Introduction
According to Michael C. Dennis (2001), most of the banks use objective and subjective data interpretation to evaluate a borrower’s financial condition from their financial statements. Objective analysis involves traditional methods of number and data analysis. Such as, review of unusual accounting methods used by the client, unusual information in the notes in the financial statement. Review of CIB (Credit Information Bureau) Report of client including financial ratios, trend analysis and financial profitability analysis of his business has been done before disbursement of a loan. Financial profitability, leverage liquidity and efficiency analysis of the client and its business considered as key denominator of a prospective client. Subjective analysis involves the overall evaluation of how a borrower is doing financially and whether extending the borrower’s credit would pose any acceptable or unacceptable risk. In particular both objective and subjective analysis is the key to interrelate and correlate the financial strengths and weaknesses of the client under review.The main product of bank is Loans and Advances. The price of a loan is determined by the cost to make the loan plus a profit or risk premium on it. Lending is the primary business of a bank and profit is a measure of its success. So the main objective of lending is/to earn profit on loans for the ongoing viability of a bank.
To extend credit facilities (or to continue the credit facilities) to an applicant, bank can make a decision only after an objective analysis and subjective evaluation. This analysis combined with information about applicant’s payment history, trends in the client’s industry, changes in the overall economy, and changes in demand for the client’s products and services are used to develop an intuitive understanding of the opportunities and challenges the client faces.
In many developed and developing countries, various analytical tools are used to assess credit risk. As a developing country, Bangladesh follows analytical tools recommended by BRDP (Banking Rules and Development Policy) of Bangladesh Bank. Bank mainly has to depend on judgment and their confidence whether borrower will pay or not Dhaka Bank Limited sanctions loan first by seeing the client’s reputation in the market. Secondly, past information helps to analyze the business pattern and industry trend. Thirdly, uses the CRG (Credit Risk Grading) scorecard to evaluate the credit risk. From the CIB report bank can identify whether the client is classified or not.
SCOPE OF THE STUDY
The report concerns about the Credit Division of Dhaka Bank Limited. Dhaka Bank Limited invested under the guidelines of the central bank framed for the banking system as a whole and for bank of individual sector to achieve the objective of the study, it covers different products and services of Credit Division, their credit operating system and procedures of loan supervision.
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
The profit of commercial banks depends on utilization of their funds and making of loans and advances profitable to the bank. As the bank mobilizes savings of general public in the form of deposit, the most important task of bank is to disburse the said deposits as loans or advances to the mass people for the development of commercial, industrial, who are in need of funds or investments. A bulk of problem loans has brought a gloomy situation in the cost of fund. Loan default culture has started in Bangladesh mainly after the nationalization of banks. However, it was enhanced by the availability of huge amount of credits in the name of developing private and industrial sectors. Industry set-up was shown as sick industry to get additional loan and relieve from interest.
Several studies have been conducted on the tools used to evaluate credit risk in commercial banks. However, in Bangladesh very few studies have been undertaken about the tools available to evaluate credit risk.
Lending is the primary business of a bank and profit is a measure of its success. Therefore, the main objective of lending is to earn profit on loans for the ongoing viability of a bank. Clients apply for loan for various purposes. The number of borrowing is increasing so is the default rate. So credit risk analysis is important for bank to reduce non-performing loans and to prosper in the banking sector.
Therefore, the researcher intends to explore the risk assessment methods in Dhaka Bank Limited. The overall performance of Dhaka Bank Limited is examined in terms of tools used to identify nonperforming loans, loans disbursement and recovery.
OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY
The main objective of the study is to develop an insight of credit risk management of Dhaka bank and tools available to identify efficient methods used to mitigate overall credit risks and to reduce loan default rate. The rational objectives are:
- To identify the main factors of the credit risk and computation of credit risk grading of Dhaka Bank Limited.
- To identify and to compare the trend of classified, unclassified and recovery of loans and advances of Dhaka Bank Limited.
- To identify the obstacles encountered when a loan is being default by Dhaka Bank Limited and the ways to overcome the problems.
- To examine the recent strategy and initiatives taken by Dhaka Bank Limited for further development or reducing loan classification.
- To identify the causes how and why a loan defaults.
- To explore the practical strengths and weaknesses of some credit risk analysis those are used by bank to manage risk
METHODOLOGY OF THE STUDY
The report is based on primary and secondary data. For data collection following methods are followed:
- On the job observation of the researcher.
- Information collected from face to face communication.
- Therefore, error depends on the response of the respondents only.
- Journals.
- Prior research reports.
- Bangladesh Bank Reports and several web sites are used.
- Website of Dhaka Bank Limited (www.dhakabankltd.com)
- The Annual Reports and different publications of Dhaka Bank Limited.
- Personal interviews with the employees. Self-developed questionnaire has been used for interview (Appendix A).
The conclusion drawn in this study is not definite and it depends on the responses collected. This study is mainly focused on the Dhaka Bank Limited to perceive what tools Dhaka Bank Limited uses to evaluate its borrower and the Bank’s Credit risk management policy.
SOURCES OF DATA
Primary and the secondary data were used to prepare the report. The details of these sources are as below:
Primary Sources
Primary data for this report has been collected through the conversation & discussion of different officers of the bank. On the job observation of the officers of credit division helped to get an insight of credit risk management activities of the bank.
Secondary Sources
The secondary sources of data are:
- Annual Report of Dhaka Bank Limited
- Internal Publications of Dhaka Bank Limited
- The website of Dhaka Bank Limited (www.dhakabankltd corn)
- The website of Bangladesh Bank (www.bangladesh-bank.org)
- Articles published on magazines and newspapers
- Annual Reports of different banks
- Bangladesh Bank Reports and several websites
- Prior Research Reports
- LIMITATIONS
Banking contains a huge volume of operation and it is quite impossible to gain knowledge about all the activities during a research period. The major limitations of the study faced in preparing this report on disclosure procedure of Dhaka Bank Limited are:
- Being public limited company, the private commercial banks like Dhaka Bank Limited keep some information restricted like the actual amount of classified loans.
- Financial Statements only portray the figures/numbers and their break down but do not clarify the justification in most of the time.
- In the literature review, researcher has mentioned several methods and tools that can be used for credit risk analysis. As in our country a very few methods are being practiced by bank to do analysis of the credit risk- Therefore, the advantages or disadvantages of those tools application were unable to review in full extent.
- For credit risk analysis bank mainly focus on personal judgment about the borrower so only the judgmental factors and Credit Risk Grading (CRG) Manuals is followed in risk analysis.
- Knowledge constraint of the researcher.
The Organization-Dhaka Bank Ltd.
SLOGAN: Dhaka Bank Limited was incorporated as a public limited company under the Companies Act 1994. The Bank started its commercial operation on July 05, 1995 with an Authorized Capital of Tk-1,000.00 million and paid up capital of Tk-100.00 million. The present paid up capital of the Bank is Tk.2128 million as on June 30, 2009. The Bank has 50 branches and 2 Offshore Banking Units across the country and a wide network of correspondents all over the world. The Bank has a plan to open more branches in the current fiscal year to expand the network. Dhaka Bank Limited offers the full range of banking and investment services for personal and corporate customers, backed by the latest technology and a team of highly motivated officers and staffs. In the effort to provide excellence in banking services, the Bank has launched online banking service, joined a countrywide-shared ATM network and has introduced a co-branded credit card. A process is also underway to provide e-business facility to the bank’s clientele through online and home banking solutions. Dhaka Bank Limited is the preferred choice in banking for friendly and personalized services, cutting edge technology, tailored solutions for business needs, global reach in trade and commerce and high yielding on investments.
“EXCELLENCE IN BANKING”
MISSION:
To be the premier financial institution in the country providing high quality products and services backed by latest technology and a team of highly motivated personnel to deliver Excellence in Banking.
VISION:
At Dhaka Bank we draw our inspiration from the distant stars. Our team is committed to assure a standard that makes every banking transaction a pleasurable experience. Our Endeavour is to offer you razor sharp sparkle through accuracy, reliability, timely delivery, cutting edge technology, and tailored solution for business needs, global reach in trade and commerce and high yield on your investments.
Our people, products and processes are aligned to meet the demand of our discerning customers. Our goal is to achieve a distinct foresight our prime objective is to deliver a true reflection of our vision- Excellence in Banking.
VALUES:
- Customer Focus
- Integrity
- Teamwork
- Respect to the Individual
- Quality
- Responsible Citizenship
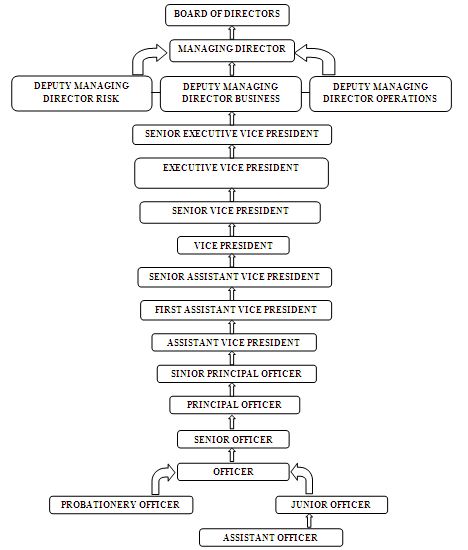
ORGANIZATIONAL HIERARCHY
FUNCTIONS OF THE DHAKA BANK LIMITED
Dhaka Bank Limited performs all types of functions of a modern commercial bank, which generally includes:
- Mobilization of savings of the people and safe keeping of all types of deposit account
- Making advances especially for productive activities and for the other commercial and socio-economic needs.
- Providing banking services to common people through the branches.
- Handling of export and import trade and foreign remittances and with special support to export activities.
- Introduce modem banking services in the country.
- Discounting and purchasing bills.
- Providing various information, guidance and suggestions for promotion of trade and industry keeping in view of the overall economic development of the country.
- Industrial finance for both capital machinery and working capital.
- Finance relating to constructions of both commercial and residential.
10. Finance under small business of self employed clients.
11. Finance of farming and non-farming activities to rural people including purchase of agricultural equipments.
12. Ensuing proper utilization of credit disbursed.
13. Developing new products.
14. Market surveys before making any finance.
15. Finance for small transport.
16. Monitoring and forecasting.
17. Developing marketing campaigns.
18. Finance for household durables.
19. Work simplification studies.
20. Monitoring diversification of portfolio among different sectors.
An Overview of Credit Risk Analysis
CREDIT RISK
Credit risk is the risk that a borrower will not make full and timely payment of debt service once a borrower falls behind in debt servicing; credit risk also involves the relative size and probable duration of default. It is one of the significant risks a bank is exposed to. Each of the risk areas requires be evaluating and aggregating to arrive at an overall risk grading measure.
i. Evaluation of financial risk: Financial analysis of leverage, liquidity, profitability and interest coverage ratios will help to analyze the risk that borrower might fail to meet obligation due to financial distress.
ii. Evaluation of Business/Industry Risk: Analyzing the business outlook, size of business, industry growth, market completion and barriers to entry or exit to understand the industry situation or unfavorable business condition that might have an impact on borrower’s capacity to meet obligation. This capitalizes on the risk of failure due to low market share and poor industry growth.
iii. Evaluation of Management Risk: Due to poor management skill, experience of the management, its succession plan and teamwork might cause the borrower to default.
iv. Evaluation of Security Risk: Risk that the bank might be exposed due to poor quality or strength of the security in case of default. This may involve the strength of security and collateral, location of collateral and support.
v. Evaluation of Relationship Risk: These risk areas cover evaluation of limits utilization, account performance, conditions/covenants compliance by the borrower and deposit relationship.
CREDIT RISK ANALYSIS
The term credit analysis is used to describe any process for assessing the credit quality of a company or individual. Credit analysis include credit scoring, it is more commonly used to refer to process that entail human judgment. Credit professionals in banks review the client’s balance sheet, income statement, recent trends in its industry, the current economic environment, etc. from this they can also assess the exact nature of an obligation. Based on this analysis, the credit manager assigns the client a credit rating, which can be used for making credit decision.
Many banks, investment managers and insurance companies hire their own credit analysts who prepare credit ratings for internal use. In Bangladesh there are two rating agencies one is CRAB (Credit Rating Agency of Bangladesh) and another is Credit Rating Information and Service Limit (CRISL). These two does the rating of all organizations.
HOW IS CREDIT RISK MEASURED
Credit risk is usually measured on a comparative scale. As per BRPD (Banking Regulation and Policy Department), CRG (credit Risk Grading) score sheet, a scale, is used to summarize risk assessments. Since there is no accurate way to combine the different risk factors, credit professionals either examine and weigh the underlying risks directly, or confirm the track record over time of a credit rating system to discriminate effectively between high and low-risk lending in a particular bank. Based on this analysis the credit manager assigns the client a credit rating, which can be used for making credit decision.
MODELS AND TOOLS AVAILABLE TO EVALUATE CREDIT RISK
The following models are used by various credit analysts around the world to evaluate credit risk:
- A. Lending Risk Analysis (LRA)
LRA is a traditional technique used by experienced people of credit department of banks to calculate the risk of loan. CRG is an upgraded tool of LRA. LRA is a ranking whose total score is 140. Among this score, 120 is for total Business Risk and 20 for Total Security Risk.
| Score | Business Risk |
| 13-19 | Poor risk |
| 20-19 | Acceptable Risk |
| 27-34 | Marginal Risk |
| Above 34 | Good Risk |
Table: Business Risk
| Score | Security Risk |
| 0-10 | Poor risk |
| 10-14 | Acceptable risk |
| 14-20 | Marginal risk |
| Above 20 | Good risk |
Table: Security Risk
Source: Bangladesh Institute of Bank Management, Mirpur, Dhaka
Loans and Advances
Loans and Advances of DBL
Loan and advances are the lifeblood of any financial institution. Like other financial institution DBL provides an array of traditional products. Its loan disbursement trend, loan classification system, setting the target group of customers, documentation of the loan products all of which are pretty traditional are going to be discussed as follows.
Types of LOANS & Advances AVAILED BY DBL
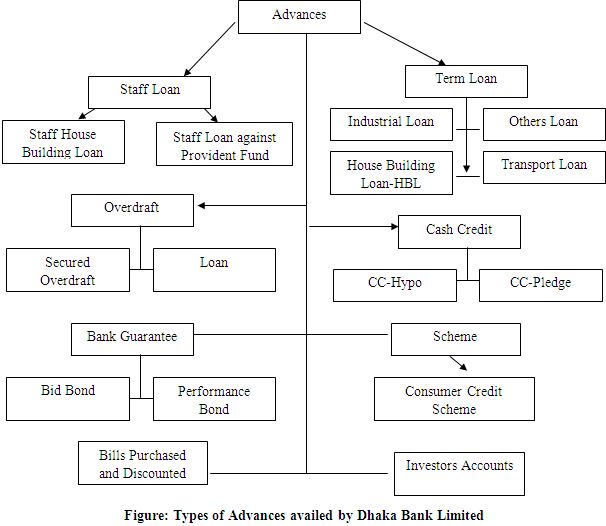
CATEGORIES OF LOANS
According to BRPD (Banking Regulation and Policy Department) of Bangladesh bank loans and advances are grouped into four categories for the purpose of classification (non-performing) which are as follows:
A) Continuous Loan: The loan accounts in which transactions may be made within certain limit and have an expiry date for full adjustment that will be treated as continuous loan. Examples are Cash Credit and Overdraft.
b) Demand Loan: This type of loans is repayable on demand by the bank and is treated as Demand Loans. If any contingent or any other liabilities are turned to forced loans (i.e. without any prior approval as regular loan) these too will be treated as Demand Loans. Such as: Forced LIM (Loan against Imported Merchandise), PAD (Payment Against Document), FDBP (Foreign Documentary Bill Purchase), and IBP (Inland Bill Purchase) etc. EBP is under FDBP and is used for export purposes e.g. client of Dhaka Bank will keep IBP as a guarantee, which is kept in another bank.
c) Fixed Term Loan: Loans, which are repayable within a specific time period under a specific repayment schedule that will be treated as Fixed Term Loans. These loans are given for either 3 or 5 years.
d) Short-term Agricultural & Micro Credit: The annual credit programs issued by the Agricultural Credit and Special Programs Department (ACSPD) of Bangladesh Bank include short-term Agricultural Credits to the agricultural sector where the loans are needed to be repayable within twelve months. Short-term micro credit include credits not exceeding twenty-five thousands and need to repay within twelve months a few examples of micro-credit are Non-agricultural credit, Self-reliant Credit, Weaver’s Credit or Bank’s individual project credit. When a loan is not paid within the valid time period it is called “Irregular loan”.
DOCUMENTATION OF THE LOAN
- These are the most frequently used and common documents for creation of above mentioned charged and for other formalities for sanctioning the loan practiced by Dhaka Bank Limited:
- Demand promissory note: Here the borrower promises to pay the loan as and when demanded by the bank to repay the loan.
- Letter of Arrangement: Here the written amount of the loan sanctioned to the borrower is specified.
- Letter of Continuity: It is used to take continuous facilities as providing continuous securities.
- Letter of Hypothecation: It is the written document of the goods hypothecated thus to put in case of need.
- Stock Report: This report is used for SOD and CC. in this report, information about the quality and quantity of goods hypothecated furnished.
- Memorandum of deposit of title deed of property duly signed by the owners of the property with resolution of board of directors of the company owning the landed property.
- Personal guarantee: It is the additional confirmation of the borrower to repay.
- Guarantee of all the directors of the company.
- Resolution of the board of directors: It is used to borrow the fund to execute documents and complete other documents.
- Letter of disclaimer: By this letter, the borrower withdraws his all claim on the property/goods lined/mortgaged.
- Form no. 18/19 for filling charges with the register of joint stock companies under relevant section.
Recommendation
Recommendations of these report has been made on the basis of the research findings of the credit facilities of Dhaka Bank Limited, Local Office. It is very difficult to recommend about this topic because of research restrictions and unavailability of data. Despite these problems there are something that the credit department of Dhaka Bank, local office should look at.
- To create better client the bank should increase the amount of consumer loans in a short-term basis.
- The bank can provide a loan, which may be student loan. Though in other countries many bank provide this facility. This may encourage the students to come forward do something for the economy.
- Most of Dhaka Bank’s loans are in the large sector. If the performance of that sector crash then the bank will fail to continue though the profit is very high. So, the bank should provide more loans of small scale in different sectors though it will decrease the profit a little. But it will be very safe.
- In some case rural area is profitable. So, the bank should provide loans in the rural areas.
- Again maximum numbers of the loan are provided in the long-term industrial loans. Bank’s clients are also limited. So, they can’t serve the economy of the country that much. So, they should diversify their loans more in agriculture, new industries etc for better economic growth of the country.
- On one hand the bank says that they want serve the economy of the country. On the other hand they are avoiding the agricultural sector and our economies still depend a lot upon the agriculture. So, they should keep similarity among their words and their works and provide loans in agricultural sectors.
- In the bank there is a credit risk analysis division. But their activities are rarely seen. This division has to work more and have to point out which sectors are profitable and which sectors are risky.
- ConclusionCredit policy is a very convenient banking tool for the business world. The value of this service is immense. It has gathered such a position in the banking sector that people at developed and also developing counties are very much depended on this service. In Bangladesh credit facilities or loans started to become very attractive in recent periods. But still lots improvements in services and facilities have to be made in this department.The study of the report refers to the fact that people are aware of loan facilities in our country but they are not fully aware of the services or features of the loan process and its rules and regulations especially in case of individual or consumer loans. From the study it seems that Dhaka Bank focuses on the corporate sectors for the credit facility. But in case of consumer loans there are lots of restrictions created by the bank.Credit Division of Dhaka Bank, Local Office has a very qualified and dedicated group of officers and staffs who are always trying to provide the best service to the clients. They always monitor the credit in different sectors and their position. Before providing the loan they analyze whether the loan will be profitable and whether the client is good enough to repay the loan within the given period of time.Credit department diversified their loans in different sectors classified by them. Among the sectors they don’t provide any loans in the agricultural side. The reason they showed is that this sector is very risky and depends on natural climate and they still didn’t expand their service in the rural side. They also didn’t provide any loan in the small & cottage industry. The reason is that the return from this sector is not very good and also the sector is very uncertain. They provide most of the credit facility in term loan mainly in long-term loans. Return from short-term loan is very good and also proves to be very safe to finance.