back credit) ships goods to the importer and presents documents to the bank as is specified in the credit. It is intended that the exporter would substitute his own documents for negotiation under the original credit, his liability under the back to back letter of credit would be adjusted out of these proceeds. The exporter L/C is marked lien and no margin is taken.
In UCBL, papers/documents required for submission for opening of back to back L/C:
A) Master L/C
B) Valid Import Registration Certificate (IRC) & Export Registration Certificate (ERC).
C) L/C application & LCA Form duly filled in signed.
D) Proforma Invoice or Indent.
E) Insurance Cover Note with money receipt.
F) IMP Form duly signed.
In addition to the above the following papers/documents are also required for export oriented garments industries while requesting for opening back to back letter of credit –
- Textile permission.
- Valid bonded warehouse license.
- Quota allocation letter issued by Export Promotion Bureau (EPB) in favor of the applicant in case of quota items.
- In case the factory premises is a rented one, letter of disclaimer duly executed by the owner of the house/premises to be submitted.
Detective points or clauses appears in the Master L/C:
- Issuing bank is not reputed.
- Advising Credit by the advising bank without authentication.
- Port of destination absent.
- Inspection clause.
- Nomination of specific Shipping/Airline or nomination of specified vessel by subsequent amendment.
- B/L to blank endorse, to third bank, to be endorsed to buyer or third party.
- No specific reimbursing clause.
- UCP clause not mentioned.
- Shipment / presentation period is not sufficient.
- Original document to be sent to buyer or nominated agent.
- FCR or HAWB consigned to applicant or buyer.
- “shippers’ Load and Count is acceptable”.
- L/C shall expire in the country of the issuing bank.
- Negotiation is restricted.
Payment of back to back Letter of Credit:
In case of back to back as 60-90-120-180 days of maturity period, deferred payment is made. Payment is given after realizing export proceeds from the L/C issuing bank.
Accounting treatment for back to back L/C:
When the document is arrived, the following vouchers are passed:
Customer’s A/c Dr.
Commission on Acceptance Cr.
While payment, if the fund is at hand, the accounting entry is –
Sundry deposit margin on acceptance Dr.
Customer’s A/c Cr.
If the party is paid in foreign currency, B.C. rate is applied in this regard. International department takes the T.T. OD. Rate. If the payment is made to ID in local currency in national rate, T.t. clean rate is followed by ID. When the party is paid O.D sight rate is followed.
If the fund is not available to make the payment, the following vouchers are to passed –
OAP Dr.
Customer’s A/c Cr.
Under the back to back concept, the seller, as beneficiary of the credit, offer it as security to the advising bank for the issuance of the second credit. As application for this second credit the seller is responsible for reimbursing the bank for payment made under it regardless of whether or not be himself is paid under the first credit. There is, however, no compulsion for the bank to issue the second credit, and in fact, many banks will not do so.
Foreign Exchange Remittance :
Remittance means sending of fund. The word remittance we understand sending/ transferring of fund through a bank from one place to another place which may be within the country or between two countries, one in abroad is called Foreign Remittance.
“Foreign Remittance” means purchase and sale of freely convertible foreign currencies as admissible “Foreign Exchange Regulations Act-1947” and “Guidelines for Foreign Exchange Transaction – VOL. 1&2 of the country. Purchase of foreign currencies constitutes inward foreign remittance and sale of foreign currencies constitutes out ward foreign remittance.
So we see that there are two types of Foreign Remittance:
- Foreign inward remittance.
- Foreign outward remittance.
Inward Remittance:
The remittances which are received from abroad are called inward remittance.
Purpose of inward remittance:
- Family maintenance.
- Indenting commission.
- Donation.
- Gift.
- Foreign investment.
- Export proceeds.
- Others.
Mode of inward remittance:
- Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
- Mail transfer (MT)
- Foreign Demand Draft (FDD)
- Payment order (PO)
- Travelers cheque (TC)
- Foreign Currency Notes.
Outward Remittance:
Remittances which are made from our country to abroad is called outward remittance.
Mode of outward remittance:
- Foreign Telegraphic Transfer (FTT)
- Foreign Mail Transfer (FMT)
- Foreign Demand Draft (FDD)
- Travelers Cheque (TC)
- Foreign Currency Notes.
Present limit of outward remittance fixed by Bangladesh Bank :
- Travel:
For Private Travel : Private travel quota entitlement of Bangladesh national total US$3000 per calendar year for visit to countries other than SAARC (India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Srilanka, Maldives) and Myanmar.
Quota for SAARC countries and Myanmar is US$1000 for travel by Air and US$500 for travel by land. At a time bank can issue full amount of above quota if required. Case dollar may be issued maximum US$600 per passport per travel. The amount of travel quota mentioned above are prescribed for adults only. The minors are eligible for 50% of the annual ceilings of adults.
Business Travel :
(1) Subject to an annual upper limit of US$5000 importers are entitled to business travel quotas 1% of their imports settled during the previous financial year.
(2) Subject to an annual upper limit of US$5000 non exporting producers are entitled to business travel quotas 1% of their turnover of the preceding financial year as declared in their tax return.
a) For Exporters: New exporters are entitled to a quota for US$ 6000 annually and old exporters can use FCAD expanse retention quota A/c as per their requirement.
b) For Foreign Nationals : The Authorized Dealers may issue foreign currency TCS to foreigners without any limit and foreign currency notes up to US$300 or equivalent per person against surrender of equivalent amounts in foreign currencies.
- Bank charges and sundries:
The Authorized Dealers may effect remittances toward settlement of dues to foreign banks of bank charges. Cost of cables and other incidental charges arising in their normal curse of the business without prior Bangladesh Bank approval. All such remittances should be reported to the Bangladesh on forms TM along with appropriate return.
- Taking out / Bringing in of Bangladeshi Taka:
Incoming, outgoing passengers may bring in/take out up to taka 500 per person in Bangladesh currency.
In all above cases for outward remittance TM form to be obtained and this will have to be reported to Bangladesh Bank Monthly basis.
Submission of Returns to Bangladesh Bank:
The Ads must maintain adequate and proper records of all foreign exchange transactions including transaction on non-resident Taka A/C in their book and furnish such particular in the prescribed statements/returns for submission to the Bangladesh Bank.
The purpose of submission of return & statements to Bangladesh Bank for keeping systematic and proper records of all dealings in foreign exchange including transactions on non-resident Taka A/Cs. Submission of the returns/statements to Bangladesh Bank is very much important. Total picture of foreign exchange transaction of the country such as reserve of FC, FCs earned through export, wage earners & other reference and FCs paid through import, treatment, education, traveling etc can be ascertained after compilation of these returns/statements submitted to Bangladesh Bank by the ADs.
Procedures for reporting transactions:
A) Export :
Export bills drawn under confirmed and/or irrevocable L/Cs:
Transactions in respect of export bills negotiated by the Ads should be reported as purchase only at the time entries are made in the currency account duly supported by EXP form and schedule:
a) EXP Original reported by Custom Authority to Bangladesh Bank at the time of shipment/export.
b) EXP . duplicate : To be reported by the Ads to Bangladesh Bank within 14 days of shipment.
c) Exp. Triplicate : To be reported after repatriation of the export proceeds.
Export bills drawn on Collection basis :
Sometimes ADs also purchase export bills drawn on collection/CAD basis. Transactions relating to such export bills should be reported as outright purchases against “export” in the summary statement on receipt of advice of realization of the export proceeds.
Export bills pertaining to Head Office or branch maintaining independent currency account:
When export bills are re-discounted with the Bangladesh Bank the transactions should be reported as purchase in the Summary statement supported by Schedule A and Exp Form and the contra entries should be reported on schedule D as sales to Bangladesh Bank.
Export bills pertaining to branch not maintaining its own currency account :
As and when the exports are re-discounted with the Bangladesh Bank the branch concerned will report the transactions as purchase in the summary statement supported by Schedule A-1/0-1 and Exp. Form.
B) Other Receipts :
Purchase of DD, TT and MT etc. should be reported to Bangladesh Bank only when the transactions are put through the currency accounts.
C) Imports :
- Foreign currency A/Cs of ADs are debited at the time of negotiation of import documents by their foreign corespondent drawn under the L/Cs established by the ADs. Sale of this F.C. should be reported on receipt of negotiated import documents and not on the basis of retirement of bills by the importer.
- All sales on account of imports are required to be supported by the original copy of the IMP form.
- Import bills received on collection/CAD basis, the transactions will be reported on Schedule E-2 supported by original IMP Form.
D) Other payment :
Transactions relating to DD, TT, MT etc issued by the Ads should be reported only at the time of entries are made in the currency accounts.
Transactions in non-resident Taka accounts of foreign banks should also be reported by the ADs.
Coding of Transactions:
AD will give code numbers for all receipts and payments transactions on the relevant forms and schedules as per code list provided by Foreign Exchange Policy Dept. Bangladesh Bank (2000 edition) and. AD will use the HS Code number form the HS Code Guide titled “The Harmonized commodity Description and Coding System” exports and imports in the relevant schedules.
Reporting Procedure for cash transaction:
Ads shall report to the Bangladesh Bank particulars of all their foreign exchange transactions i.e. all outward and inward remittances effected. Whether through their accounts in foreign currencies or through the Taka accounts of non-resident banks. The original copies of statement / schedules to be sent directly to the Statistics Dept. Bangladesh Bank Head Office, Dhaka the duplicate copies along with the relevant forms should be endorsed to the concerned area office of Bangladesh Bank. these monthly statement / schedules to be sent to Bangladesh Bank by the 5th day of the following month.
Compilation of summary statement:
Each summary statement will be an abstract of the Ads ledger A/c and will consist of totals under specified heads. Opening and closing balances should be added making each summary a complete and balance statement.
Supporting schedules and forms of the summary statement:
Every summary statement must be accompanied by schedules and the relative forms as indicated in the summary statements.
Preparation of schedules:
Schedule A-1 :
When EXP form is certified against purchase of FCS the transaction must be listed in schedule A-1 in triplicate showing the number of EXP form and the amount.
Schedule A-2:
a) Advance receipt for goods to be exported this is to be reported through “Advance Receipt Voucher” (A[ppendix-19 Vol-2)
b) Where the duplicate EXP form has already been lodged with the Bangladesh Bank and the triplicate is not available at the time when proceeds are received. This is to be reported through “EXP form not attached voucher” (Appendix 20-Vol-2).
Schedule A-3:
Schedule A-3/0-3 is used to report purchase of F.C. against export to Myanmar under Bangladesh – Myanmar Border Trade Arrangement.
Schedule –C :
Currencies purchased from other Ads or branches in Bangladesh to be reported in schedule – C to be attached with relative S-1, S-2 and S-6 statement.
Schedule – G:
Currencies sold to other Ads or branches in Bangladesh to be reported in schedule-G to be attached with S-1, S-2, and S-6.
Schedule – D:
FCs purchased from and sold to Bangladesh Bank to be reported as Schedule-D.
Schedule – E-2/P-2, E-3/P-3 and EL 1/2/3:
All import transactions to be reported schedule E=2/P-2 and the charges (interest reimburse etc.) there against and other sales other than import Traveling, Treatment, Service/Technical charges etc in schedule E-3/P-3. Transactions relating to Loans/Grants will be reported through EL-1/2/3.
Reporting of Inland L/C settlements:
Payment against inland L/Cs in foreign exchange will be reported in summary statement S-1 or sales side as “Payment against Inland L/C” and the recipient AD will report the receipt on the purchase side of S-1 as “Receipt in settlement of Inland L/C”.
Date of submission of statements to Bangladesh Bank:
Schedule Time
| 1. Operations on private non-resident Taka accounts of non-bank clients. | Quarterly with 12th day of following month. |
| 2. Monthly statement of outstanding payment commitments abroad | By 15th of following month |
| 3. Commodity wise statement of imports L/Cs outstanding as on each month end. | 10th of the following month |
| 4. Monthly statement of outstanding exports bills as of each month end. | 15th of the following month. |
Currency wise daily position statements should be kept ready for immediate submission to Bangladesh Bank as and when called for.
CHAPTER-04
Recommendations for uplifting of Habib Bank Limited
With a view to ensure exciting services and opening up the new window of progression as well as uplift, we should like to present the Habib Bank Ltd. Ltd with several recommendations like:
General Banking:
- Introducing the “customer Day” or “Care U” week and new advertisement on different TV channels.
- Launching one stop service cell.
- More skilled persons are needed for reducing busyness.
- Two branches should be under on line banking.
Foreign trade:
- More persons are needed for instant service.
- High executive should deal this department directly.
Human Resources:
- Some qualified officers should be promoted properly. Without it they become demoralized.
- Sending the assistant officers and officers to BIBM for better view over pragmatic knowledge they know what they doing but don’t know how and why they are adopting different banking practice.
- Motivating employee with special bonus and tour to foreign country
- Should be developing more interpersonal relation.
Sales promotion and Ad Campaign:
- Arranging the Habib Bank Ltd. Inter College Debate Contest and quiz test for children.
- Offering scholarship for the Varsity Students and School goers.
- Offering pre shipment and post shipment finance.
These initiatives will ensure healthy sales volume as well as well progression for the Habib Bank Ltd. And a new door of possibility will open up.
Conclusion:
The education or study / training are then effective when it is related with practical. Students are very much practical oriented in the department of science because they are laboratory room oriented. In the business world the study also must be related with practical field. The principles, operations whose we read and memorize from various books, we should know whether it implemental in practical field. There has no alternative to make the business study effective. Though the books are available in the syllabus of business administration was written according to the operation of generally recognized industries but in implementation of those theoretical principals, procedures are not same in every industry. Especially in the environment of Bangladesh there has a lot of deviation is seen. Why this deviation how to overcome from that deviation, try to find out the reason and try to give solution and recommendation.
In the organizational environment I feel very cozy to work in that type of convenient ambience. The premises expedite me for enhancing my knowledge as well as give me a proper safeguard about upcoming future circumstances.
















