Credit Management Policy of Mutual Trust Bank Limited
Banking sector is one of the fastest growing sectors in Bangladesh like the whole world. Therefore understanding the policies of banks and financial institutions has become a mandatory issues for everyone and especially for business graduate.
This internship report was prepared to fulfill the Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) degree and to evaluate my knowledge regarding credit policy. As a part of the internship program I had to work in Mohammadpur Branch of Mutual Trust Bank (MTB). Therefore I have prepared the whole report on the credit management policy of Mutual Trust Bank Limited.
The report will be divided in five chapters completed with references and appendix. The chapters will be introduction, profile of MTB, literature review, analysis and findings and conclusion.
Credit Risk Management: Bangladesh Scenario
Credit risk management needs to be a robust process that enables banks to proactively manage loan portfolios in order to minimize losses and earn an acceptable level of return for shareholders. Central to this is a comprehensive IT system, which should have the ability to capture all key customer data, risk management and transaction information including trade & Forex. Given the fast changing, dynamic global economy and the increasing pressure of globalization, liberalization, consolidation and dis-intermediation, it is essential that banks have robust credit risk management policies and procedures that are sensitive and responsive to these changes.
Bangladesh Bank provides directional guidelines to the banking sector that improves the risk management culture, establish minimum standards for segregation of duties and responsibilities, and assist in the on-going improvement of the banking sector in Bangladesh.
Objectives of the report
The report will try –
- To know the lending procedure of Mutual Trust Bank Limited.
- To evaluate the actual position in classified Loan and provisions maintained by MTB.
- To know the terms and conditions of credit management of Mutual Trust Bank Limited.
- To analyse the work process and monitoring system of credit department.
- To appraise the actual recovery position of MTB.
- To identify problems and recommend solution in credit management of Mutual Trust Bank Ltd.
Methodology
Methodology implies more than simply the methods used to collect data. It is often necessary to include a consideration of the concepts and theories which underlie the methods(Kumar, 2005). For instance, if one intends to highlight a specific feature of a sociological theory or test an algorithm for some aspect of information retrieval, or test the validity of a particular system, s/he have to show that s/he understand the underlying concepts of the methodology. This reports mainly works with secondary data source due to lack of availability of primary data source.
Research Type:
This is an analytical research work, which tries to provide a brief on the “Credit Management” of Mutual Trust Bank.
Sources of Data
To prepare this report all the necessary information collected from secondary sources of data. Being an analytical report there was little to no option for collection primary data.
Secondary sources of data are of two kinds, Internal:
Annual Reports of Mutual Trust Bank, Other published documents of the bank, Mutual Trust Banks Website.
External: Books, Articles, Journals, Newspaper, Web browsing.
Beside the secondary sources of data, practical desk work and observation techniques are also used as primary sources of data to prepare this report. Though me agree in amount it has still helped the writer a lot on the progress of this work.
Background Profile of MTB
The Mutual Trust Bank was incorporated as a public limited company on September 29, 1999 under the Companies Act 1994. The Bank started its commercial operation on October 05, 1999 with an authorized capital of BDT 200 Million divided into 2,000,000 ordinary shares of BDT 100 each(Mutualtrustbank.com, 2014). Aiming at offering commercial banking service to the customers’ door around the country, Mutual Trust Bank Limited establishes 67 branches up-to this year. This organization achieved customers’ confidence immediately after its establishment in domestic and international markets.
Mutual Trust Bank is one of the few banks permitted by the Bangladesh bank in the early 90s; the other banks permitted earlier were Dutch-Bangla Bank, Al-ArafahIslami Bank, Prime Bank, Dhaka Bank, Eastern Bank, ONE Bank. These banks are known as the second generation banks and fortunate to remain immune from the bad loan culture. The emergence of Mutual Trust Bank Limited at the junction of liberation of global economic activities, after the URUGUAY ROUND has been an important event in the financial sector of Bangladesh(Bankinfobd.com, 2014).
Mutual Trust Bank Limited has been licensed by the Government of Bangladesh as a Scheduled Bank in the private sector in pursuance of the policy of liberalization of banking and financial services and facilities in Bangladesh. In view of the above, the Bank within a period of 15 years of its operation achieved a remarkable success and met up capital adequacy requirement of Bangladesh bank.
Capital Structure
The capital structure of Mutual Trust Bank Ltd. is quite strong. At present, Authorized Capital of the company is BDT 10.00 Billion (BDT 1000.00 crore) divided into 100,000,000 ordinary shares of BDT 100 each.
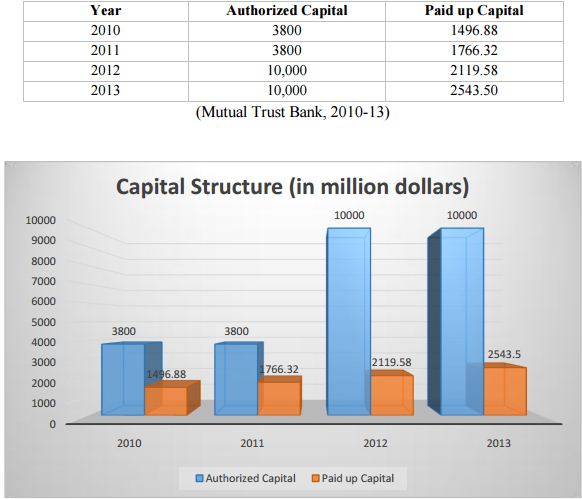
From the graph it is seen that in2010 the authorized capital was 3800 million and paid up capital was 1496.88 million. The authorized capital and paid up capital both are increased year by year. In 2013 its authorized capital increased by10000 million and paid up capital also increased by 2543.50 million.
Departments of Mohmmadpur Branch
General Banking (GB) Department:
Some of the day-to-day activities of this department are the following.
- Account Opening
- Receiving Cheques for Clearing, Transport, and Dispatch
- Issuance of Cheque
- Issuance of PO (Pay Order), DD (Demand Draft), etc.
- Fund Transfer
- Closing and Transfer of Accounts
- Maintaining the Locker of the Bank
- Outward Clearing of IBC and OBC
- Opening and Maintaining of FDR and other Scheme Deposits
- Utility bill, Rent of building and work of accounts department was done by GB because they don‟t have any separate accounts department
- Maintaining On-line Voucher
Cash Department:
This department is responsible for cash payment and receipt. The employees in this department are also liable for computer posting, passing cheques, and accuracy of posting, balancing on-line accounts, etc.
Credit Department:
This department is responsible for the following jobs:
- Preparing CIB Statements
- Preparing Credit Proposal and Statement
- Prepare the application form to provide loan
- Administration of Retail Credit
Foreign Exchange Department
- Verification of L/C application
- L/ C opening.
- Advising L/C
- Sanction the application
- Export trade financing
- Remittance
Marketing and Customer Care Department
Searching for new customer, answer the inquiry about the product to the customer. They also look whether customer all documents are given or not ofMohmmadpurBranch
General Banking (GB) Department:
Some of the day-to-day activities of this department are the following.
Account Opening
- Issuance of Cheque
- Receiving Cheques for Clearing, Transport, and Dispatch
- Issuance of PO (Pay Order), DD (Demand Draft), etc.
- Opening and Maintaining of FDR and other Scheme Deposits
- Fund Transfer
- Closing and Transfer of Accounts
- Maintaining the Locker of the Bank
- Outward Clearing of IBC and OBC
- Maintaining On-line Voucher
- Utility bill, Rent of building and work of accounts department was done by GB because they don‟t have any separate accounts department
Cash Department:
This department is responsible for cash payment and receipt. The employees in this department are also liable for computer posting, passing cheques, and accuracy of posting, balancing on-line accounts, etc.
Credit Department
- This department is responsible for the following jobs:
- Prepare the application form to provide loan
- Preparing CIB Statements
- Preparing Credit Proposal and Statement
- Administration of Retail Credit
Foreign Exchange Department
- L/ C opening.
- Verification of L/C application
- Sanction the application
- Advising L/C
- Export trade financing
- Remittance
Marketing and Customer Care Department
Searching for new customer, answer the inquiry about the product to the customer. They also look whether customer all documents are given or not.
Credit
The word credit comes from the Latin word “Credo” meaning “I believe”. It is a lender‟s trust in a person‟s or firms or company‟s ability or potential ability and intention to repay. Credit is a contractual agreement, in which a borrower receives something of value now, with the agreement to repay the lender at some date in the future(Kothari, 2013). One of the basic functions of the bank is deposit extraction and credit extension. Managing credit operations is the crying need for any bank.
The objective of the credit management is to maximize the performing asset and the minimization of the non-performing asset as well as ensuring the optimal point of loans and advances and their efficient management.
Factors Considered for Credit
- Time
- Operating Expense
- Risk
- Interest Rate
- Legal Considerations
- Finance Charge
- Inflation
Significance of Credit
- Business cycle can run well only by the help of lending system
- It helps to create employment opportunities
- Credit plays a vital role in national economy in the following ways-
- It provides working capital for industrialization
- Credit controls almost all kinds of production activities of the country
- It brings social equity
- Cash generation occurs for its successful performance
- Economic stabilization
- Raise standard of living.
Credit Management
Credit management is a dynamic field where a certain standard of long-range planning is needed to allocate the fund in diverse field and to minimize the risk and maximizing the return on the invested fund. Continuous supervision, monitoring and follow-up are highly required for ensuring the timely repayment and minimizing the default. The overall success in credit management depends on the banks credit policy, portfolio of credit, monitoring, supervision and follow-up of the loan and advance. Therefore, while analysing the credit management of MTB, it is required to analyse its credit policy, credit procedure and quality of credit portfolio.
Credit Policy of MTB
One of the most important ways, a bank can make sure that its loans meet organizational and regulatory standards and they are profitable. It is important to establish a loan policy. Such a policy gives loan management a specific guideline in making individual loans decisions and in shaping the bank‟s overall loan portfolio. In Mutual Trust Bank Limited there is perhaps a credit policy but there is no credit written policy.
Principles of Credit
In the feature, credit principles include the general guidelines of providing credit by branch manager or credit officer. In Mutual Trust Bank Limited they follow the following guideline while giving loan and advance to the client(Edwards, 2004).
- All credit extensions must comply with the requirement of Bank Company Act and the Central bank.
- Not to extend credit to the persons/entities not supported by CIB report.
- To maintain judicious ratio between loan and deposit.To allow credit in a manner which in no way compromises with banks standard of excellence.
- Extension of credit normally from customer‟s deposits and not out of short term funds or borrowing from other banks.
- To optimize risk and reward.
- To ensure ethical standard in all credit activities.
- To extend credit in the areas, risk of which can be sufficiently understood and managed.
- To extend credit facility upon adequate pre investment analyses and repayment capacity of the clients.
- To avoid excessive credit concentration through rational diversification of credit.
- To avoid name lending.
- To allow credit on business consideration after ascertaining viability, credit requirement, quality of advance, security offered, cash flows and level of risks.
Principles of Sound Lending
It should be clearly understood that the criteria/principles are not inflexible laws & are given as guidelines for protecting credit. In a practical competitive world, risks are defined, accepted and credit is often granted even though a proposal does not strictly with some of the criteria described below.
The basic lending criteria can be considered as eight main headings, as follows:
1) Principle of Safety
2) Principle of Liquidity
3) Principle of Purpose
4) Character and ability of the borrower
5) Principle of Security
6) Principle of profitability
7) Source of repayment
8) Principle of National Interest
Each of the headings will now be discussed further in the following paragraph:
Principle of Safety
The first lending Principle of sound lending is safety. The very existence of a bank depends upon the safety of its advances. So utmost care should be exercised to ensure that the funds go to the right type of borrower, are utilized in such a way that they remain safe and the repayment comes in the normal course.
Principle of Liquidity
Liquidity means the availability of Bank funds on short notice. The liquidity of an advance means it repayment on demand on due date or after a short notice. Therefore, the banks must have to maintain sufficient liquidity to repay its depositors and trade-off between the liquidity and profitability is must.
Principle of Purpose
The bank should not lend money for any purposes for which a borrower may be free from all risks but if the funds borrower are employed for unproductive. Purpose like marriage ceremony, pleasure trip etc. or speculative activities, the repayment in the normal course will become uncertain. Banks therefore discourage advances from boarding stocks and refuse advances for speculative activities.
Character and ability of the borrower:
The primary responsibility of the leading banker is “know your customer and his business”. While considering the character and ability of a borrower, the following point must be kept in mind.
Do know your customer already?
Was he respectively introduced?
- If he was previously customer of another bank, why has he come to United Commercial Bank Ltd. Try to see previous bank statement?
- Have you made the account opening inquiries required by the bank?
- hat are the business its ownership?
- What is the customer‟s background and financial track record?
- Customer‟s honesty & integrity and personal stability?
- How has the customer managed his financial circumstances in the past?
The branch manager should have the answer of the above queries and should be to judge his ability to use the credit facilities to his advantage. Advance should be granted only to those borrowers in whom the branch manager has full confidence.
Principle of Security
The security offered by a borrower for an advance is insurance to the banker. It serves as the safety value for an unforeseen emergency. The security accepted by a banker to cover a bank advance must be adequate, readily marketable, easy to handle and free from any encumbrance.
Principle of Profitability
The working funds of a bank are collected mainly by means of deposit from the public and interest has to be paid on those deposits. Banks have also to meet their establishment charges and other expenses. Interest earned by a bank on its advance is the main source of its income(Bucci, 2011). The difference between the interest received on advances and the interest paid on deposits constitute a major portion of the banker‟s income. The bank will not enter into a transaction unless a fair return form it is assured.
Source of Repayment
After the branch manager has ensured that the credit will be a profitable propositioning for the bank, he should then turn his attention to the cash flow situation of the borrower. The bank‟s credit can be classified into three main categories, as follows:
- A very short-term advance will be liquidated by funds received in the very near future, such as advances against foreign or local bills or bridge functioning where evidence of credit sanction from another financial institution is available.
- Provision for current assets; this type facility is needed for trading and /or manufacturing activities.
- Long term loans, generally over 5 years; example of such facilities as investment in plant and machinery, a farm or a shop, generally, a long term is repaid out profits generated by the business.
Principle of National Interest
The development of banking has reached a stage where a banker is required to identify his business with national policies. Banking Industry has significant role to play in the economic development of a country. So, the savings of the people which are mobilized by banks must be distributed to those sectors which require development in the country‟s Planning Program.
Global Credit Portfolio Limit of MTB
The features which deals with how much total deposits would be used as lending the proportion of long term lending, customer exposure, country exposure, proportion of unsecured facility etc. the most notable ones are:
The aggregate of all cash facility will not be more than the 80% of the customers‟ deposit and Long term loan must not exceed 20% of the total loan portfolio. Facilities are not allowed for a period of more than 5 (Five) years. Credit facilities to any one customer group shall not normally exceed 15% of the capital fund or TK. 100 cores.
Type of Credit Activities:
Credit may be classified with reference to elements of time, nature of financing and provision base.
3.9.1 Classification on the basis of time
On the basis of elements of time, bank credit classified as:
Continuous loan:
These are the advances having no fixed repayment schedule but have a date at which it is renewable on satisfactory performance of the clients. Continuous loan mainly includes “Cash credit both hypothecation and pledge” and “Overdraft”.
Demand loan:
In opening letter of credit (L/C), the clients have to provide the full L/C amount in foreign exchange to the bank. To purchase this foreign exchange, bank extends demand loan to the clients at stipulated margin. However, as soon as the L/C documents arrive, the bank requests the clients to adjust their loan and to retire the L/C documents. Demand loans mainly include “Payment against Documents,” “Loan against imported merchandise (LIM)” and “Later of Trust Receipt”(Laurin and Majnoni, 2003).
Methods of Charging Securities
The following modes of charging securities are applied in the Mutual Trust Bank Limited.
- Lien
A lien is right of banker to hold the debtor‟s property until the debt is discharged. Bank generally retains the assets in his own custody but sometimes these goods are in the hands of third party with lien marked.gives banker the right to retain the property not the right to sell. Permission from the appropriate court is necessary.
- Pledge
Pledge is also like lien but here bank enjoys more right. Bank can sell the property without the intervention of any court, in case of default on loan, But for such selling proper notice must be given to the debtor. To create pledge, physical transfer of goods to the bank is must.
- Hypothecation
In this charge creation method physically the goods remained in the hand of debtor. But documents of title of goods are handed over to the banker. Since the goods are in the hand of the borrower, bank inspects the goods regularly to judge its quality and quantity for the maximum safety of loan.
- Mortgage6
Mortgage is transfer of interest in specific immovable property. Mortgage is created on the immovable property like land, building, plant etc. Another method called equitable mortgage is also used in bank for creation of charge. Here mere deposit of title to goods is sufficient for creation of charge.
- Trust Receipt
Generally goods imported or bought by bank’s financial assistance are held by bank as security. Bank may release this lien / pledge these goods against trust receipt. This means that the borrower holds goods in trust of the bank; trust receipt arrangement is needed when the borrower is going to sell these goods or process it further but borrower has no sufficient fund to pay off the bank loan
- Advance against Work-Order
Advances can be made to a client to perform work order. The following points are to be taken into consideration. The client‟s management capability, equity strength, nature of scheduled work and feasibility study should be judiciously made to arrive at logical decision.
- Advance against Approved Shares
Credit facilities to extend against shares will be called “Investment Scheme against Shares”. Advance may be allowed against shares of companies listed with the Stock Exchange Ltd.
- Advance against Fixed Deposit Receipts
Advance against Fixed Deposit Receipt will be subject to credit Restrictions imposed from time to time by Head Office / Bangladesh Bank. Mutual Trust Bank Limited usually sanctions credit limit up to 80% of the FDR value. Scrutinize the Fixed Deposit Receipts with regard to the following points.
a) The Fixed Deposit Receipt is not in the name of minor.
b) It is discharged by the depositor on revenue stamp of adequate value& his signature is verified.
c) Creation of liability on Fixed Deposit issued in joint names by any one of the depositors is regular.
d) If the Deposit Receipt is offered as a security for allowing advances, a letter of lien shall be obtained from the depositors, on the appropriate form.
e) If the Deposit Receipt has been issued by the branch-allowing advance, lien against that specific Deposit Receipt to be marked in the fixed Deposit Register of the branch.
Credit Risk Grading (CRG) System
Credit risk grading is an important tool for credit risk management as it helps the Banks & financial institutions to understand various dimensions of risk involved in different credit transactions. The credit risk grading system is vital to take decisions both at the pre-sanction stage as well as post-sanction stage .At the pre-sanction stage, credit grading helps the sanctioning authority to decide whether to lend or not to lend, what should be the loan price, what should be the extent of exposure, what should be the appropriate credit facility, what are the various facilities, what are the various risk mitigation tools to put a cap on the risk level. At the post-sanction stage, the bank can decide about the depth of the review or renewal, frequency of review, periodicity of the grading, and other precautions to be taken. Usually there includes six steps for CRG. These are:
- Identify all the Principal Risk Components
- Allocate weights to Principal Risk Components
- Identify the Key Parameters
- Assign weight to each of the key parameters
- Input data to arrive at the score on the key parameters.
- Arrive at the Credit Risk Grading based on total score obtained.
Analysis, Discussion and Findings
Analysis is the most crucial part of a report. Quantitative analysis has been done in this report. This analysis will give an idea about the credit performance of Mutual Trust Bank Limited. Included quantities analysis will be: Time Series Analysis, Ratio Analysis, and Comparative Analysis.
Performance of Loan & Cash Credits Overdraft of 2012 compared with 2013
Table: Performance of Loan & Cash Credits Overdraft Comparison (2012-13)
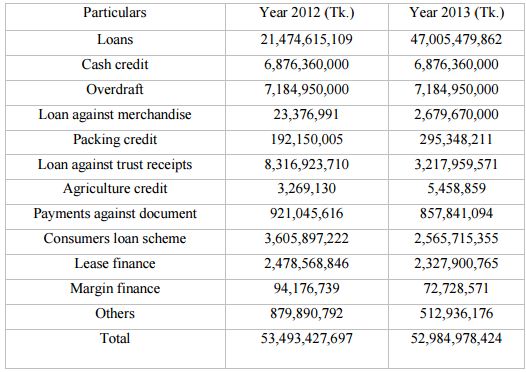
Findings: Here cash credit, loan against trust receipt, payment against document, consumer loan scheme, lease finance, margin finance, was increasing by comparing with previous year. Others are decreased.
Total amount of Loan increased by Tk.508, 449,270 from the year of 2012.
Performance of Industrial Advances of 2012 comparison with 2013
Table: Performance of Industrial Advances of 2012 comparison with 2013
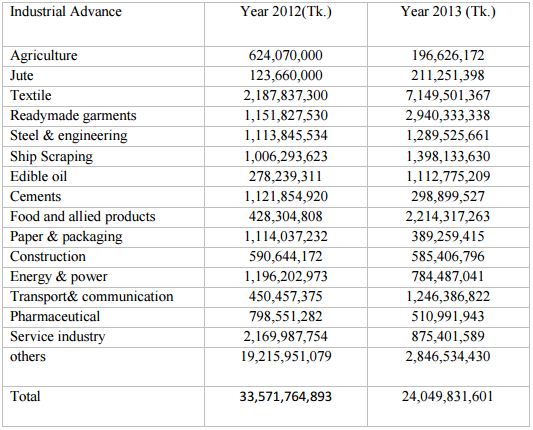
Findings: According to this chart, all the sectors of industrial advances were increasing compare to previous year except paper and packaging, construction. In industrial sector specially textile, jute, readymade garments are playing a major role in our national economy. So by increasing advance in this sector, Mutual Trust Bank Limited performs well in productive unit in our country which can help to increase the total GDP.
Total industrial advances increased by Tk. 9,521,933,290 from the year of 2012.
Sector wise Loan & Advances:
A wide range of business industries and sectors constitutes the Bank’s advance portfolio. Major sectors where the Bank extended credit include steel & engineering, readymade garments, textile, ship breaking, edible oil, sugar, housing & construction, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, electronic & automobiles, energy & power, service industries, trade finance, personal or consumer credit, leasing etc. The Bank continued to support Small and Medium Enterprises (SME) and expended credit facilities to them through its SME Cell. Sectoral allocation of advances reveals a well-diversified portfolio of the Bank with balance exposure in different sectors.
Table: Sector wise Loan & Advances
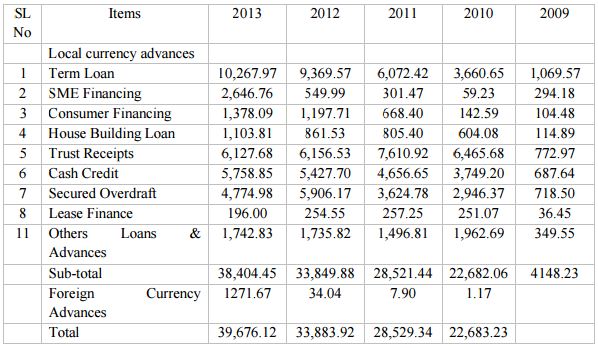
From the table, Mutual Trust Banks high concentration is in term loan which was increasing year by year. In the year 2009 it was only 1,069.57million which was increased by 10,267.97 million in 2013.In trust receipt it has been seen that the amount as decreasing. Although trust receipt was high in 2011 at 7,610.92 million but it decreasing at 6,127.68 million in year 2013.In the sector of cash credit the total amount was increasing year by year. In 2010 cash credit was 3,749.20million which increased at 4,656.65 million in year 2011 and it stood at 5,758.85 million in year 2013.The amount of secured overdraft was fluctuating from year 2009 to 2013. Secured overdraft was high in 2012 at 5,906.17 million and low in year 2011 at 2,946.37 million. In SME financing, Mutual Trust Bank utilized huge amount in year 2013 at 2,646.76 million where it was 549.99 million in 2012, 301.47 million in 2011 and 59.23 million in 2010.Consumer financing was also increasing year by year. Consumer finance was only 15.45 million in 2010 where it was 1,378.09 million in year 2013.House building loan was also increasing year by year. Bill purchased and discounted amount were fluctuating. It was low in year 2013 at 1777.65 million and high in year 2011 at 3027.34 million. Loan to MTB securities Ltd was 2,656.83 million in year 2013 and it was not perform in previous years.
Summary of Findings
- The total investment of the bank is growing year by year. And from the current rend it can be expected that this growth rate will continue in future.
- The standard loan and advances of mutual Trust Bank is increasing year by year. And it carries positive sign for Mutual Trust Bank. It also induces trust ability among its stakeholders.
- The interest income from loan and advances of Mutual Trust Bank limited is increasing year by year. This means the bank‟s net profit will increase further and it can expand more widely.
- From the last two years analysis it has been seen that Mutual Trust bank was providing more credit facilities in urban areas than rural areas which encourages governments to be more sympathetic their causes.
- Total Deposit is increasing which represent the positive sign for the bank as deposits are increasing than the bank can use more proportion of deposit for loans and advances.
- The recovery rate of Mutual Trust Bank has increased year by year which means number of bad debts has decreased.
- Day by day non-performing loan of Mutual Trust Bank has been decreasing.
- Debt ratio of Mutual Trust Bank has been decreasing year by year.
- Capital adequacy ratio was above the standard line which is crucial for any bank.
- Higher rate of interest plays a great role in credit management. Some times the rate is so high that the return from the investment is not so adequate enough to repay the loan. And hence default occurs.
- Mutual Trust Bank is providing loan to those who are experienced enough in their respective field. But this practice is discouraging small entrepreneurs and startups.
- Mutual Trust Bank has no written lending guideline which includes Industry and Business Segment Focus, Types of loan facilities, Single Borrower and group limit, Lending caps, Discouraged Business Types, Loan Facility Parameters.
Conclusion
Proper financial system of country can contribute towards the development of the country‟s economy. In our country banks are leading in the financial system. Again private commercial banks, which are much better than state owned bank, are playing significant as well as imperative role and the development of our country. Certainly MTB is mobilizing all of its resources on this same track to achieve maximum possible contribution to the nation.
Despite stiff competition among banks operating in Bangladesh both foreign and local, MTB has achieved satisfactory progress in areas of its operations and earned an impressive operating income over the previous years. The bank hopes to achieve a satisfactory level of progress in all areas of its operations including target of profitability.
In achieving the aforesaid objectives of the bank, credit operation is of paramount importance as the greatest share of total revenue of the bank is generated from it, maximum risk is centered in it and even the very existence of bank depends on prudent management of its credit portfolio. The writer would like to suggest, a bank requires some special personal traits that not every bank possesses. Among the most important of these are honesty, reliability, thoroughness and willingness to always be open to new ideas and new ways of meeting customer needs.
Today is not like yesterday and tomorrow will be different from today. Given the fast changing, dynamic global economy and the increasing pressure of globalization, liberalization, consolidation and disintermediation, it is essential that Mutual Trust bank limited has a robust credit risk management policies and procedures that are sensitive to these changes.
Recommendation
- Mutual Trust bank was focusing urban areas to provide credit facilities. Still they are ignoring rural areas. But they can earn from agro sector so Mutual Trust Bank should provide more credit facilities in rural areas.
- Proper and effective monitoring system should be developed in order to minimize the amount of non-performing loan.
- Capital adequacy is important for a financial institution. Mutual Trust bank capital adequacy ratio was in better position and they should maintain it.
- The bank should strictly follow „The Principle of Sound Lending‟. The bank should not sanction loan to the customer without all necessary documents.
- As we have seen that the bank was providing a large portion in unproductive sector, which is not a good sign for our economy. So the bank should pay more concentration on productive sectors like industrial loan instead of unproductive sector as car loan.
- As recovery rate from classified loan was in satisfactory level but still 18% of loan goes default. So Mutual Trust Bank should have to increase more of its recovery rate of classified loan.
- Mutual Trust Bank should strictly follow the Bangladesh Bank guideline for credit deposit ratio as its credit deposit ratio was quite higher than Bangladesh Bank guideline.
- The bank should increase more of its investment to deposit ratio as it decreased in year 2010. It should increase in order to generate more profit.Mutual Trust Bank should maintain a satisfactory level of interest rate for managing the credit to minimize the rate of default.
- Mutual Trust Bank should maintain a written guideline for credit management. If all documents are available than it will help to analyze their client.