Current Stock Market of Bangladesh: Study on Lankabangla Limited
Lankabangla started its operation with technical support from the Sampath Bank Limited of Sri Lanka in 1996. At that time the company started its operation as LankaBangla Finance Limited (LBFL) which is now one of the leading listed non banking financial institutions in Bangladesh. With the passage of time and expansion of operation the company now has three subsidiaries along with LankaBangla Securities Ltd. The other two subsidiaries are: LankaBangla Investment Ltd. And LankaBangla Asset Management Ltd.
LankaBangla Securities Ltd. commenced its operation in 1997 as Vanik Bangladesh Ltd; confining its activities only within Chittagong Stock Exchange. In 1998 it started its operation at Dhaka Stock Exchange. In 2005 the company rebranded itself as LankaBangla Securities Ltd following restructuring of the company. With its scrupulous investment in time and labor to create a better investment pathway in the Bangladesh Capital Market; the company has already made itself a leading brokerage house in the country. In 2008 the company inaugurated Integrated Back Office Software System first ever in Bangladesh Capital Market. As the leading company of the industry LankaBangla was crowded as the largest brokerage house in terms of transaction value for the 6th consecutive time in DSE and 7th In 2009 the company was converted from private limited to public limited company, following the submission of IPO in 2010 for public listing as a first brokerage house. In 2010 the company subscribed for the Bloomberg professional service as first ever local company in Bangladesh.
The company introduced a full-fledged financial web portal and order management system for the first time in Bangladesh in 2012. Consecutive time in CSE in 2011.
With the vision of “ Growing together with our stakeholders by implementing the most comprehensive, efficient and state of the art brokerage platform to maintain the excellence and minimize the wealth of shareholders” the company is achieving all the milestones of success and becoming a hive for international investors with a comfortable investment environment.
Introduction
At some point of every business cycle companies need to raise capital for further growth of the companies’ business operation. To accomplish those, companies can either borrow money from other business entities or from bank or companies can raise the amount by selling ownership of the company. This sale of ownership is known as Issuance of Stock. Issuing stock is advantageous for the company to pay back the money or make interest payments along the way.
Corporate may raise capital in the primary market by way of an initial public offer, rights issue or private placement. Because of the aforesaid system the companies can be tapped into a wide pool of liquidity that provides capital to fuel future growth. An Initial Public Offering (IPO) is the selling of securities to the public in the primary market. The public limited companies can issue IPOs and go for enlistment. An enlisted company can avail more diversification; increases liquidity and can establish a value for the firm over the non listed companies.
Along with the advantages enlistment has some drawbacks as well. Firstly, a Public Limited Company (PLC) must file periodic reports with the SEC and with various state agencies and it may raise the cost of the company, especially for small firms. Secondly, if the stock of any company would not get an efficient market or the price of the share is low then despite of the incensement of the value of the company it may go down. Finally, companies control over its various matters is reduced at the same time.
However, despite of the disadvantaged IPO has overwhelming advantages that outweigh the issuance of share.IPO can be made through fixed price method, direct listing method and Book Building Method. For minimize the risk and attract more investor to the market IPO has three part as mention in the following diagram.
Objective
The objective of this report is to analyze the Book Building method in the capital market of Bangladesh. To accomplish this following specific objectives have been covered:
- To highlight the Bangladesh capital market status with having book building method
- To identify the problems regarding this method that impeded the developmetnof capital market in Bangladesh
- To suggest some important policy measures regarding IPO procedure for the development of Capital market.
Methodology
The report is mainly based on secondary data which will be collected from different published research articles, World Bank reports, and annual reports of Bangladesh Bank, portfolio, published journals, textbooks, websites and various published and unpublished materials. I also conduct some face to face interview as I worked in a brokerage house.
General Process of listing with Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE)
The unlisted companies are required to complete certain procedures to get listing at DSE. The way of listing, in short, may describe as follows:
- Every company intending to enlist its securities to DSE by issuing its securities through IPO is required to appoint issue manager to proceed with the listing process of the company in the Exchange;
- The Issue Manager prepares the dreaft prospectus of the company as per Public Issue Rules of Securities and Exchange Commission( SEC) and submit the same to the SEC and the Exchange for necessary approval;
- The Issuer is also required to make agreement with the Underwriter(s) and Bankers to the Issue for IPO purpose;
- After receiving the draft prospectus, the Exchange examine and evaluate overall performance as well as financial features of the companywhich may have short term and long term impact on the market;
- The Exchange send its opinion SEC within 15 days of receipt of draft prospectus for SEC’s consideration;
- After proper scrutiny, SEC gives its consent for floating IPO as per Public Issue Rule;
- Having consent from SEC, the Issuer is required to file application to the Exchange for listing its securities within 5 days of issuance of its prospectus;
- On successful subscription, the company is required to complete distribution of allotment/ refund warrants within 42 days of closing subscription;
- After 100% distribution of shares/refund warrants and compliance of other requirements, the application for listing of the Issuer is placed to the Exchange’s meeting for the necessary decision of the Board of DSE;
- The Board of DSE takes the decision regarding listing/non-listing of the company which must be completed within 75 days from the closure of the subscription.
A brief description of three processes is given below:
Fixed price method:
In the fixed price method, the company or issuer values the company and prices the share at a pre-determined price. Therefore, Price at which the securities are offered and would be allotted is made known in advance to the investors.
In case of fixed price method the price determined by the issuer can lead to an undervaluing of the issuing company as the price of the company’s shares at IPO is often lower than a fair market value. As a result the low price attracts investors and the share price often rises dramatically in the first few days of trading after the IPO, as investor positively revalue the company.
Direct listing method:
Direct listing allows a public company first to list its shares in stock exchange(s); and then offers its owners’ shares for sale to investor. Whereas, initial public offering facilitates a public company first to offer its shares for sale to investors; and then, list its shares in stock exchange. IN a word, Direct Listing involves Offer for Sale of existing shares by the owners; and IPO involves Offer of new shares by a company.
Amongst, the aforesaid methods, direct listing has three benefits. First, in the case of direct listing, the company’s shares get the best price as the shares are directly offered for sale to investors in stock exchange In case of Book Building IPO, the prices of shares are discovered by institutional investors fraught with the danger of not getting fair price; and chance of manipulation. In the case of normal IPO, prices of shares are limited by rules, leading to lower price.
Secondly, in the case of direct listing, the owners sell their shares to investors in stock exchange and the moneys from such sale are received by them. Thus, the owners can invest the moneys in the company itself; or in one or more new projects. This can speed up industrialization and growth.
Finally, because of the foregoing, direct listing can bring successful and profitable companies to the stock exchange. This may improve supply of good shares; and stabilize capital market which is so necessary presently.
Book Building Method
Book Building Method is the process by which an underwriter attempts to determine the offer price of an IPO based on demand from institutional investors. This method is basically a process to aid price and demand discovery. It is a mechanism where, during the period for which the book for the offer is opened, the bids are collected from investors at various prices, which are within the price band specified by the issuer. The process is directed towards both the institutional as well as the retail investors. The issue price is determined after the bid closure based on the demand generated in the process.
Under the book building method, in our country underwriters or book runners ask selective institutional investors (i.e. merchant banks, pension and provident funds, mutual funds, banks and non-banking financial institutions, stock dealers, insurance companies, registered venture capitalists, authorized foreign intuitional investors etc.) to reveal their demand for IPOs and offer prices that they are willing to pay. This process is also known as IPO road-show i.e. issuing firms and underwriters host seminars; workshops etc. and try to explain and market their IPOs. The road-show basically allows underwriters and issuing companies to determine the demand for IPOs and their prices.
Based on expressions of interests by numerous institutional investors (the SEC set at least five in Bangladesh), underwriters will set an indicative price; for IPOs and send it to the SEC and stock exchanges. All institutional investors are then allowed to participate in an automated but restrictive bidding (e.g. no more or less than 20% price variation from indicative price; no more than five bids; none can express to buy more than 10% of IPOs etc). The weighted average of all bid prices or the average of the highest and lowest bid prices determines the final market price for an IPO to institutional investors.
In case of over-subscription, individual investors are unlikely to receive shares of oversubscribed offers in many developed markets including the USA but are guaranteed in many emerging markets including Bangladesh to receive shares through a lottery.
Book Building System in Bangladesh
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) of Bangladesh had initiated to developed Book Building System in collaboration with Dhaka Stock Exchange(DSE), Chittagong Stock Exchange(CSE) and Central Depository of Bangladesh Limited(CDBL) for the efficient, fair and transparent price discovery and allocation of securities using Book Building System at the time of initial public Offerings. In this context, SEC made required modifications in the rules and regulations and notified the stakeholders’ through its circular. The Stock market regulatory body of Bangladesh introduced Book Building Method on 5th March 2009 to ensure fair price in IPOs for the entrepreneurs whose companies would go public. However, because of many reasons the system is now postponed.
The distribution of security to be issued under book-building method will be made in accordance with the following ratio:
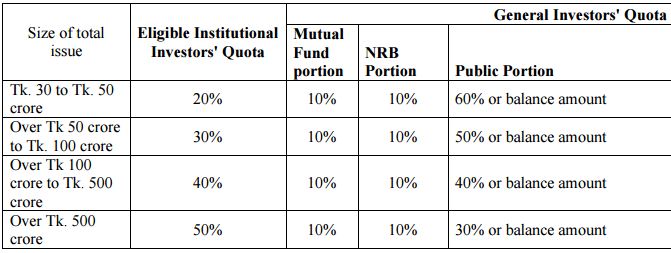
The details of the Book Building System in our country are given below:
Prerequisites of an issuer for becoming eligible for book building method:
An issuer may determine issue price of its security being offered following book-building method (i.e. price discovery process) subject to compliance with the following namely:- The issuer
- Must have at least Tk. 30 crore net-worth;
- Shall offer at least 10% shares of paid up capital (including intended offer) or Tk. 30 crore at face value ,whichever is higher;
III. Shall be in commercial operation for at least immediate last three years;
- Shall have profit in two years out of the immediate last three completed financial year;
- Shall have no accumulated loss to the time of application;
- Shall be regular in holding annual general meeting;
VII. Shall audit at least its latest financial statements by a firm of chartered accountants from the panel of auditors of the Commission;
VIII. Shall appoint separate person as issue manager and registrar to the issue for managing the offer; and
- Shall comply with all requirements of these Rules in preparing prospectus.
Price discovery for determining indicative price:
The price discovery process for determining indicative price of security will involve the following institutional investors registered with or approved by the Commission in this regard:-
- Merchant bankers excepting the issue manager concerned to the proposed issue;
- Foreign institutional investors registered with or approved by the Commission;
- Recognized pension funds and provident funds;
- Bank and non-bank financial institutions under regulatory control of Bangladesh Bank;
- Insurance companies regulated under Insurance Act, 1938 ( Act No.IV of 1938);
- Institutional venture capital and institutional investors registered with or approved by the Commission;
- Stock Dealer registered with the Commission; and
- Any other artificial juridical person permitted by the Commission for this purpose.
Procedures to be followed for determining price under Book-Building Method:
- Issuer shall invite for indicative price offer from the eligible institutional investors through proper disclosure, presentation, document,seminar,road show etc;
- Issuer in association with issue manager and eligible institutional investors shall quote an indicative price in the prospectus and submit the same to the Commission with copy to the stock exchange;
- Such indicative price range shall be determined as per price indications obtained from at least five eligible institutional investors covering at least three different categories of such investors;
- Rationale for the indicative price must be included in the prospectus i.e. the issuer is required to disclose an detail about the qualitative and quantitative factors justifying the indicative price;
- The indicative price shall be the basis for formal price building with an upward and downward band of 20% of indicative price within which eligible institutional investors shall bid for the allocated amount of security;
- Eligible institutional bidding shall commence after getting consent from the commission for this purpose;
- If institutional quota is not cleared at 20% below indicative price, the issue will be considered cancelled unless the floor price is further lowered within the face value of security;
- Provided that, the issuer’s chance to lower the price shall not be more than once;
- Prospectus will have to be posted on the websites of the Commission, stock exchanges, issue manager and issuer at least two weeks prior to the start of the bidding to facilitate investors to know about the company and all aspect of offering;
- No institutional investor shall be allowed to quote for more than 10% of the total security offered for sale, subject to maximum of 5 bids;
- Institutional bidding period will be 3 to 5 working days which may be changed with the approval of the Commission;
- The bidding will be handled through a uniform and integrated automated system of the stock exchanges, or any other organization as decided by the Commission,especially developed for book building method;
- The volume and value of bid at different prices will be displayed on the monitor of the said system without identifying the bidder;
- The institutional bidders will be allotted security on pro-rata basis at the weighted average price of the bids that would clear the total number of securities being issued to them;
- Institutional bidders shall deposit their bid with 20% of the amount of bid in advance to the designated bank account and the rest amount to settle the dues against security to be issued to them shall be deposited within 5 working days prior to the date of opening subscription for general investors;
- In case of failure to deposit remaining amount that is required to be paid by institutional bidders for full settlement of the security to be issued in their favor, the Commission shall forfeit 50% of bid money deposited by them. The securities are marked for the bidder who defaulted in making payment shall be added to the general investor quota;
- General investors, which include mutual funds and NRBs, shall buy at the cut off price
- There shall be a time gap of 25 working days or as may be determined by the Commission between closure of bidding by eligible institutional investors and subscription opening for general investors;
- Subscription for general investors shall remain open for the period as specified by the Commission;
- General investors shall place their application through banker to the issue; and
- All application money shall be kept in a separate escrow account opened with a designated bank with prior intimation to the Commission. Issuer will not be allowed to utilize such money until all the process of issue is completed and Commission’s consent to this effect is obtained.
Advantages of Book Building Method
Book building method is widely used in many developed countries because it has some advantages over the fixed price method.
Firstly, the method is more efficient as it solves the “leakage” of value often seen with fixed priced IPOs. Here the issuer sets price range within which the investor is allowed to bid for shares. The range is based on where comparable companies are trading and an estimate of the value of the company that the market will bear. The investors then bid to purchase an agreed number of shares for a price which they feel reflects fair value. By compiling a book of investors, the issuer can ascertain what price range the shares should be valued at, based on the demand of the people who are going to buy them, that is the investors. In a word, in this process supply and demand are matched.
Secondly, in the fixed price method the offer price is determined by the issuing company whereas book building system enables to discover the fair market price of the security by the eligible institutional investors if it is not being manipulated.
Thirdly, globally book building method is favored for its mutually beneficial nature: investors get the shares at a fair price that typically has potential upside, and the issuing company receives fair compensation.
Finally, though the fixed price method gives the investors return within short time but book building system provides the investors with a long term return. Therefore, in the long run efficient pricing can be seen as a sign of growing maturity of the capital market and upsurge the investors return for the long term. However, this may upset some investors in the short term, who are used to making a lot of money from these fixed price IPOs.
Reasons behind the commencement in Bangladesh
Prior to the introduction of book building system, IPO price was determined only under foxed price method. Under this method, when issue price of the ordinary share is higher than the face value premium is required to be justified with reference to certain parameter. These reference points were net asset value per share, earning based value per share, projected earnings per share for the next three years, average market price per share of similar stock and other factors taken into account by the issuer. Clearly, this system is not rigid and there is sufficient scope for the determination market based IPO price. However, a company intending to issue IPO is required to obtain prior approval of the SEC. The commission approves a proposal when it is satisfied on all points including the proposed price of IPO. Therefore, ultimately IPO price depends on discretionary authority of the Commission. This may not be an acceptable position to an issuer.
Besides in view of rather blurred criteria, judgment of the commission could be questionable. To be on the safe side, the Commission may also prefer to take a conservative position. In view of these constraints, a market based method was being considered by the Commission for some time and book building method was the outcome of such deliberation.
Improper use of Book Building Method
At the time of its commencement it was anticipated that Book Building Method will ensure fair price of a stock, enhance the depth of our local market and strengthen the corporate governance.
Moreover, it was expected that the method would make disclosure and reporting to public more transparent and credible and more importantly, help accelerate to help industrialization.
Paradoxically, the method has been found to be used as a mechanism to raise money from capital market by inflating the stock price.
In practice, the price of the proposed issue has been determined using methods like price earnings multiple, market value multiples, price to book value multiple of the similar companies, expected earnings per share (EPS) and so forth. In the price earning multiple, the issuer company takes P/E ratios ( either P/E at certain time point, or average P/E of last six months, or average P/E of long period corresponding the EPS) of the similar listed stocks( selected by company’s issue manager itself) in the related sector etc. and then multiply it with the issuer company’s latest audited EPS, weighted average EPS to determine the price
If we recall the fair value of a security, it indicates that the value of a stock is the present value of future cash flows to be generated in the foreseeable period considering a risk adjusted discount rate (which includes risk premium commonly derived from CAMP). However, such method of determining price is not highly noticeable in our country. During the method when book building method was so much popular, a company used market value multiple where it showed that market value of similar stocks is 53.4 times of face value. So according to this method, the market value of the said company should be 53.4 times of its face value, leaving aside any fundamentals of its perspective.
Moreover, most of the methods used in determining the price are P/Es of market, or respective industry or similar stocks. As our market was overheated during period( 2009 to 2012) under consideration having a market P/E over 25 times, would have not ever generate a fair price. The issuing companies generally have a tendency to pick the highest P/E, so that the indicate price would be higher. Moreover, when Issuer Company arranges road show with this inflated price to invite offer for indicative price from the institutional investors, it has been observed that institutional investors usually agree to give very high price or even higher one then proposed by the company. Strong allegations are there that there is a prior understanding among the issuer company and the institutional investors participating in the road shows. The situation is further worsened when formal bidding is arranged with such inflated indicative price where it is observed that all the bidders offer at upper band( 20% more of indicative price) although lower band( 20% less of indicative price) is allowed. Perhaps only 15 days lock-in-period provides incentives to bid for such higher prices.
Manipulators benefiting from Book Building Method
The introduction of book building system has turned out to be a tool for manipulating market prices, observed by the experts. Instead of ensuring competition among big investors at the ‘price discovery’ stage, the market syndicates are abusing it for placement of shares at an artificially high price. This artificial price was being maintained for 15 days i.e. Particularly till the lifting of the lock-in-period and after that investors are found to offload their shares at higher prices.
Moreover, it was also observed that those who hold the private placements took out a substantial amount of money by selling shares at high prices during the first one month. As result, share prices of a particular company fell by33 percent within one month and 50 percent in the next two months and did not rise thereafter.
Performance of the companies under book building method
The companies that issued share under book building method; their short profile are given below:
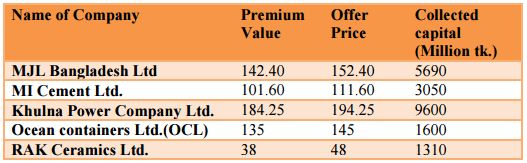
From the above table we can see that first four companies charged very premium for its share and withdrawn huge amount of capital from market at the same time. When these companies asked for very high price, shares of other companies of same industry tends to rise on an expectation that it is highly undervalued that increases the general price index.
I would like to describe some fundamentals of Khulna Power Company Ltd.(KPCL) and Ocean Containers Ltd.(OCL):
Khulna Power Company Ltd:
Khulna Power Company Ltd. is a power generation company under private ownership that sells supply electricity to consumers through national distribution system. Its security was first traded in 18 April, 2010 and price of the securities is being discovered by eligible institutional investors through Book Building system. The company was registered in 15 October, 1997. Its NAV was 17.09 and 18.53 respectively for the year 2008 and 2009 while EPS was 0.97 and 2.79 respectively for the year 2008 and 2009.
Listing related information regarding the company is given below:
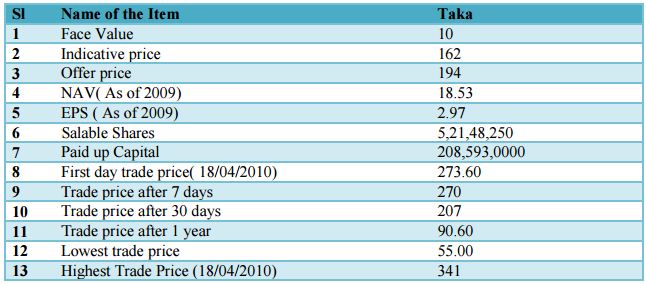
The above table shows that Net Asset Value of KPCL was Tk. 18.53 and indicative price was Tk. 162 that is Ten times higher than the asset value of the company. Since indicative price is determined by the eligible institutional investors’ so they always tries to overvalue it, hence the scenario of KPCL.
Ocean Containers Ltd:
It is the pioneer for Inland Container Depot (ICD) and Container Freight Stations(CFS) and is the largest privately owned land container port in Bangladesh. It is located at Patenga Industrial Area of Chittagong on the International Airport Road, which is only 6 km from the country’s largest seaport,Chittagong Port. It was listed with DSE in 2010 through book building method. Listing related information regarding the company is given below:
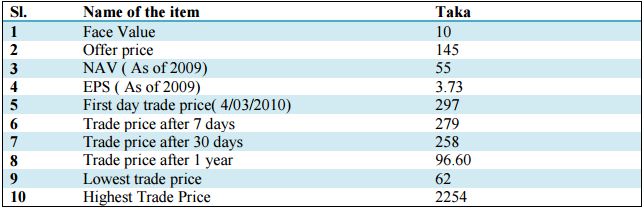
From these figured, we find that the maximum price of the stock was Tk. 2254 and minimum price was Tk. 62 only against face value of Tk. 10. The lowest price of the securities was half of the offer price of the securities that indicates that many shareholders caused huge losses out of this security.
Stakeholders demand further change to Book Building Rules
Market stakeholders have urged the Securities and Exchange Commission to erase a proposed clause on valuation from the draft on an amended book building method. The clause is related to determining the indicative price of shares of a company, which will use the book building system for an initial public offer, based on the firm’s EPS and NAV. They have urged that if the clause is included in book building rules, an amendment to other sections or inclusion of new clauses will be meaningless. The proposed clause reads: indicative price will be such that it does not exceed the following yardstick; 15 times of weighted average EPS of the preceding three years or three times of net asset value, whichever is lower but no less than NAV of a share.
After the stock market debacle, the government in January 2011 directed the SEC to suspend the book building method. Following recommendations by a high- profile probe committee on the share market scam, the government instructed the SEC to alter the book building rules, instead of stopping the system, as it is well practiced in other countries. The stakeholder also recommended increasing the number of category of institutional investors who builds up the indicative price.
As per the draft amendment, the indicative prices should be supported by at least 20 EIIs including at least five quotations from each of the following category; merchant banks, commercial banks and asset management companies.
The stakeholders also opposed the proposal of having a committee composed of experts that will scrutinize and verify the audited financial statements submitted in connection with an IPO.They argued that it would increase the complexity in the IPO process. Some of them also recommended reducing the lock-in period for eligible institutional investors from six months to three months, while some others requested to keep the existing lock-in period of 15 days.
Stock market performance
Stock market gains on August 2011
Dhaka stock returned to the black yesterday amid expectations of a turnaround in the market on the middle of August 2011. The benchmark gauge of the Dhaka Stock Exchange,DSE general index, gained 0.8 percent to 6,212 points. Gainers beat losers 184 to 66, with eight securities remaining unchanged on the premier bourse. Among the major sectors, the telecom sector advanced 0.6 percent, banks 1.05 percent, non-banking financial institutions 1.29 percent and pharmaceuticals 1.11 percent. Total turnover on the prime bourse also increased almost 20 percent to tk 536 crore on a transaction of 7.5 crore shares and mutual fund units.
Chittagong stocks also gained on 11th August 2011, with Selective Categories Index increasing 0.47 percent to 11,377 points. Advancers beat losers 132 to 39, with 11 securities remaining unchanged on the CSE that traded over 87 lakh shares and mutual fund units worth to 60.15 crore changing hands on the trading floor.
Stock market gains on 29th
Country’s stock market marked a nominal gain in terms of indices and turnover on Thursday 29the December 2011. The DSE general index rose over 36 points minus to stand at 5257 at the close on the last trading day of the week. The volume of transactions, however, rose to Tk 559 crore from Wednesday’s Tk 526 crore. Trade deals stood at 147,184 against the previous day’s 134548. Of the issue trades, 197 advanced, 52 declined and 19 remained unchanged.
MICEMENT topped the turnover list with shares worth Tk 135 million having changed hands. The other turnover leaders were BDTHAI, BSRMSTEEL, GP, KEYACOSMET, MERCANBANK, UNITEDAIR, BEXIMCO, RNSPIN and SALAMCRST.
December 2011
CSE also allowed suit, with the CSE Selective categories index climbing up to 9,572 by gaining over 80 points. Out of the issue traded, 127 gained, 41 declined while 25 remained unchanged. Ina latest bid to stabilize the Stock market, the SEC on December 7 erased the rule for sponsor- director of listed companies to hold 30 percent shares of their respective companies within six months.
Besides, the government on November 23 had formed a committee under a special scheme of incentives to hand out compensation to small investors after assessing within two months the losses they suffered for scam and recurrent market crash.
Stock market gains and losses in 2012
The general index had a bumpy ride with a generally declining trend through 2011, with a recovery apparent since February 2012. The most recent period decline was in mid-January 2012 in anticipation of further tightening by central bank. The market reached its lowest on February 6, 2012 when the benchmark index closed at 3,616 representing a 60 percent decline from the December 2010 peak of 8,919. Since then the market had been on a generally upward trend, crossing the 5000 mark in the last week of March. Trade volumes had also picked up. The uptrend can be attributed to i) market entry by some overseas private equity funds, as the fund manager consider good stocks to have reached their bottomed out, ii) re-entry by some of the local institutional buyers, as they find the stocks’ current price attractive for long-term holding, and iii) reaffirmation of a stable outlook for Bangladesh by Moody’s and S&P in January and February 2012.
Recommendations
Book building method is considered more transparent and market determined than the fixed price IPOs since the price is not pre-determined and the demand is also from the investors’ side.
Therefore, it is one of the most popular methods for issuing IPO around the world but in the context of Bangladesh the scenario is totally different. Therefore, the method has been postponed and that is being demanded for cancellation, in the face of strong criticism though a good numbers of large and profitable companies were in pipeline to go public under this method
Hence, we recommend some of the changes in the system:
- Since the salient reason behind its closure was the high indicative price so the issuing companies should determine the indicative price looking primarily on its inherent ability to generate future cash flows;
- The number of Eligible Institutional Investors including some foreign investors should be increased for more transparent bidding;
- Instead of 20% of the indicative price it can be 10% more or less of indicative price during the bidding so that even if everyone bid at the upper band the indicative price cannot upsurge;
- For determining the indicative price a combination of net asset value, past earnings per share and future earnings per share can be used rather only using one parameter. For example, 25 percent of net asset value, 25 percent of past earnings per share and 30 percent of future earnings per share can be used rather than using a higher P/E by manipulation;
- The lock-in period can be increased to discourage higher bidding by the institutional investors and devising specific and consistent pricing mechanism to be used by all companies intending to go public;
- Room should be allowed for the IPO issued to be somewhat under-priced to attract the general investors for a win-win situation from both issuers and investors’ perspective;
- More importantly, the overall system should not be manipulated by any party involving in the process of book building for their own benefit.
Conclusion
It was expected that by ensuring market based price of the public offer the new policy will encourage bigger and performing companies to come to the capital market. But the expectation went in vain because of the improper use of the book building system. Though it is widely used both in developed and developing countries even in our neighboring county India, but in the context of Bangladesh a large difference is observed. As listing methods play a vicious role to boost up a capital market and at the same time damage the stability of the market like ours one so it should be proper and proper IPO price is likely to open up an alternative source of cheaper funding. Though Book Building System was introduced to boost up our capital market but it had an adverse effect. The reason behind was not the book building method itself but its improper use and to some extent misuse. Therefore, to put it in the right perspective, capital market must be allowed to operate on its mechanism where like any other market; the price of a particular security should be determined by matching the demand for and supply of the same.
















