ACKNOWLEDGEMENT:
The internship program is very helpful to bridge the gap between the theoretical knowledge and real life experience as part of Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) program. This internship report has been designed to have a practical experience through the theoretical understanding.
It is my privilege that I had the opportunity to do internship in Trust Bank Limited, Dhanmondi Branch. I would like to thank all the people on whom I carry out my internship.
I express my deep gratefulness to Mr. Iqbal U. Ahmed, Managing Director; Mr. Ishtiaque Ahmed Chowdhury, Deputy Managing Director & Mr. Shahud Ahmed, SVP & Head of HRD for selecting me to do internship at Trust Bank Limited, Dhanmondi Branch, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
I am grateful especially to Mr. Md. Mozakkerul Islam, AVP and Manager; Mr. Mohammad Mostafa, AVP and Sub- Manager; and all the staffs of this branch for giving me the pleasure of doing internship.
My heartfelt appreciation and thanks should reach to Mr. Md. Mosharraf Hossain, senior officer, Mr.Khandaker Abdul Hafiz, Nure Alam khondaker officer who co-operated to collect various requirement supports from various sources & helped me to complete this internship report.
I am also thankful to all other officers & all the personnel working at TBL, Dhanmondi Branch for their cordial co-operation and support.
Especially, I would like to extend my great gratitude to my department supervisor Mr. Mohammad Maksudul Karim for his guidance and useful comments on the preparation of the report.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY:
Today necessity of a Bank as a financial institution is undeniable. A country is financially rich when it has modern financial institutions of its own. These institutions play a vital role in the field of financial stability of a country. Banking sector is one of the stable financial institutions of a country. Due to Globalization and Technological changes, the banking business has become very competitive now a day. All banks are competing to give effective real time service to their customers. For giving friendly service to the customers they need experienced and well-educated working force.
The overall approach of the report is a Descriptive one as it goes into the depth of service quality of Trust Bank Ltd. Here both primary and secondary information were used. Interview was the basic techniques comply to collect primary data from any people within the organization. Information about the varieties of activities within the Correspondent Banking Department was collected through interviewed. Among the secondary sources to collect data regarding the company’s performance over the past six years are Publications, Annual reports of Trust Bank Ltd., Different circulars and papers of Trust Bank Ltd, Term papers of TBL Training manuals, Guidelines for Foreign Exchange Transactions, General Banking Operation manual, Banking Lecture sheet within the organization helped me to gather data about the organization.
The report contains six chapters. The first chapter of the report describes the introductory words of the internship report in which Introduction of Topic, Rationale of the Study, Objective of the Report, Scope of the Report, Methodology, Activity Schedule & Limitations. The second chapter contains the Background of “Trust Bank Ltd.”, Organization Structure of “Trust Bank Ltd.”, Vision of “Trust Bank Ltd.”, and Mission Statement of “Trust Bank Ltd.” In third chapter, it contains the Topic Analysis and Description.
Based on the study, findings in different departments of the bank have come in the chapter four. In general banking department, the banking procedure is not fully computerized, cash counter is congested, service of remittance section is not as prompt as the customers demand and introducer is one of the problems to open a new account etc. The loans and advance department takes a long time to process a loan.
Different Problems, suggestions, recommendations have come at the end of the report. The Problems findings during the three-month long internship period & suggestions are given from observation, comparative analysis, strategic point of view etc. To increase the efficacy in customer service Trust Bank Ltd. should try to develop the process of providing services.
Trust Bank Ltd. has passed a long way since it is providing services. Already it has earned a strong positioned in the field of customer service. To continue to hold the position and be perfect in this sector it will have to keep more and more attention to the customer retention and development.
TABLE OF CONTENTS:
| ACKNOWLEDGEMENT EXECUTIVE SUMMARY | ||
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION
| ||
1.0 Introduction 1.1 Introduction of Topic 1.2 Rationale of the Study 1.3 Objective of the Report 1.3.1 Specific Objective 1.3.2 Broad Objective 1.4 Scope of the Report 1.5 Methodology 1.6 Conceptual Framework of the Report 1.7 Model Used Trend Analysis Ratio Analysis 1.8 Limitation CHAPTER TWO COMPANY Overview 2.0 Company Overview 2.1 Background of “Trust Bank Ltd.” 2.2 Nature of Business 2.3 Board of Director 2.4 Organization Structure of Trust Bank Limited2.5 Vision of Trust Bank 2.6 Mission Statement of Trust Bank 2.7 Branches
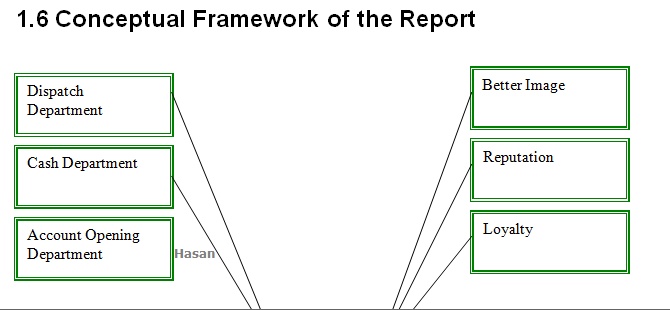
3.0 Topic Analysis and Description 3.1 Dispatch Department 3.1.1 Inward Register 3.1.2 Outward Register 3.2 Cash Department 3.3 Deposits Department 3.4 Remittance & Bills Department 3.5 Product & Schemes 3.5.1 Deposit Products 3.5.2 Investment Products 3.5.3 International Trade 3.5.4 Others 3.6 Account Opening Department 3.6.1 Savings Account 3.6.2 Current Account 3.6.3 Short Term Deposit (STD) Account 3.6.4 Fixed Deposit Account 3.7 New Deposit Products 3.7.1 Trust Smart Savers Scheme (TSSS) 3.7.2 Trust Digoon Laav Scheme (TDLS) 3.7.3 Trust Money Making Scheme (TMMS) 3.7.4 Trust Education Scheme (TES) 3.8 Other Services 3.8.1 Locker Service 3.8.2 ATM Card 3.9 Loans & Advances Department 3.10 International Banking 3.11 Foreign Exchange Department 3.11.1 Import Operation 3.11.2 Export Operations
3.12 Credit Department 3.13 Foreign Remittance Department 3.14 Performance of the Bank: As a Whole 3.13.1 Trend Analysis 3.13.2 Ratio Analysis 3.15 Performance of the Bank: Dhanmondi Branch 3.14.1 Profitability Analysis 3.14.2 Inter Branch Profitability Analysis | ||
CHAPTER FOUR OVERALL FINDINGS
| ||
4.0 Overall Findings | ||
CHAPTER FIVE PROBLEMS AND RECOMENDATIONS
| ||
5.0 Problems and Recommendations 5.1 Problems 5.2 Recommendations
| ||
CHAPTER SIX CONCLUTION
| ||
6.0 Conclusion
| ||
| APPENDIX BIBLIOGRAPHY
| ||
CHAPER ONE:
Introduction:
Introduction of Topic:
This internship is a part of the Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) program that provides an on-the-job experience to students. I was placed at Trust Bank Limited, Dhanmondi Branch as an internee officer for three months. This internship program was my very first on-the-job exposure and provided me with learning experience and knowledge in several areas. During the first few weeks of my internship period, I was able to get accustomed to the working environment of Trust Bank Limited. As the internship continued, I not only learned about the activities and operations of correspondent Bank, but I also gathered some knowledge about the basic business activities of banking in first one-month of my internship period.
Generally by the word “Bank” we can easily understand that the financial institution deals with money. But there are different types of banks such as; Central Banks, Commercial Banks, Savings Banks, Investment Banks, Industrial Banks, Co-operative Banks etc. But when we use the term “Bank” without any prefix, or qualification, it refers to the ‘Commercial banks’. Commercial banks are the primary contributors to the economy of a country. So we can say Commercial banks are a profit-making institution that holds the deposits of individuals & business in checking & savings accounts and then uses these funds to make loans. Both general public and the government are dependent on the services of banks as the financial intermediary. As, banks are profit-earning concern; they collect deposit at the lowest possible cost and provide loans and advances at higher cost. The differences between two are the profit for the bank.
A company can increase efficiency through a number of steps. These include exploiting economies of scale and learning effects, adopting flexible manufacturing technologies, reducing customer defection rates, getting R&D function to design products that are easy to manufacture, upgrading the skills of employees through training, introducing self-managing teams, linking pay to performance building a companywide commitment to efficiency through strong leadership, and designing structures that facilitate cooperation among different functions in pursuit of efficiency goals.
Efficacy of customer service is related with progression of operation. We can identify the efficacy of customer service by studying the progress of “Trust Bank Ltd.” from starting to at present. The progress of “Trust Bank Ltd.” is very rapid with the concern of its profit making and growth of its operation within the country towards the country’s economy.
Trust Bank Limited pursues decentralized management policies and gives adequate work freedom to the employees. This results in less pressure for the workers and acts as a motivational tool for them, which gives them, increased encouragement and inspiration to move up the ladder of success. Overall, I have experienced a very friendly and supporting environment at Trust Bank Limited, which gave me the pleasure and satisfaction to be a part of them for a while. While working in different departments of this branch I have found each and every employee too friendly to us to cooperate. They have discussed in details about their respective tasks. I have also participated with their works.
Rationale of the Study:
The internship program is very helpful to bridge the gap between the theoretical knowledge and real life experience as part of Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) program. This internship report has been designed to have a practical experience through the theoretical understanding.
Internship program is essential for every student, especially for the students of Business Administration, which helps them to know the real life situation. For this reason a student takes the internship program at the last stage of the degree, to launch a career with some practical experience. As a Complete fulfillment of Internship Program introduce the students with the real life business situation.
This report is a part of my academic program. The internship program has been set for three (3) months period at “Trust Bank Ltd” as a part of my BBA program. In our BBA Program all courses based on theoretical and we have to learn practically. The program has helped me a lot to understand the organizational atmosphere and behavior and I gather some practical Knowledge about “General Banking Operation of Trust Bank Ltd.”
Objective of the Report:
Broad Objective:
The objective of the internship program is to familiarize students with the real market situation, to compare them with the business theories & at the last stage make a report on assigned task. The main objective of this report is to have an assessment about overall activities of “Trust Bank Ltd.”. How the Bank is providing facilities to its clients & to suggest remedial measure for the development of overall banking activities of “Trust Bank Ltd.”. In addition, the study seeks to achieve the following objectives:
Specific Objective:
- To present an overview of “Trust Bank Ltd. ”
- To get an overall idea of banking from banker’s point of view.
- To apply theoretical knowledge in the practical field.
- To make a bridge between the theories and practical procedures of day to day Banking operation.
- To assess the decision undertaken by the top-level management to keep the rein with the competitiveness of the market.
- To understand the recent complexity of banking in the wake of rising terrorism and fundamentalism.
- To relate the theories of banking with the practical banking activities.
- To review the techniques used by the bank to make it lucrative
- Determining the drawbacks of the existing system.
- To study existing banker-customer relationship, particularly the efficacy of customer services of the bank.
- Recommending some guidelines to improve the effectiveness
Scope of the Report:
This internship report covers all the trade related products handled by the “Trust Bank Ltd.” such as Foreign Exchange, Cash Dept., Dispatch, Account Opening, Remittance, Accounts, Administration and Loans & Advances etc.
This report has been prepared through extensive discussion with bank employees and with the customers. While preparing this report, I had a great opportunity to have an in depth knowledge of all the banking activities practiced by the “Trust Bank Ltd.” It also helped me to acquire a first hand perspective of a leading private Bank in Bangladesh.
Interview was the basic technique complied to collect primary data from any people within the organization. Information about the varieties of activities within the Correspondent Banking Department was collected through interviews. Data regarding the types of product offered to the clients and the descriptions for each of those products were gathered through interviews. Besides, on-the-job experience has also helped me learn quite a few things about the Correspondent Banking Department and the organization as well.
On the other hand, secondary sources were used to collect data regarding the company’s performance over the past five years, Publications, Database, Annual report of Trust Bank Ltd (2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005 and 2006), Different papers of Trust Bank Ltd, Different textbooks, Term papers of TBL Training manuals,
Transaction in foreign Exchange, Principles & Practice (By M.R. Sinha), Guidelines for Foreign Exchange Transactions, General Banking Operation manual and Lecture sheet within the organization helped me to gather data about the organization. Data have also been collected by going through different circulars issued by the head office and Bangladesh bank during the tenor of the internship.
MODEL USED :
The performance evaluation of the TBBL has been conducted based on the trend analysis and ratio analysis.
Trend Analysis: In the report trend analysis has been used in order to indicate the changes in the level of progress and growth over the last three years starting from 2003. It would show whether the present growth trend of the TBBL is excellent, good, satisfactory or bad.
Ratio Analysis: In the report, significant analysis has been made through the following ratios –
- Capital Adequacy Ratio
- Capital Fund to Deposit Liabilities Ratio
- Liquid Asset to Deposit Liabilities Ratio
- Loan to Deposit Liabilities Ratio
- Earning Asset to Deposit Liabilities Ratio
- After Tax Return on Average Asset Ratio
- Net profit to Gross Income
- After Tax Return on Equity
Limitations:
The present study was not out of limitations. But it was a great opportunity for me to know the banking activities of Bangladesh specially “Trust Bank Ltd.” Some constraints are appended bellow–
- The main constraint of the study is inadequate access to information, which has hampered the scope of analysis required for the study. As it is a new bank it could not start all its operation, it was unable to provide some formatted documents data for the study.
- Due to time limitations, many of the aspects could not be discussed in the present report.
- Every organization has their own secrecy that is not revealed to others. While collecting data i.e. interviewing the employees, they did not disclose much information for the sake of the confidentiality of the organization.
- Another problem is that creates a lot of confusions regarding verification of data. In some cases more than one person were interviewed to clarify each concept as many of the bankers failed to provide clear-cut idea about the job they perform.
- The clients were too busy to provide me much time for interview.
- I have had no opportunity to compare the general banking system of the TBBL with that of other contemporary and common size banks. It was mainly because of the shortage of time and internship nature.
CHAPTER TWO:
Company overview:
Background of “Trust Bank Ltd:
Trust Bank Ltd. is a private, commercial, scheduled Bank, which obtained license from Bangladesh Bank on July 15, 1999. Presently Army Welfare Trust is the major shareholder. The authorized capital of the Bank is Taka two thousand million and paid-up capital of Taka five hundred million. Public shares are expected to be floated in the near future. The Bank was formally inaugurated and listed as a scheduled Bank on November 1999.
The idea of setting up a Bank by Bangladesh Army was first conceived in 1987 and on November 29, 1999 the first branch of Trust Bank Ltd came into operation
Composition of the Board of TBL consists of Ex-officio Directors of in-service senior Army personnel, with the Chief of Army Staff as its Chairman and the Adjutant General as its Vice-Chairman.
Trust Bank Ltd. having a spread network of 20 branches across Bangladesh and plans to open few more branches to cover the important commercial areas in Dhaka, Chittagong, Sylhet and other areas in 2006. The Bank sponsored by the Army Welfare Trust (AWT), is first of its kind in the country with a wide range of modern corporate and consumer financial products. Trust Bank Ltd. has been operating in Bangladesh since 1999 and has achieved public confidence as a sound and stable Bank.
In order to provide up-to-date information on the bank at fingertips to the trade and business communities of the world, their own IT team has developed a E-mail address and a web page for the bank. It can be accessed to under the domain: tbl@global-bd.net and www.trustbankbd.com
In addition to ensuring quality, Customer services related to general banking the bank also deals in Foreign Exchange transactions. In the mean time, the bank has extended credit facilities to almost all the sector of the country’s economy. The bank has plans to invest extensively in the country’s industrial and agricultural sectors in the coming days.
It has also plans to promote the agro-based industries of the country. The bank has already participated in syndicated loan agreement with other banks to promote textile sectors of the country. Such participation would continue in the future for greater interest of the overall economy. Keeping in mind the client’s financial and banking needs the bank is engaged in constantly improving its services to the clients and launching new and innovative products to provide better services towards fulfillment of growing demands of its customers.
Trust bank limited recently at the end of the year 2006 changed their name from “The Trust Bank Limited” to “Trust Bank Limited” and also changed their logo to bring the bank more closer to the general public.

CORPORATE INFORMATION AT A GLANCE:
- Banking License received on : 15th July. 1999
- Certificate of incorporation received on : 17th June 1999
- Certificate of Commencement of business received on: 17th June 1999
- First branch licenses on : 9th August 1999
- Formal inauguration on : 29th November 1999
- Sponsor Shareholders : Army Welfare Trust
- Number of Branch : 20
Nature of Business:
Trust Bank Ltd offers full range of banking services that include:-
- Deposit banking
- Loans & advances
- Export
- Import
- Financing inland
- International remittance facilities
The bank offers a full scale commercial banking includes:–
- Personal
- Credit
- Consumer & Corporate Banking
The bank has plans to invest extensively in the country’s industrial and agricultural sectors in the coming days. The bank has participated in syndicated loan agreement with other banks. Such participation would continue in the further for greater interest of the overall economy. The bank is keen to constantly improve its services to the clients and launching new & innovative products to provide better services towards fulfillment of growing demands of its customers.
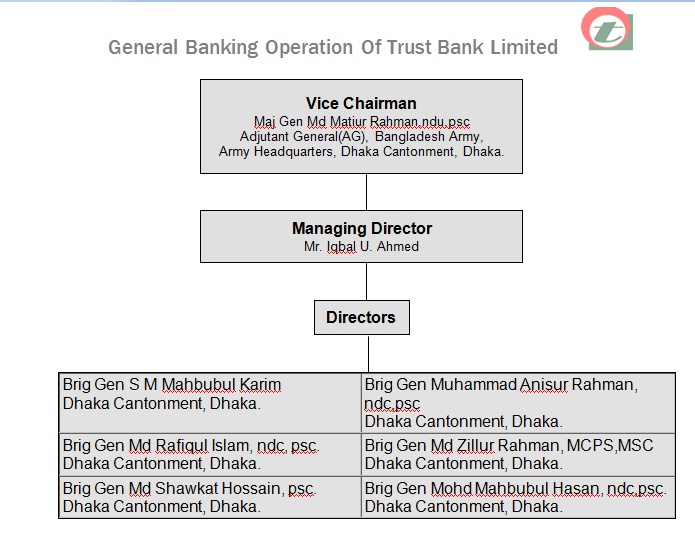
Board of Directors:
Chairman |
Organizational Structure of Trust Bank Ltd.
Vision Statement of “Trust Bank Limited:
- To build a sustainable and respectable financial institution.
- To be a leading Commercial Bank, with a social focus, assisting in the economic development of the country.
- The Profit of the bank used for the Socio-economic development of the members of the Bangladesh Army and thereby the nation as a whole.
Mission Statement of “Trust Bank Limited:
- Achieving sound and profitable growth in Assets & Liabilities, with focus to maintain non-performing assets at acceptable levels.
- To build long-lasting, credible and mutually dependable relationships with customers.
- Efficiently managing interest and operating costs.
- To excel in rendering superior customer service.
- To be the preferred employer among Banks in Bangladesh.
Branches:
The bank now continues its operation with 27 branches across the country mainly in Dhaka, Chittagong, Jessore, Sylhet, Sirajgong and Mymensingh. The district wise pictorial presentation of the branches appears as follows:
Twenty Seven branches of Trust Bank Limited are located in the following areas:
SL No. | Branch Name | Region |
01. | Head Office | 36, Dilkusha, Dhaka |
02. | Principal Branch | Dhaka Cantonment, , Dhaka |
03. | SKB Branch | 195, Motijheel, , Dhaka |
04. | Bogra Cantt. Branch | Bogra |
05. | Comilla Cantt. Branch | Comilla |
06. | Ctg. Cantt. Branch | Chittagong |
07. | Rangpur Cantt. Branch | Rangpur |
08. | Jessore Cantt. Branch | Jessore |
09. | Mymensingh Cantt. Branch | Mymensingh |
10. | Savar Cantt. Branch | Savar |
11. | Jalalabad Cantt. Branch | Sylhet |
12. | Agrabad Branch | Chittagong |
13. | SSC Branch, Ghatail | Tangail |
14. | Dhanmondi Branch | Road-02, Dhanmondi R/A, Dhaka |
15. | Khatungonj Branch | Chittagong |
16. | Gulshan Branch | Gulshan, Dhaka |
17. | Dilkusha Branch | Dilkusha, Dhaka |
18. | RWGH Branch | Mohakhali, Dhaka |
19. | KYAMCH Branch | Enayetpur, Sirajgong |
20. | CDA Branch | Chittagong |
21. | Sylhet Branch | Sylhet
|
22. | Halishahar Branch | Chittagong |
23. | Uttara Corp. Branch | Uttara,Dhaka |
24. | Beani Bazar Branch | Sylhet
|
25. | Maulavi Bazar Branch | Maulavibazar |
26. | Millenium Corp. Branch | B S Jahangir Gate,Dhaka
|
27. | Goalabazar Branch | Sylhet
|
CHAPTER THREE
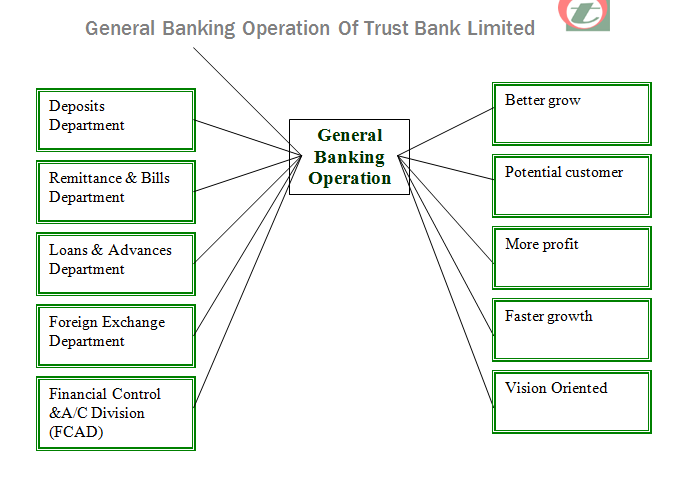
Topic Analysis and Description:
Dispatch Department:
Dispatch is one of the primary departments of banking activities. Dispatch can be categorized into two parts:
Inward Register:
Outward Register – (a) Courier
(b) By Post
Inward Register :
In inward register all the incoming documents are received and registered according to date. Then, Documents are transferred to different departments according to their destiny.
Outward Register:
The documents, which are needed to mail to different branches of TBL in Bangladesh or outside Bangladesh, are registered in outward register and mailed by courier or by post, which one is suitable.
Cash Department:
- ØOpening of Cash: Beginning balance is used to start daily transaction.
- ØMaintenance of Receipt and Payment Registers while receiving & paying
Different amount of cash.
- Previously issued cheque will be paid if issued 6 months before.
- Advance issued cheque cannot be made payment even one day before.
- Evening Banking: Can only receive cash. No payment can be made except
some special cases.
- TBL Dhanmondi Branch provides “Sheba Service” in this branch
- Issue Note: Notes issued by the bank & accepted by the people, fresh
notes.
- Non-issue Note: Notes cannot be issued for public like torn, mutilated
notes Soiled Notes etc.
Deposits Department:
- Payment through Cash
Clients give their cheques with their signatures. These signatures are justified with specimen signature cards. If these signatures are correct, then A/C numbers are posted into the computer and required balances are given to them after checking that they have sufficient balance in their accounts.
- Payment through Transfer
This transfer is made through account to account, not in cash.
- Payment through Clearing House
Payment is made through clearing house. In this case the parties are account holders different banks. The clearing-house in Bangladesh bank makes the clearing tasks in working day where the representatives of every scheduled bank are present there to collect their own banks’ cheque.
- Objections to unpaid cheque
- When cheque are returned from clearinghouse, they mention the cause of
returning. TBL Return memo includes the following causes:
(A) Insufficient Fund
(B) Not arrange for.
(C) Effects not cleared, may be presented.
(D) Exceed arrangements.
(E) Full Cover Not Received.
(F) Payment stopped by drawer.
(G) Payee’s endorsement irregular\ illegible\ required.
(H) Payee’s endorsement irregular, required bank’s confirmation.
(I) Drawers, signature differs/ required.
(J) Alterations in date/ figures/ words require drawer’s full signature.
(K) Cheque is post dated/ out of date/ mutilated
(L) Amount in words and figure differs
(M) Crossed cheque must be presented through a bank
(N) Clearing stamp required/ requires cancellation.
(O) Addition to bank discharge should be authenticated
(P) Cheque crossed “Account, Payee Only”.
(Q) Collecting Bank’s discharge irregular/ required.
2. After returning of cheque the cause is notified to the client to take necessary
action.
3. Also the vouchers are made reversal after returning of cheque i.e. Bills lodged debited and Bills for collection credited.
- Secrecy
1. The account information of a client is a secret matter.
2. Bank will not disclose it to unauthorized persons.
3. Only the account holder has the opportunity to get information of his
personal account or, who have got the authority from the account holder to
get such information,
- § Summation
Summation is nothing but the sum of the debit and credit sides. Now using computer automatically does it.
- § Supplementary
Formation of different head of accounts separate in supplementary forms. Supplementary is made every end of the working day. As now transactions are computerized, computer gives an output of such supplementary at the end of the day and matched with the manual supplementary. There are two types of supplementary:
(a) Debit Supplementary
(b) Credit Supplementary
- § Different heads of supplementary form are:
- Account Number, name of accounts
- Cash Balance
- Clearing Balance
- Transfer Balance
- Total Balance
- § Dormant Account:
After opening an account if no transaction is made within 6 (six) months, then it is known as dormant account.
- § Inoperative Account:
It is also like the above account. The account is not operating by the client for a long time/3 years.
- § Standing Instruction:
The client himself gives this type of instruction. Account holder instructs his bank not to make payment from his account before further instructions.
- § Stop Payment:
Due to unavoidable circumstances like burned or lost cheque, the client will make an application to the branch manager to stop all payments from his account and the will immediately freeze the particular account.
- § Statement of Account:
Bank will give statements if the account holder wants it. This statement will be about the amount consists in account / the latest balance amount in the particular account.
- § Transfer of Accounts:
The transfer of accounts can be of two types:
1) Fund transfer from one account to another
2) Account Transfer from one branch to another
- § Closing of Account & Disposal of Unutilized Cheque:
- Application to the manager for closing the account
- Bank takes Tk.50 as closing charge
- The application form and specimen sign card is marked as closed
- The customer has to submit any unutilized portion of cheque and bank will destroy these.
Remittance & Bills Department :
Local remittance is one of the main components of general banking. The components of local remittance are —
Telegraphic Transfer,
Demand Draft issue,
Saving Certificate Issue (Sanchaypatra issue),
Pay order.
Remittance & bills section plays a very vital role in case of Banks Customer Service Section. Roles & Responsibilities of remittance section knows no bound. The activities of
Remittance & Bill sections are:
- Ø Issue and payment of Pay Order, Pay Slip, Demand Draft, SDR etc.
- Ø Execution of Inward and Outward Telegraphic Transfer
- Ø Non client services like T.T. and Pay Order
- Ø Follow up with clients
- Ø Internal and local collection of cheque and bills.
Telegraphic Transfer (TT):
It is an order from the issuing branch to the drawee bank / branch for payment of a certain sum of money to the beneficiary. The payment instruction is sent by telephone and funds are paid to the beneficiary through his account maintained with the drawee branch or through a pay order if no account is maintained with the drawee branch. No charge is required for TT.
ii. Demand Draft (DD) Issue:
Sometimes customers use demand draft for the transfer of money from one place to another. It is must need for sending money out side Dhaka city. For getting a demand draft, customer has to fill up an application form. The form contains date, name and address of the applicant, signature of the applicant, cheque number (if cheque is given for issuing the DD), draft number, name of the payee, name of the branch on which the DD will be drawn and the amount of the DD. The form will be duly signed by the applicant and by the authorized officer. TBL charges 15% commission on the face value of DD as service charge.
iii. Shanchaya Patra:
Shanchaya patra is received from Bangladesh bank (BB). People purchasing these bonds by depositing money in this branch and payment are made on maturity to customers from this branch only. Every transaction is reported to Bangladesh bank. In case of issuance, report to be reached to BB within 48 hours, otherwise penalty is imposed. Money is realized from BB after making payment to customer.
Various types of Shanchaya Patras are sold here. They are as follows:
- 5 years Bangladesh Shanchaya patra (5 BSP) :
Duration of this Shanchaya patra is 5 years. Any person who purchase this Shanchaya patra can withdraw his/her interest only after 5 years at the time of maturity along with capital.
Any single individual can buy Bangladesh Shanchaya patra for up to TK. 50 lac. And jointly can buy for up to TK.1 Crore. Interest Rate: 12.00% After 5 years.
- 3 Month Profit Based Sanchaya patra(3MPBS):
Duration of this Shanchaya patra is 3 years. Any person who purchases this Shanchaya patra can withdraw his/her interest in every 3 month but capital can be withdrawn after the maturity period.
Any single individual can buy 03 MPB Shanchaya patra up to TK. 50 lac. And jointly can buy for up to TK.1 Crore.
Interest Rate: 11.50% after 3 year
After every three (03) month 2,875/= Tk. will be given against 1 Lac. Taka.
- Pensioner’s Sanchaypatra:
Duration of this Shanchaya patra is 5 years. Any person who purchases this Shanchaya patra can withdraw his/her interest in every 3 month but capital can be withdrawn after the maturity period. Any single individual can buy Pensioner’s Sanchaypatra up to TK. 30 lac.
Interest Rate: 12.50% after 5 year
After every three (03) month 3,125/= Tk. will be given against 1 Lac. Taka.
iv. Pay Order
For issuing a pay order, the client is to submit an application in the prescribed form. This form should be properly filled up and signed. The procedure of the issuing pay order is similar to that of the Telegraphic transfer. For issuing pay order TBL charges commission on the following rate—
|
| Pay Order [Local] issuance | No charge for account holder Tk. 20/- for non-customers/clients |
| Pay Order[Local] cancellation | Tk. 20/- per instrument
| |
| Issuance of Duplicate Instrument | Tk. 100/- per instrument plus stamp charges for indemnity at actual. |
Note: No charge for army personnel
SOURCE: From interview with the In-charge of remittance department of Trust Bank Ltd, Dhanmondi Branch.
Payment of Pay Order: The pay order is presented to the bank either through clearance or for credit to the client’s account. While payment, relative entry is given in the pay order register with the date of payment.
In case of collecting DD, P0, PS following things are to be carefully checked:
- Ø Instrument of TBL
- Ø Crossing Seal
- Ø Clearing Seal
- Ø Branch Name
- Ø Amount same in word & figure
- Ø Signature verification
- Ø Avoid the stop order PO, DD
- Ø Test key verification. Every TT must have test key. DD over Tk.50000/
- Ø must have test key
- Ø Maintenance of PO/TT/DD issue & payable books
- Ø Balancing at the end of the month.
Product & Schemes :
Deposit Products:
- Current Deposit Account
- Savings Deposit Account (interest calculated on monthly minimum balance of Tk.2000 and above)
- Fixed Deposit (3 months to 3 years term)
- Savings Certificate
- Trust Smart Savers Scheme(TSS)
- Trust Digoon Laav Scheme(TDLS)
- Trust Money Making Scheme(TMMS)
- Trust Education Scheme(TES)
- Corporate Financing
- Trust Consumer Durable Scheme (TCDS)
- Trust Marriage Loan Scheme (TMLS)
- Trust Car Loan Scheme (TCLS)
- Trust House Building Loan Scheme (THLS)
- Trust Micro Credit for Renovation & Reconstruction of Dwelling Houses
International Trade:
- International Banking
- Private Foreign Currency Accounts
- Non Resident Foreign Currency Deposit Account
- Resident Foreign Currency Deposit Account
- Travelers’ Endorsement (Cash and Travelers Cheque)
- Remittance of Foreign Currency
- Import and Export Transaction
- Foreign Exchange Dealing
- Purchase of Foreign Currency Drafts, Cheque, Travelers Cheque
- Wage Earner’s Development Bond
Others:
- Trust Locker Service (TLS)
- Trust Tele Banking
Account Opening Department:
A bank has to maintain different types of accounts for different purposes. Trust Bank limited (TBBL) offers the general deposit products in the form of various accounts.
Savings Account:
Savings bank deposit is popular account maintained in Banks. The different matters relating SB account are described in the following discussion. The summary of the rules and regulations to open a savings account is as follows:-
- Any person or persons of more than 18 years having sound mind can open and operate this account singly or jointly.
- In case of a minor (a person below 18 years), a guardian can open and operate this account on his or her behalf.
- Clubs, Societies, Sole Proprietorship firms, Partnership firms, Limited Companies either public or private and other similar organization are eligible to open such account.
- More than one account cannot be opened in the same name.
- A minimum initial deposit of Tk. 500.00 is required to open such account.
- Money will be withdrawn through cheque. Withdrawal cannot be more than twice a week and generally the amount will not be more than 25% of the balance available, subject to maximum Tk. 20,000.00.
- In case of closure of any account, the bank deducts Tk. 100.00 as closing charge.
Current Account AND Short Term Deposit (STD) Account:
Most businessmen maintain Current Deposit accounts in order to make their daily business activities. This account’s funds change most frequently than any other accounts because customers use to withdraw and deposit funds in regular basis. The summary of the rules and regulations to open a current account & short term deposit (STD) account as follows:-
- A minimum deposit of Tk. 1000.00 is needed to open a current account.
- The bank charges an incidental charge of Tk 50.00 for every six (6) months
for the maintenance of the account.
- In case of the closure, the bank charges Tk. 100.00 as closing charge of the account.
- Withdrawal of money is allowed only through the leaves of the cheque
book issued by the bank.
Fixed Deposit Account:
The bank allows people to keep their idle money secured and profitable as Fixed Deposit. The interest rate that the bank offers to the fixed depositors is as follows:
SL No | Amount or Slab wise Deposit | Interest rate on Deposit: Maturity wise but based on amount | |||
1 Month | 3 Months | 6 months | 1 Year and above | ||
| 01. | Any amount but less than Tk 5 crore. | 11.00% | 11.25% | 12.00% | 12.00% |
| 02. | Tk 5 crore & above but less than Tk. 10 crore. | 11.00% | 11.25% | 12.00% | 12.00% |
| 03. | Tk 10 crore & above but less than Tk. 25 crore | 11.00% | 11.25% | 12.00% | 12.00% |
| 04. | Tk. 25 crore and above | 11.00% | 11.25% | 12.00% | 12.00% |
| * Subject to 10% government tax on interest earnings.
| |||||
The Bank deducts the Excise duty, the compulsory levy of the government, on the interest earnings in the following structure:
Minimum Deposit | Maximum Deposit | Excise Duty |
10,001 | 1,00,000 | 120.00 |
1,00,001 | 10,00,000 | 250.00 |
10,00,001 | 1,00,00,000 | 550.00 |
1,00,00,001 | 5,00,00,000 | 2500.00 |
5,00,00,001 | 99,99,99,99,999 | 5000.00 |
- § Afferent Provisions:
For FDR minimum period is 01 month and maximum period has no limit. FDR may be joint or individual.
- § Payment on Maturity:
After maturity period the customer gets the interest plus principal back.
- § Payment on death:
It is a critical process when FDR holder dies. The rest of the family members must have to submit the following documents:
- Succession Certificate: Court mentioning, who will get & what portion.
- Death Certificate: The payee must make an application including the above documents. The branch will forward it to the head Office. It is very important to note that in these cases, the bank have to be very careful. Some FDR mentions either or survivor, in this case survivor will get the amount.
- § Either or Survivor:
In case of Joint FDR, if one partner dies, then the survivor i.e. who is alive will get the money at maturity or the person’s name in favoring.
- § Renewal of FDR:
The FDR account will be renewed automatically on the maturity date. The renewed period shall be the prevailing rate for Fixed Deposits.
- § Duplication:
If the customer lost the FDR receipt, then he has to make application to the bank by filling up an Indemnity bond. For duplicate FDR TBL charges TK.25
- § Indemnity Bond:
Here the reason of loosing FDR receipt shall be stated in detail. Stamp of
Tk.1501/- is needed in this case.
- § Custody Indemnity Bond:
The bank will have to maintain these indemnity bonds with care in a safe custody or vault.
- § FDR Block
A receipt, given to the applicant after opening the FDR account, will show it after maturity to take his money back.
- § Specimen Card:
The signature of the FDR account holder is maintained in the specimen card.
- § Closure:
After payment at maturity period the FDR account is closed. The FDR account holder must surrender his FDR receipt during the payment. It is to notify that in case FDR, the bank entries the full amount at maturity date in advance when a customer opens a FDR account. After the maturity FDR receipt and FDR form are attached together and on the front page of the FDR form bank authority writes “Close of FDR account” and gives entry in the ledger.
PRE REQUISITE OF OPENING AN ACCOUNT:
To open a savings, current, STD account, the following documents are mandatory:
a) FOR INDIVIDUAL ACCOINT:
- Two copies of Passport size Photograph of the Clients (Attested by introducer or Verified with Passports)
- Passports/ Nationality Certificate/ Employer’s Certificate of the Proprietor.
- Customer Profile.
- Transaction Profile.
- Photograph of the Nominee(s) attested by the account holder.
- TIN Certificate.
b) FOR JOINT ACCOUNT:
- Passports/ Nationality Certificate/ Employer’s Certificate of the Proprietor.
- Customer Profile.
- Transaction Profile.
- Photograph of the Nominee(s) attested by the account holder.
- TIN Certificate.
- Relationship between the account holders.
- Purpose of opening of the Joint account.
c) FOR PROPRIETORSHIP ACCOUNT:
- Two copies of Passport size Photograph of the proprietor
(Attested by introducer or Verified with Passports)
- Passports/ Nationality Certificate/ Employer’s Certificate of the Proprietor.
- Customer Profile.
- Transaction Profile.
- Photograph of the Nominee(s) attested by the account holder.
- TIN Certificate.
- Trade License.
- VAT Registration (if available)
d) FOR PERTNERSHIP CONCERN:
- Two copies of Passport size Photograph of each partner(Attested
by introducer or Verified with Passports)
- Passports/ Nationality Certificate.
- Company Profile.
- Transaction Profile of the concern.
- Personal Profile of the partners.
- Photograph of the Nominee(s) attested by the account holder.
- TIN Certificate.
- Trade License of the concern.
- VAT Registration (if available)
- Relationship between the partners.
- Attested Photocopy of the Partnership Deed (Deed on Tk 1000.00 stamp)
- Resolution regarding opening and operation of the account.
e) FOR COMPANY ACCOUNT:
- Attested or Certified copy of the Memorandum and Articles of
Association.
- Certificate of Incorporation.
- Certificate of Commencement of Business.
- Two copies of Passport size Photograph of all Directors (Attested by introducer or Verified with Passports)
- Passports/ Nationality Certificate of all Directors of the company.
- Company Profile.
- Transaction Profile of the company.
- Personal Profile of all Directors as per enclosed sheet in the
Company’s letterhead pad.
- TIN Certificate.
- Trade License.
- VAT Registration (if available).
- Board resolution of the company regarding opening and operation of the account.
f) FOR PRIVATE SCHOOL/COLLEGE/MADRASA:
- Attested or Certified copy of the Constitution.
- Registration Certificate.
- List of all Executive Members (as per enclosed format).
- Two copies of Passport size Photograph of the account operators (Attested by introducer or Verified with Passports)
- Passports/ Nationality Certificate of the account operators.
- Personal Profile of all members of the governing body and Managing Committee.
- Board resolution regarding opening and operation of the account.
g) FOR NGO/ CLUB-SOCIETY/CO-OPERATIVE ACCOUNT:
- Registration Certificate from the Joint Stock Company/ Ministry of Social Welfare.
- List of all Executive Members (as per enclosed format).
- Board resolution as per Memorandum regarding opening and operation of the account.
- Attested or Certified copy of the Constitution/Bylaws.
- Two copies of Passport size Photograph of all Members (Attested by introducer or Verified with Passports)
- Passports/ Nationality Certificate of all Members.
- Profile of the Firm.
h) Minor’s Account:
- Putting the word “MINOR” after the title of the account (with red color).
- Recording of the special instruction of operation of the account.
The AOF is to be filled in and signed by either the parents or the legal guardian appointed by the court of law and not by the minor.
“No Objection Certificate” from the Ministry of Social Welfare.
NEW DEPOSIT PRODUCTS:
To keep in touch with competitive market, the bank has recently introduced four attractive deposit products. The products having their distinctive have already gained and are gaining the response from the existing and prospective clients. The products are as follows:
Trust Smart Savers Scheme (TSSS):
Under the TSSS, the following category of deposit and maturity payment has been declared:
Monthly Deposit | Amount Payable at Maturity (3 years) | Amount Payable at Maturity (5 years) | Amount Payable at Maturity (7 years) | Amount Payable at Maturity (10 years) |
500 | 20,897 | 38,514 | 59,801 | 1,00,000 |
1,000 | 41,794 | 77,027 | 1,19,601 | 2,00,000 |
2,000 | 83,588 | 1,54,055 | 2,39,202 | 4,00,000 |
3,000 | 1,25,380 | 2,31,100 | 3,58,800 | 6,00,000 |
4,000 | 1,67,170 | 3,08,100 | 4,78,400 | 8,00,000 |
5,000 | 2,08,970 | 3,85,100 | 5,98,000 | 10,00,000 |
RULES AND REGULATION:
- The maximum number of TSSS account from a single family can not exceed five.
- The first installment is to be deposited on any date of the month but the subsequent installment is to be deposited by the 10th day.
- Advance payment of three installments is acceptable.
- One copy of Passport size Photograph of the account holder is needed to open TSSS.
- One copy of Passport size Photograph of the Nominee(s) [attested by the account holder] is also required.
- In the event of failure of to pay installment, the arrear installment(s) should be paid before or along with the next due installment subject to the penalty of Tk. 50.00 for per installment to be paid.
- In case of premature closure of the account, Tk 100.00 is charged as closing charge.
- Loan may be allowed up to 80% of the deposited amount but not below Tk 1,00,000.00 against lien or pledge of the same account.
- Any account can be transferred from any branch to another subject to Tk. 25.00 as Account transfer fee.
In any installment remains unpaid for six consecutive months, the account will be closed automatically and the account will be settled as below:
| Different duration Treatment | Applied rate of Interest |
| Less than six month | No interest |
| More than six month but less than three years | Prevailing interest rate on Savings Account |
| More than three years but Less than five years | Matured value of three years and rest as per the prevailing interest rate on Savings Account |
| More than five years but Less than seven years | Matured value of five years and rest as per the prevailing interest rate on Savings Account |
| More than seven years but Less than ten years | Matured value of seven years and rest as per the prevailing interest rate on Savings Account |
SOURCE: From interview with the In-charge of FDR department of Trust Bank Ltd, Dhanmondi Branch.
Trust Digoon Laav Scheme (TDLS):
Under the Scheme, the amount deposited at the very inception is doubled in 7 years. The basic structure of this Scheme is as follows:
Deposit Value | Matured Value | Year | Effective Rate of Interest (EAI) |
| 10,000.00 or multiple thereof | Double of the deposited amount | 7 years | 10.40% |
SOURCE: From interview with the In-charge of FDR department of Trust Bank Ltd, Dhanmondi Branch.
The bank lags behind in this project. Other contemporary banks offer the scheme with a maturity period of 6 years that result in the Effective Interest Rate (EAI) of 12.25%.
Trust Money Making Scheme (TMMS):
Under the Scheme, the client has to pay a down payment of Tk 7,500.00 or multiple thereof and the bank contributes Tk 42,500.00 or multiple thereof to form a fixed deposit of Tk 50,000.00 or multiple thereof with the bank. The client is allowed an interest rate of 10.00% on that deposit. The client has to pay the amount due to the bank through monthly equal installment of Tk 855.00 or multiple thereof in 6 years. The client is entitled to get the interest on FDR.
Summary of the scheme:
| Client’s Own Deposit | Tk 7,500.00 or multiple thereof |
| Bank’s Contribution | Tk 42,500.00 or multiple thereof |
| FDR Value | Tk 50,000.00 or multiple thereof |
| Tenor | 6 years |
| Installment Size | Tk 855.00 or multiple thereof |
| Interest Size | 10.00% |
SOURCE: From interview with the In-charge of FDR department of Trust Bank Ltd, Dhanmondi Branch.
Trust Education Scheme (TES):
The TES has been introduced to assist the poor students financially and chronologically. Under the scheme, a student may deposit Tk 10,000.00 for a period of three or five years. After the maturity period he or she may get a lump-sum amount of Tk 13,400.00 (for three years maturity) or Tk 16,000.00 c or he/she may get monthly education allowance of Tk 430.00 (for three years maturity) or Tk 520.00 (for three years maturity) for a period of three years after maturity.
Summary of the scheme:
Term | Deposit Amount | monthly education allowance after maturity of 3 years continuity | lump-sum amount payable at maturity |
3 years | Tk. 10,000.00 | Tk. 430.00 | Tk. 13,400.00 |
5 years | Tk. 10,000.00 | Tk. 520.00 | Tk. 16,000.00 |
SOURCE: From interview with the In-charge of FDR department of Trust Bank Ltd, Dhanmondi Branch.
There are two services offered by the bank exclusively on distinguishable terms and conditions. The aforesaid services are-
Locker Service:
There are some more than 500 lockers at the Dhanmondi Branch of TBBL. The lockers are now rented on Security Deposit Basis instead of yearly or monthly rental Basis. The lockers are allotted on most flexible term and meager Security Deposit refundable at the time of closing the locker.
Size of Locker:
| Size | ||||||||
| Small | Medium | Large | ||||||
| Height | Width | Length | Height | Width | Length | Height | Width | Length
|
| 4.5” | 7” | 21.5” | 4.5” | 14” | 21.5” | 9” | 14” | 21.5”
|
Security Deposit of Locker
Floor | Security Deposit | ||
Small | Medium | Large | |
| Ground Floor | 7,500 | 10,000 | 15,000
|
| First Floor | 5,000 | 7,500 | 10,000
|
ATM Card:
The bank offers its clients “Free of Cost” ATM (Q- Cash) card. To be a holder of the Card the person needs nothing but to be a client or account holder of the bank. The bank charges no initial card processing cost or no yearly or monthly service charge. It seems to be a value added service to the clients.
Loans & Advances Department:
The bank lends the deposited money on different sectors and at different rates. A summary of sector wise lending and lending rate is as follows:
There are two types of Loan:
1) Short-Term Loans: Time period is less than 1 year
2) Long -Term Loans: Time period is 1 year & above
Loans and advances Department is the most important department of a bank. Banks borrows money from the public by accepting Deposits from them and then lending it to a borrower for a specific period of time to be repaid with a certain amount of interest. This Dept. is one of the main sources of TBL’s profits.
When bank wants to give loans of advances to a borrower, first of all he has to do LRA (Lending Risk Analysis) and when loan amount is 20, 00,000 & above this analysis is compulsory. Because the amount, which is given to, a borrower, actually comes from the public and it is repayable on demand. So, bank has to be careful when giving loans and advances. When banks can not collect the loan amount with interest, they have to bear losses.
If TBL agrees to give loans and advances to a borrower after analyzing all sorts of risk, then the borrower writes an application addressing the manager and the amount, business types, securities etc. also are mentioned in the application. After getting the application the manager scrutinizes it for justifying all information whether genuine or not. and after doing this he sanctions the loan. He can also collect the borrower’s credit report from CIB(Credit Information Bureau ) Department of Bangladesh Bank (If the borrower takes loans above Tk. 1,00,000 from any bank, that bank will send this credit reports to the Bangladesh Bank.
The manager can sanction specific amount of loans and advances (In this branch it is Tk. 15, 00,000). If the loan amount crosses this limit, then he will recommend it to regional office. Regional manager also has limit for sanctioning loans and advances. If the amount of loans and advances above his limit, he will recommend it to the head office. Then head office will sanction that loans and advances.
TBL sanctions loans and advances under certain terms of conditions. When the borrower‘s loan is sanctioned, he is known through intimation/ a copy of sanction letter. If he accepts all terms of conditions, then he has to come within 3, 7, or 15 days whatever mentioned in the sanction letter.
- § Selection of Borrower:
In extension of bank credit, nothing is more significant than selection of borrower. While choosing a borrower, bank must study three things: Character, Capacity and in Capital or in other words Reliability, Responsibility, Resourcefulness of a party.
- § LENDING SCHEMES:
The bank lends the deposited money on different sectors:
a) TRUST CONSUMER DURABLE SCHEME :
Loans up to Tk, 60,000.00 available for purchase of household durable. Tenure ranges from 6 months to 24 months.
b) TRUST MARRIAGE LOAN SCHEME:
Bank Provides loan up to Tk. 1,00,000.00 for marriage. Easy monthly installment for a maximum period of 48 months.
c) TRUST CAR LOAN SCHEME:
Loan up to Tk. 3,00,000.00 available for purchase of car. Maximum period for repayment is 48 months only.
d) TRUST HOUSING LOAN SCHEME (THLS):
House Building loan up to Tk. 12.50 lac available for expansion of residential buildings. Easy monthly installment for a maximum period of 07 years.
e) TRUST MICRO CREDIT FOR RENOVATION & RECONSTRUCTION OF DWELLING HOUSE:
Small loans of Tk. 20,000.00 Tk. 30,000.00 and Tk. 40,000.00 are given to the low-income group for improving standard and quality of living.
Retail Products:
- TBL Car Loan,
- TBL House Hold Durables Loan,
- TBL Doctors Loan,
- TBL Advance Against Salary Loan,
- TBL Any Purpose Loan,
- TBL Hospitalization Loan,
- TBL Education Loan,
- TBL Travel Loan,
- TBL Marriage Loan,
- TBL CNG Conversion Loan,
- TBL Apon Nibash Loan
INTERNATIONAL BANKING:
Trust Bank Limited, with its wide correspondent relationship with major banks in the world is totally capable to meet your needs of foreign currency transactions and foreign trade services. You can open and maintain Accounts in foreign currencies like US Dollar, Pound Sterling, and Japanese Yen and even in Euro with us. With its own Dealing Room, TBL is able to offer competitive Exchange Rate for all major currencies of the world.
- FA Account (Foreign Nationals)
- FC Account (Bangladeshi Nationals)
- NFCD A/C
- RFCD A/C
PREREQUISITE OF OPENING AN FC ACCOUNT (Foreign Nationals):
- Completed Account opening Form signed by the account holder/s and introduced by an existing customer who has a relationship with us at least for 6 months.
- Copy of 1st six pages of passport and relevant page with more than 6 months visa of staying in Bangladesh. (Photocopy of document must be certified as “Original seen/sighted”) Photograph/s of the signatory/signatories/account holders duly attested by the introducer. Form QA- 22 (in duplicate) Copy of work permit from Ministry of Industries (where applicable) Documented proof of address verification to be retained with the mandate. This is also applicable for;
- To open an account when the person not being present personally i.e. in a non-face to face scenario is to obtain at least one additional form of evidence (e.g. copy of utility bills/bank statements/tax clearance certificate/ employer letter/home visit) over and above what would have been obtained in the corresponding face to face situation.
- Local Legal & Compliance should be consulted, in case of doubt on the acceptable identification evidence for a particular customer type.
- Welcome & follow-up letter’ as part of additional address verification.
- Completed KYC template.
Foreign Exchange Department:
Foreign exchange means the exchange of currency in terms of goods from one country to another. This is the most well-known and well-organized business uniform in world business. Foreign exchange mainly has two parties:
Import Operations:
There are different other parties who are also related to this foreign exchange process. But Bank is the most important of all the other parties. Bank works as
Intermediary in case of foreign exchange. So, we can say that the foreign exchange is nothing but the combination of export and import in international platform.
If an importer wants to buy goods from foreign countries he has to communicate with the exporter or he may also communicate through indenting firms.
When an importer & exporter are agreed to come into a contract for buying & selling goods, then the importer issues a L\C for the exporter, for issuing a L\C at TBL the importer has to submit some necessary papers\ documents. These are the following:–
- § IRC (Import registration certificate):
To become an importer a person has to get IRC which is issued by CCI& E (Chief Controller of Import & Export).
- § Proforma Invoice/ Indent Letter:
After the agreement between importer & exporter for buying & saling goods, the exporter will send a proforma invoice for the importer. If the importer is unknown about the foreign sellers, he may contact with indenting firms \ agent’s \ dealers. In this case the exporter will send an indent letter for the exporter through the indent firm. Proforma invoice indent letter includes quality; price etc of ordered the goods/ products.
- § Current VAT& TAX Certificate:
An importer is definitely a businessman. As a businessman he must has to pay VAT & TAX to the govt. For opening L\C has to submit VAT & TAX certificate.
- § L\C Authorization Application form:
TBL provides this form for opening a L\C. Importer fill up this form.
- § IMP (Import) form:
Importer also has to fill up this form which is provided by TBL.
- § Letter of Application:
After getting the proforma invoice/indent letter from the exporter, the importer writes an application favoring the manager of the branch where the subject is “Request to open a L/C”.
- § Application & Agreement for confirmed irrevocable without:
Resource to drawer’s letter of credit:
This form includes either the goods \ products will come directly by ship \ air or by transshipment & other necessary condition.
Export Operations:
- § For becoming an Exporter a person needs:-
- Current A/C in TBL
- ERC (Export Registration Certificate) issued by CCI & E (Chief Controller of Import & Export).
- Permission from sponsoring Authority such as Board of Investment for industries, Department of Textile for garments etc.
- Traders Association’s certificate
- VAT (Value Added Tax) & TIN (Tax Identification Number) certificates.
- § Common documents involved in the transportation of goods:
The main documents required are Airway Bill / Bill of Lading, Commercial Invoice, Consular Invoice, Packing List, Certificate of Inspection, Certificate and Certificate of origin.
- § Airway bill:
This document is a receipt issued by an its for the carriage of goods. Goods are delivered to the consignees when they have identified themselves as the party named in the airway bill. It has two variants: (1) Master Airways Bill (MAWB) and (2) House Airway Bill (HAWB). The Forwarder of the cargo incorporation the L/C terms uses it.
- § Bill of Lading (B/L).
The bill of lading is not the actual contract between the owner of the goods and the carrier, although it does provide evidence of the contract. It is a receipt for goods shipped on board a vessel (for marine B/Ls), and is a document of title to the goods, which are the subject of the contract between the buyer and the seller. This is why a marine B/L can be negotiated.
- § Commercial invoice:
As in a domestic transaction, the commercial invoice is a bill for the goods from the buyer to the seller. A commercial invoice should include a description of the goods, address of shipper and seller, and the delivery and payment terms. The buyer needs the invoice to prove ownership and arrange payment. Some government agencies use the invoice to access customs duties.
- § Certificate of Origin:
Certain countries, especially USA, Canada, EU, Japan, Australia etc. require a signed statement to verify the origin of the export item in order to monitor import tariffs and quotas. Such certificates are usually obtained through a semi-official organization such as a local chamber of commerce, and must be certified by the chamber of commerce. A certificate may be required even though the invoice
contains all the necessary information. Documentation that requires a notary stamp or chamber of commerce stamp can be completed by freight forwarder.
- § Export packing list:
The export-packing list is considerably more detailed and informative than a standard domestic packing list. An export packing list itemizes the material in each individual package, and shows the individual net, legal, tare and gross weights. Package markings should be shown along with the shipper and buyer’s references. The packing list is attached to the outside of the package in a clearly marked waterproof envelope. The list can be used to determine the total shipment weight and whether the correct cargo is shipped. Customs officials may use it to check the cargo at inspection points.
- § Inspection certificate:
Some purchasers and countries may require a certificate of inspection, which authenticates the specifications of the goods shipped, this is usually performed by a third party and obtained from independent testing companies.
- § Insurance certificate:
If the seller provides insurance, the insurance certificate states the type and amount of coverage.
- § Consular invoice:
Consular invoice are generally required by Middle East countries issued by the embassy of the importer’s country. A consular invoice allows the importer’s country to collect information on the value, volume, quality, and source of the goods. The invoice is purchased or obtained from the consulate of the country to which the goods are being shipped and must be prepared in the language of that country.
Credit Department:
Credit is an arrangement whereby bank acting at the request and on the instructions of a customer or on its own behalf to make a payment to or to the order of a third party or is to accept and pay bills of exchange drawn by the beneficiary. In an economy banks play the role of an intermediary that channels resources from the surplus group to the deficit group. So, one of the core functions of Commercial banks is to sanction credit facility to its customers as per requirement. Trust Bank Limited Mission is to actively participate in the growth and expansion of our national economy by providing credit to variable borrowers in most efficient way of delivery and at a competitive price.
Bank can lend up to 15% of its capital fund without having any approval from Bangladesh bank. The maximum limit can go up to 100% of the bank’s capital fund. Trust Bank Limited complies with the ceiling set by Bangladesh Bank.
PRINCIPAL OF CREDIT:
Basic principle governs the extension of credit. These principles are strictly maintained to shape and define the acceptable risk profile of Trust Bank and guides to respond business opportunities as they arise. Basic lending principles are;
- Know your customer
- Liquidity of the customer
- Safety
- Security
- Profitability (from both bank’s and customer’s purpose of the loan’s perspective)
- Diversification
- National interest
Types Of Loans And Advances Offered By Trust Bank:
Basically Trust Bank offers both funded and non-funded credit facilities.
Funded Loan Facility:
Any type of credit facility which involves direct outflow of Bank’s fund on account of borrower is termed as funded credit facility, the funded facilities of loans and advances are:
Cash Credit:
Cash credit is a continuous credit facility usually provided for working capital fund requirements purpose of the customer. Cash credit is generally given to traders, Industrialist for meeting up their working capital requirements. Cash Credit can be given on Hypothecation of goods or pledge. Trust Bank only practices Cash Credit on Hypothecation.
ð Features of Cash Credit:
- A certain limit of credit amount is set at the time of initiation of Cash Credit facility.
- An expiration date is set, which is not more then one year.
- The drawings are subject to drawing power.
- A service charge, which in effect an interest charge is normally made as a percentage of the value of purchases.
- The primary security of Cash credit facility is stock of goods, which maybe hypothecated to Trust Bank as collateral.
Over Draft:
Over draft facility is also a continues loan arrangement on a customer’s current account permitting him to overdraw up to a certain approved limit for an agreed period. Here the withdrawal of deposits can be made any number of times at the convenience of the borrower, provided that the total overdrawn does not exceed the agreed limit.
Customer can return any amount at any time within the pre-fixed time of the facility. Turn over of an OD facility is the most important phenomenon on which renewal of the facility depends. Over draft facility is given to the businessman for financing working capital requirement and high net worth individual to overcome temporary liquidity crisis.
Secured over draft:
This is a type of over draft facility given by keeping sufficient collateral from the customer. This facility provides specific right to a client to over draw within a pre fixed limit for a certain period of time. SOD is normally granted against the security of tangible asset such Lien of FDR, Bonds, Sanchay Patra etc. Interest charge on SOD is calculated on the basis of the security liened.
- Incase of FDR with Trust Bank 13%, with other bank is 14%
- Incase of Sanchay Patra purchased from Trust Bank 13%, from other bank is 14%
- The common thing is 2.5% spread is kept in charging interest. Interest is calculated on outstanding amount at daily basis.
Term loan:
Term loans are given to finance the acquisition of capital asset. Loan agreements often contain restrictive covenant and loan is repayable in accordance to amortization schedule. Collateral is must for term loan.
Under term loan there are three categories:
- Short term loan – less then 1 year falls with this category
- Midterm – this loan facility is extended for more then 1 year but less the 3 year. Trust Bank encourages midterm loan.
- Long term – tenure of long term loan is more then 5 years
- Inland Bill Purchased (IBP)
- House Building Loan
- Marriage Loan
- Car loan(Staff & Others)
- Consumer Durable Scheme(CDS)
- Loan Against Trust Receipt (LTR)
- Any Purpose Loan
Non-funded facilities:
Non-funded facilities also known as “contingent facilities” are those where bank fund is not required directly. A non-funded facility can turned to a funded facility as per situation creates. Bank receives commission rather than interest income by providing non-funded facilities. Following non-funded facilities are provided by Trust Bank –
Letter of Credit (L/C):
A letter of credit is a credit line given by a bank to an importer to facilitate both foreign and inland transactions. This is a contingent liability which can be converted to a funded facility incase bank makes the payment on behalf of the importer. A letter of credit can be revocable or irrevocable, restricted or negotiable so on.
Guarantee:
Trust Bank offers guarantee for its reliable and valuable customer as per requirements. This is also a Credit facility in contingent liabilities from extended for participation in development work like supply of goods and services.
ð Features of Bank Guarantee;
- It is a written document on non-judicial stamp
- Expiry date is mentioned specifically with other terms and conditions
- Trust Bank receives commission quarterly @ 0.50% of the guaranteed amount.
Trust Bank offers two types of Guarantee, which are as follows:
Tender or Bid Bond Guarantee:
In time of tender bidding either cash or bank guarantee is required in case payment of earnest money. The tender guarantee assures that the tenders shall uphold the conditions of his tender during the period of the officer as binding and that he /she will also sign the contract in the event of the order being granted.
Process of Bid bond Guarantee:
- Request letter from customer along with board resolution in case of Limited company
- Trade license in case of Proprietorship Company
- Copy of tender form
- Margin:
- Incase of reliable client 10% to 20%
- For a new client 100% margin is required
- Bank guarantee is issued in 150 Tk Stamp pad
- Note is initiated
- Approval of Bank guarantee is given.
Performance Guarantee:
Trust Bank also gives guarantee on behalf of the customer on completion of the delivery or performance after getting the tender. Beneficiary finds that as a guarantee, the contract will be fulfilled in every respect and can retain the guarantee as per provision for long time. Including a clause stating that the supplier can claim under the guarantee, by presenting an acceptance certificate signed by the buyer, can counteract this. Document required for performance guarantee;
- Tender schedule.
- Guarantee letter.
A guarantee can be converted into funded facility if it is en cashed. If the client is unable to meet up banks demand a loan account is created like Over Draft as Bank is liable to pay to the beneficiary of the guarantee. If Bank guarantee is not used then the beneficiary or party to whom the guarantee was given on behalf of the client will sign on the back of the Bank Guarantee stamp and write the word ‘Released’. Then the facility will be expired as well as banks liability.
Special Loan facility given by Trust Bank:
Syndicate Loan:
Bank can lend up to 15% of its paid up capital with out any approval by Bangladesh Bank. If the loan amount is more then 50% of its paid up capital Bank goes for Syndicate loan. Lead bank makes the arrangement. Head office makes facility agreement by bank’s lawyer. All terms and conditions such as security sharing, mode of repayment, covenants of the loan are written on this facility agreement.
ð Loan Portfolio Management & Credit Admin. Strategies of Trust Bank:
- § Lending Authority:
Trust Bank’s organizational structure has two levels – Branch and Head office. The credit proposal moves through different management approval levels according to the amount of risk. There are three approval Levels in Trust Bank:
1. Branch manger
2. Credit committee of corporate office
3. Board of directors of the bank
- Lending Policies:
A loan policy gives loan officers and the bank’s management specific guidelines in making individual loan decisions and in shaping the bank’s overall loan portfolio. One of the most important ways a bank can make sure its loans meet regulatory standards and are profitable is to establish a written loan policy.
Trust Bank Limited also has a good loan policy and the most important elements of that policy are as follows:
- A goal statement for the bank’s loan portfolio (in terms of types, maturities, sizes, and quality of loans).
- Specification of the lending authority given to each loan officer and loan committee (measuring the maximum amount and types of loan that each person and committee can approve)
- Lines of responsibility in making assignments and reporting information within the loan department.
- Operating procedures for soliciting, reviewing, evaluating, and making decisions on customer loan applications.
- The required documentation that is to accompany each loan application and what must be kept in the bank’s credit files (required financial statements, security agreements, etc.)
- Lines of authority within the bank, dealing who is responsible for maintaining and reviewing the bank’s credit files.
- Guidelines for taking, evaluating, and perfecting loan collateral.
- A presentation of policies, and procedures for setting loan interest rates and fees and the terms for repayment of loans.
- A statement of quality standards applicable to all loans.
- A statement of the preferred upper limit for total loans outstanding (i.e. the maximum ratio to total loans to total assets allowed).
- A description of the bank’s principal trade area, from which most loans should come.
- A discussion of the preferred procedures for detecting, analyzing, and working out problem loan situations.
A written loan policy statement carries a number of advantages for the bank adopting it. It communicates to employees working in the loan department what procedures they must follow and what their responsibilities are. It helps the bank moves toward a loan portfolio that can successfully blend multiple objectives, such as promoting the bank profitability, controlling its risk exposure, and satisfying regulatory requirements.
ðBorrower’s credit worthiness analysis by Trust Bank following 6 “C”s:
The question that must be dealt with before any other is whether or not the customer can service the loan – that is pay out the credit when due with a comfortable margin for error. This usually involves a detailed study of six aspects of the loan application:
character, capacity, cash, collateral, conditions, and control. All must be satisfactory for the loan to be a good one the lender’s (Trust Bank’s) point of view.
Character:
The loan officer must be convinced that the customer has a well-defined purpose for requesting bank credit and a serious intention to repay. Responsibility, truthfulness, serious purpose, and serious intention to repay all the monies owed make up what a loan officer calls character.
Capacity:
The customer requesting credit must have the authority to request a loan and the legal standing to sign a binding loan agreement.
Cash:
The borrower should have the ability to generate enough cash, in the form of cash flow, to repay the loan. This cash flow of borrower can be generated from sales or income, from the sale of liquidation of assets or funds raised by using debt or equity securities.
Collateral:
The borrower must possess adequate net worth or enough quality assets to provide adequate support for the loan.
Conditions:
The recent trend of borrower’s line of work or industry must be aware of by the lender.
Control:
The lender should careful about whether changes in law and regulation could adversely affect the borrower and whether the loan request meets the bank’s and the regulatory authorities’ standards for loan quality.
ðLending procedure of Trust Bank:
The lending procedure starts with building up relationship with customer through
account opening. Control of credit operations is done at branch and Corporate Office
level.
- Step-one:
A loan procedure starts with a loan application from a client who must have an account with the Bank. At first it starts form the branch. Branch receives application from client for a loan facility. In the application, client mentions what type of credit facility he/she wants form the bank including his personal information and business information. Branch Manager or regarding Officer in-charge of credit department conducts the initial interview with the customer.
- Step-two:
After receiving the loan application form, the bank sends a letter to Bangladesh Bank for obtaining a credit inquiry report of the customer from there. This report is called CIB (Credit information Bureau) report. This report is usually collected if the loan amount exceeds Tk. 50 thousand. The purpose of this report is to be informed that whether the borrower has taken loan from any other bank or not, if ‘yes’ then whether these loans are classified or not.
- Step-three:
If Bangladesh Bank sends positive CIB report on that particular borrower and if the Bank thinks that the prospective borrower will be a good one, the bank will inspect the documents. Required documents are:
– Incase of Corporate Client, Financial documents of the company of last three to five years. If the company is new then projected financial data are required.
– Personal net worth of the borrower/Borrowers.
– In this stage, the Bank will look whether the documents are properly filled up and signed. Credit in charge of the relevant branch is responsible to know about the ins and outs of the client’s business through discussing with him.
- Step-four:
Bank officially inspects the project for which the loan is applied. Project’s existence, distance from bank office, viability, monitoring cost and possibilities are examined.
- Step-five:
Any loan proposal needs to be evaluated on the basis of financial information provided by the applicant. Lending Risk Analysis (LRA) is a technique by which the risk of the loan is calculated. Banker must analyze LRA when loan application is above 1 crore. Experienced people of Credit department in Trust Bank do this analysis. It is a ranking whose total score are 140. Among this score, 120 is for Total Business Risk and 20 for Total Security Risk.
In LRA, following aspects are analyzed:
- Suppliers risk
- Sales risk
- Performance risk
- Resilience risk
- Management ability.
- Level of Managerial teamwork
- Management competent risk
- Management integrity risk
- Security control risk
10. Securities cover risk.
- Step-six:
Obtain vetting or legal opinion on the collateral provided by the applicant, whether those are properly submitted -regular and up to date or else those documents will be asked to regularize by the client.
- Step-seven:
Then come, the processing stage of loan. In this stage, the Bank will prepare a Proposal. The proposal contains following relevant information.
a) Name of the Borrower/borrowers
b) Nature of Limit
c) Purpose of Limit
d) Extent of Limit
e) Collateral
f) Margin
g) Rate of Interest
h) Repayment
i) Validity
- Step-eight:
If the proposal meets Trust Bank’s lending criteria and is within the manager’s Discretionary powers, the credit line is approved. The manager and the sponsoring officer sign the credit line proposal and issue a sanction letter to client.
If the value of the credit line is above the branch managers’ limit then it is send to head office or zonal office for final sanction with detailed information regarding clients, business or purpose of the loan, security papers.
- Step-nine:
Head office processes the credit proposal and afterwards puts up a memorandum to credit committee. The credit committee reviews the credit proposal and accepts or rejects the proposal.
- Step-ten:
After approval by the Credit Committee head office or zonal office gives an approval letter to the branch and branch gives a sanction letter. The client should accept sanction advice with seal, which will prove his agreement with the terms and condition offered by the bank.
- Step-eleven:
After the sanction advice, Bank will collect necessary charge document. Charge documents vary on the basis of types of facility, types of collateral.
- Step-twelve:
Finally loan is disbursed and monitoring of loan starts as well.
Source: Primary
ð Credit Planning at different level of Trust Bank
Credit Planning implies estimating first the total lend able resources that are likely to be available within the given period and then allocating the same amongst various alternative uses in conformity with national plan and priorities.
Necessity of credit planning in context:
- Demand for Credit is much more than its supply.
- Providing credit at right person at right time at right quantity.
- Getting maximum output as a result of credit allocation.
- Ensuring the best of alternative investment opportunities
- Achieving declared objective such as providing credit to priority sectors.
Lending Risk Analysis (LRA): A Risk Mgt. Technique by Trust Bank:
Lending Risk Analysis (LRA) are based on two important pillars –
- Business risk pillar
- Security risk pillar
These are for addressing two frequently asked questions of the bankers. The questions are –
- Is the business good enough to ensure regular repayment of my loan?
- Do the securities cover adequate exposure, if the business fails to produce returns?
In answering these two basic questions, business risk and security risk have been examined with their different parameters of risk, as business risk is nothing but the
Combination of the risk of different parameters of business and industry and so is for security risk, under LRA forms with a view to reaching the ultimate Security risk pillar
and Business risk pillar. In this regard, the FSRP authorities have prescribed a total 11 forms, for the bankers for facilitation their decision-making.
Source: Primary
ð Modes of Charging Securities by Trust Bank:
Securities are the cover against loans and advances. On the other hand it ensures recovery of loans and advances from the borrowers who offer properties to the lending banker as security. Properties are converted into securities. But for conversion some conditions are to be full filled as required by the Trust Bank and these are as follows:
a) The properties are to be acceptable to the lending bankers for securities.
b) Creation of the charge on the concerned properties.
- The Acceptability of properties as securities are mainly depends on:
1. Value of property must cover the loan amount with margin.
2. Consideration of different qualities of properties
3. Free from credit restrictions of Bangladesh Bank (if any).
- Within the credit policy of the bank.
- There are two types of securities i.e. primary and collateral.
- Modes of Creation of chares are of different types. These are dependable on the basis of nature of loans and advances and nature of properties for securities.
- Charges may be of different types like legal Charge, Equitable charges, fixed charges, floating charges etc.
- Following are the different modes of creation of charges by the bank:
- Pledge
- Hypothecation
- Mortgage
- Lien
Pledge:
When goods and produces are handed over to the lending banker by the trader or manufacturer who borrow against those goods and produces for short term i.e. for working capital. But if any goods and produces are kept with the bank for security purposes will not be treated as pledge. In otherwise it is the Bailment of goods as per Bailment of goods act.
In case of Pledge, control and possession of goods and produces will remain with bank but ownership will remain with borrower. There will be a storehouse either of banks or rented for safe keeping of goods. Insurance of pledged goods are compulsory. And all related expenses would be born by borrower.
Hypothecation:
Hypothecation is just opposite of pledge. When a borrower ownership, control and possession of trading goods but legal right and indirect control is created by lending banker for security against short term advances i.e. Equitable charge is created is known as Hypothecation. Just control and possession of trading goods are kept under borrower. In these types of securities lending banker generally asks for collateral securities. This type of mode of securities is allowed only for the case of first class borrowers.
Mortgage:
When bank create charge on immovable property in the form of mortgage against any lending to the borrower. Therefore a mortgage is a transfer of interest of a specific immovable property. The immovable property means land and the property attached to land but not grass, trees and crops. Mortgage is to be created for securing loan or performing any contract. And there will be a Mortgagor, Mortgagee, Mortgaged Property and Mortgage deed.
Lien :
A lien is defined as the right to retain property belonging to a debtor until he has discharged a debt due to the retainer of the property. Lien may be of two types, General Lien and Particular Lien.
A particular Lien confers a right to retain a property in respect of a particular debt involved in connection with a particular transaction.
But a General Lien confers a right to retain goods not only in respect of a debt incurred in connection with a particular transaction but also in respect of any general balance arising out of the general dealing between two parties.
Banker’s Lien is defined as an implied pledge. An ordinary lien does not imply a power of sale, but a pledge implies a power of sale. A banker’s right of sale is generally regarded as extending only to fully negotiable instrument, with regard to other securities.
LOAN PRICING TECHNIQUES BY TRUST BANK:
Loan Pricing:
- The price of a loan is the “interest rate” that the borrowers must pay to the bank; in addition to the amount borrows (principal).
- The price or the “Interest rate” of a loan is determined by the true cost of the loan to the bank (base rate) plus profit/risk premium for the bank’s services land acceptance of the risk.
- The components of the true cost of a loan are:
- Interest expense
- Administrative cost
- Cost of capital
These three components add-up to the bank’s “base rate”.
- Interest Expense = Deposit Interest + Central Bank Borrowing cost
- Administrative cost = Deposit as well as Loan administrative cost.
- Cost of capital = Return on capital or the Rate of Return investors would expect to receive from their investment in a bank.
- Risk is the measurable possibility of loosing or not gaining value.
- The Primary risk of making loan is Repayment Risk, which is the measurable possibility that a borrower will not repay their obligation as agreed.
- The Price a borrower must pay to the bank for assessing and accepting the risk is called the risk premium.
- Since past performance of a sector, industry or company is a strong indicator of the future performance, risk premium is generally based on the historical, quantifiable amount of losses in that category.
- Interest Rate Charge = Base Rate + Risk Premium.
Interest Rate Charged at Different Credit Scheme:
| SL# | Particulars | Rate of Interest |
| 1. | Agriculture loan including raw jute | 11.00% P.A. |
| 2. | Term loan (project loan) | 15.00% P.A. |
| 3. | Working capital loan (except jute) | 16.00% P.A. |
| 4. | Export loan (packing credit, export cash credit) | 7.00% P.A.
|
| 5. | Commercial loans (cash credit, hire- purchase, LTR, IBP etc.) | 15.00% P.A. |
| 7. | Small & cottage industry loan (Without subsidy of Bangladesh Bank) | 15.00% P.A. |
| 8. | Loans under various credit schemes such as consumer’s credit, small loan, Doctor’s credit, rural development credit etc. | 15.00% P.A. |
| 10. | Secured overdraft (SOD) | |
| SOD against financial obligation (PSP, BSP, ICB unit certificate etc) | 14.00% P.A. | |
| SOD against FDR of MBL | 3.00% above of the FDR rate | |
| SOD against deposit of various savings instruments of MBL | 15.00% P.A. | |
| SOD against shares / work order / export bills / quota etc | 15.00% P.A. | |
| SOD (General) | 15.00% P.A. |
ðLoan Classifications and Provisioning By Trust Bank:
Loan Classifications:
Loan classification is required to have a real picture of the loan and advances provided by the Bank. It helps to monitor and take appropriate decision regarding each loan account like other banks, all types of loans of BA fall into following four scales:
Unclassified: Repayment is regular
Substandard: Repayment is stopped or irregular but has reasonable prospect of improvement.
Doubtful debt: Unlikely to be repaid but special collection efforts may result in partial recover.
Bad/Loss: Very little chance of recovery.
Table – CL Statement:
| Loan Type | Unclassified (Month | Substandard (Month) | Doubtful (Month) | Bad (Month) |
| Continuous Loan Demand Loan | Expiry up to 5 month | 6 to 8 month | 9 to 11 month | 12 month+ |
| Term loan up to 5 year | 0 to 5 month | 6 to 11 month | 12 to 17 month | 18 month+ |
| Term Loan more then 5 years | 0 to 11 month | 12 to 17 month | 18 to 23 month | 24 month+ |
| Micro Credit | 0 to 11 month | 12 to 13 month | 36 to 59 month | 60 month+ |
Source: Publication of Trust Bank
Loan Provisioning:
A Certain amount of money is kept for the purpose of provisioning. This percentage is set following Bangladesh Bank rules.
| Type of Classification | Rate of Provision |
| Unclassified | 1% |
| Substandard | 20% |
| Doubtful | 50% |
| Bad debt | 100% |
Source: Publication of Trust Bank
Statement Send By Credit Department To Bangladesh Bank:
Statements are sent to Bangladesh bank on monthly, quarterly, half yearly and yearly basis. These statements are based on advance and inland Bill purchase/Discounted, Statement over due advances, CIB Statement, Statement of Credit, and Monthly Statement of deposit, Monthly Statement of Bank Loan & advances and other as per central bank time-to-time requirement.
Financial Analysis:
ð Performance of the Bank
q Profit and Operating Results: The bank earned as operating profit Tk. 296,261,558 during 2005 after all provisions including the 1% general provision on unclassified Loan & Advances. Provision for income tax for the year amounted to Tk. 105,000,000 resulting into a net profit after tax of Tk. 121,286,368 million.
Deposit: A strong deposit base is necessary for the success of a Bank. During the year 2002 the Bank mobilized a substantial amount of deposit from mid-level
income group people under Deposit Savings Scheme. After critical handling the Bank mobilized total Deposit Tk. 12,704,902,083 as at December 31,2005, thus
recording an increase of 36.39% in comparison with Tk. 9,314,952,180 as at December 31, 2004. The significant growth in deposit enabled the Bank to expand its business, performing assets and also had an impact on the profit position of the Bank.
Advance: The Bank Loans & Advance portfolio also indicates an impressive growth. Total Loan and Advances amount to Tk. 9,738323,349 in 2005 against Tk. 6,804,448,553 in 2004 and the growth being 43.11% TBL’s Advance portfolio is well diversified and covers a wide range of businesses and industries. The sectors financed include Manufacturing, Trading, Construction, Transport, Agriculture, Fishing & Forestry, Information Technology, and Consumer Credit amongst others.
Advances constitute the most significant indicator of the health of a Bank. The Bank has formulated its policy to give priority to SMES (Small and Medium Enterprise) and at the same time the Bank is financing large-scale enterprises through consortium of Banks. The Trust Bank Limited is committed to maintain a very high quality of assets. Close monitoring and efficient asset management has resulted in minimal creation of classified loans to total Loans and Advances.
International Trade constitutes the main stream of business activities of the Trust Bank. Trust Bank Limited offer a full range of trade and services namely, issue, advice and confirmation of Documentary Credit; arranging forward exchange coverage; pre-shipment and post-shipment finance; negotiation and purchase of export bills; discounting bill of exchange; collection of bills, inward and outward remittance etc.
Import Business: The Bank established Letter of Credit amounting to Tk. 35,726,574 during 2005; showing a growth of 16.83% over the volume of Tk. 30,578,688 in the year 2004.
q Foreign Correspondents: The number of foreign correspondents and agents of Trust Bank Limited is increasing day by day. The Bank has maintained excellent relationship with leading international Banks and has successfully established credit lines with major Banks to support global Foreign Trade Business.
ð Financial Highlights:
| Sl No | Particulars | Base | 2005 | 2004 |
| 1 | Paid up capital | Taka | 500,000,000 | 500,000,000 |
| 2 | Total Capital | Taka | 1,115,068,646 | 940,513,833 |
| 3 | Capital surplus/ (deficit) | Taka | 311,749,871 | 383,596,050 |
| 4 | Total Assets | Taka | 14,807,905,231 | 15,059,710,225 |
| 5 | Total Deposits | Taka | 12,704,902,083 | 9,314,952,180 |
| 6 | Total loans & Advances | Taka | 9,738,323,349 | 6,804,448,553 |
| 7 | Total contingent liabilities and commitments | Taka | 4,681,077,063 | 3,123,318,980 |
| 8 | Credit deposit ratio | % | 76.65 | 75.25 |
| 9 | % of classified loans against total loans and advances | % | 1.32 | 1.47 |
| 10 | Profit after tax & provision | Taka | 121,286,368 | 216,384,186 |
| 11 | Amount of classified loans during current year | Taka | 28,617,561 | 13,236,523 |
| 12 | Provisions kept against classified loans | Taka | 58,000,000 | 41,293,255 |
| 13 | Provision surplus/ debit | Taka | 2,315,796 | – |
| 14 | Cost of funds ( Deposit Cost & Administrative cost) | % | 9.23 | 9.30 |
| 15 | Interest earning Assets | Taka | 13,401,393,133 | 11,380,077,637 |
| 16 | Non-interest earning Assets | Taka | 1,406,512,098 | 678,632,588 |
| 17 | Return on investment (ROI) | % | 10.88 | 23.01 |
| 18 | Return on Assets (ROA) | % | 0.82 | 1.79 |
| 19 | Income from Investment | Taka | 194,479,592 | 177,745,964 |
| 20 | Earning per share | Taka | 24.26 | 44.16 |
| 21 | Net Income per Share | Taka | 24.26 | 44.16 |
| 22 | Price earning Ratio | % | N/A | N/A |
ð Total Deposit Collection:
| 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 |
| 2,991,193,352 | 4,483,256,901 | 9,314,952,180 | 12,704,902,083 |
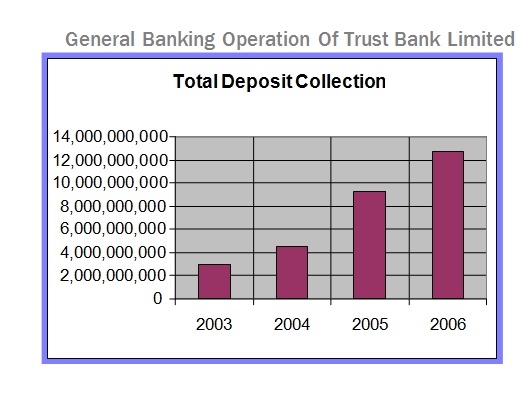
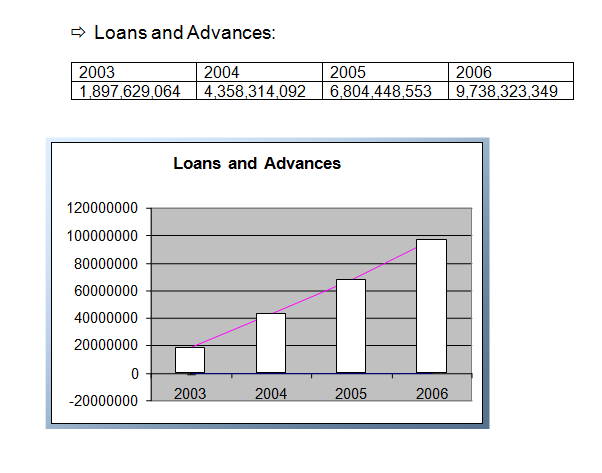
ð Net Profit or Loss after Tax:
| 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
| -140,162,397 | 68,144,268 | 216,384,186 | 121,286,368 |
ð PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT :
For the year ended 31 December 2004
| 2004 Taka | 2003 Taka | |||
| Interest Income Less: Interest Paid on Deposits and Borrowings |
|
| ||
| Net Interest Income | 130,094,938 | 79,338,791 | ||
| Income from Investments Commission, Exchange and Brokerage Other Operating Income |
|
| ||
| 297,334,181 | 131,679,722 | |||
| Total Operting Income | 427,429,119 | 211,018,513 | ||
| Salaries and Allowances Staff Gratuity Rent, Taxas, Insurance, Electricity, etc. Legal Expenses Postage, Stamps, Telecommunications, etc, Stationery , Printing , Advertisement etc, Managing Director’s salary and benefits Directors’ Fees Auditors’ Fees Depreciation on fixed assets Depreciation on Leasehold Assets Repairs and maintenance of fixed assets Others Expenses |
|
| ||
| Total Operating Expenses | 163,155,123 | 122,586,728 | ||
| Total before Provisions | 264,273,996 | 88,431,785 | ||
| Specific Provision for Classified Loans and Advances General Provision on Unclassified Loans and Advances |
|
| ||
| Total Provisions | 47,889,810 | 20,287,517 | ||
| Total Profit before Income Tax for the year | 216,384,186 | 68,144,268 | ||
| Provision for Income Tax | _ | _ | ||
| Net Profit after Tax for the year | 216,384,186 | 68,144,268 | ||
| (Loss) brought forward from previous year | (70,303,050) | (124,818,464) | ||
| 146,081,136 | (56,674,196) | |||
| Appropriations | ||||
| Statutory Reserve @ 20% on profit before Tax Accumulated Profit /(Loss) transferred to Balance Sheet |
|
| ||
| 146,081,136 | (56, 674, 196) | |||
| Earning per share (EPS) (value per share : Tk;100;2003:Tk.1000) | 44.16 | 194.70 | ||
ð Capital Structure:
| Authorized Capital | 2005 |
| 20,000,000 Ordinary shares of Tk. 100 each | 2,000,000,000 |
| Issued, Subscribed and paid up Capital | |
| 5,000,000 Ordinary shares of Tk. 100 each | 500,000,000 |
Profitability Ratios:
- Return On Equity(ROE)
(Net Income/ total equity Capital) X 100
ROE 2005 = [121,286,368 / 991,972,309] x 100 = 12.23%
ROE 2004 = [216,384,186 / 870,685,941] x 100 = 24.85%
The Return on Equity of The Trust Bank has decreased as because its capital is increase over this period 2004 to 2005. It will increase the bank’s access to new capital. The main reason of this increase is their net income.
- Return on Assets (ROA)
(Net Income/Total Assets) X100
ROA 2005 = [121,286,368 /14,807,905,231] x 100 = 0.82%
ROA 2004 = [216,384,186 / 12,059,710,225] x 100 = 1.79%
We can see a decrease in the Return on Asset of The Trust Bank over the period 2004 to 2005. It measures that the management should utilize the real and financial resources of the bank to generate return.
- DU Pont Analysis:
A DU point analysis can be done by breaking down the ROE & ROA into different parts.
Return on Equity
= Return on Asset X Equity Multiplier
= Profit Margin X Asset Utilization X Equity Multiplier
= (Net Income /Operating Revenue) X (Operating Revenue/ Total Assets)X
(Total Assets/ Total Equity)
In the year 2005= (121,286,368/511,456,510) X (511,456,510/ 14,807,905,231) X (14,807,905,231/991,972,309)
= 12.23%
In the year 2004= (216,384,186/427,429,119) X 427,429,119/ 12,059,710,225)X
(12,059,710,225/ 870,685,941) = 24.85%
From this DU point analysis, we can say that the ROE of The Trust Bank has decrease over the period 2004 to 2005. The major reason for this increment is their decrease Profit margin, which indicates that the management’s should more emphasis to invest their money properly and they should control over expenses especially. Although their asset utilization rate is very low, it is somewhat stable. Their lower asset utilization rate represents their disability to
employ assets effectively to generate revenue. Equity multiplier of The Trust Bank has decreased means that the bank became more levered during the period. Most of their assets are financed through debt.
- Other Profit Measures:
Net Increase Margin (%) = (Total Interest Income- Total Expanse)/
Average Earning Assets
Net Interest Margin 2005={[1,100,213,582 –933,141,426] /14,807,905,231}X 100
= 1.13%
Net Interest Margin 2004 = {[749,027,299– 618,932,361] /12,059,710,225}X100
= 1.08%
Here, the Net Interest Margin shows a increment over the period. So, total interest income increased largely in comparison with total interest expense.
- Risk Ratios:
Provision for Loss ratio (%) =
(Provision for loan losses/total Loans & Leases) X 100
Provision for Loan Loses 2005 = [69,975,190 / 9,738,323,349] X100 = 0.72%
Provision for Loan Loses 2004 = [47,889,810 / 6,804,448,553] X100 = 1.03%
So, The Trust Bank has decreased their provision for loan loses over the period 2004 to 2005, means that their loan/ credit (asset) quantity become lower over the period, and thereby their risk has increased over time.
- Loan Ratio
= Net loans/ total Assets
= Net Losses/ total Assets
= [(Loans & Advances- Provision for Loans & Advances)/ Total Assets] X 100
Loan Ratio 2005 = {[9,738,323,349 – 69,975,190] / 14,807,905,231} X 100
= 65.30%
Loan Ratio 2004 = {[6,804,448,553 – 47,889,810] / 12,059,710,225} X 100
= 56.02%
These loan ratios indicate the extent to which assets are devoted to loans as opposed to other assets. The loan ratio of The Trust Bank has increased over years, means most of their assets are in the form of loan and the ratio is increasing continuously. Of course, The Trust Bank has become more risky over the period.
After analyzing all these financial ratios, I can conclude here by saying that the performance of The Trust Bank LTD. has become somewhat satisfactory over the period of 2004 to 2005. Their liquidity position is good. They should provide more loans. Their asset mix is not satisfactory enough. They should improve their performance. They should provide more loans & advances to less risky sector in-order to improve their net income and build strong equity based.
Foreign Remittance Department:
For reimbursement in foreign exchange businesses different banks that are intermediary between importers and exporters maintain internationally three types of account. These accounts are:
(a) NOSTRO A/C:
Our accounts with them. This means TBL maintains its accounts in different banks outside Bangladesh for reimbursement in foreign exchange businesses.
(b)VOSTRO A/C:
Their accounts with us. This means different banks outside Bangladesh maintain their accounts in TBL for reimbursement in foreign exchange businesses.
(c) LORO A/C:
Your accounts with me. When two banks from one country maintain their A/C’s in one bank outside their country.
Ex. Suppose TBL and IFIC have A/C’s in American Express Bank (AMEX) in New York. Then, TBL’s A/C maintaining in AMEX is LORO to IFIC Bank. IFIC’s A/C maintaining in AMEX is LORO to TBL
PERFORMANCE OF THE BANK: AS A WHOLE:
The comparative performance of the bank among different years appears as follows:
TREND ANALYSIS:
ANALYSIS FROM THE BALANCE SHEET:
For the purpose of analysis the financial data of 2003, 2004 and 2005 have been taken based on the availability of the data. The key points of the financial statements take the following figure:
Particulars | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 |
| Authorized Capital | 2000000000 | 2000000000 | 1000000000 |
| Paid-up Capital | 500000000 | 500000000 | 350000000 |
| Statutory Reserve | 113138916 | 67881642 | 24604805 |
| Shareholders’ Equity | 991972309 | 870685941 | 454301755 |
| Fixed Assets | 110616082 | 86179587 | 61369226 |
| Total Assets | 14807905231 | 12059710225 | 7858833009 |
| Total Deposits | 12704902083 | 9314952180 | 4483256901 |
| Long-term Debt | 660000000 | 1430000000 | 2340000000 |
| Loans and Advances | 9738323349 | 6804448553 | 4358314092 |
| Investment | 2447953778 | 3220777070 | 1896920200 |
- AUTHORIZED CAPITAL:
- The authorized capital of the bank was Tk 100.00 crore in 2003 which was increased in subsequent year 2004 by twofold. In 2005 and also in 2006 the authorized capital stands for the same worth of Tk. 200.00 crore. It is due to the bank’s future expansion philosophy and to keep rein with the market competitiveness.
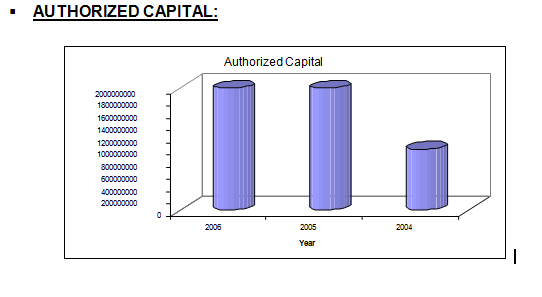
- PAID-UP CAPITAL:
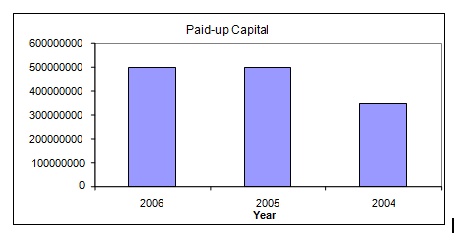
- The equity of the Shareholders in 2003 was Tk. 454,301,755. In 2004 it has increased by 91.65% as the total of Tk. 870,685,941. In 2005, it was amounted Tk. 991,972,309, being the increase of 118.38% on that of 2003. It is due to the expansion of the bank and the financial more strength of the army Welfare Trust.
- STATUTORY RESERVE:
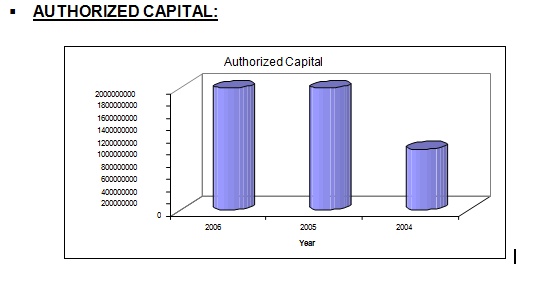
- In 2003, the Statutory Reserve of the bank was Tk. 24,604,405 which stands at Tk. 67,881,642. It was an increase by a gross amount of Tk 43,276,837 or by 175.88% on that of 2003. In 2003, the statutory reserve stands at Tk 113,138,916, an increase by 359.83%. It is due to the rise of the bank’s overall capital and the regulation under the Banking Act 1991 to keep a certain percentage of share capital or profit as statutory re serve.
- Fixed assets include Furniture and Fixture, Office equipment, Motor vehicles, office renovation and leasehold land. The depreciation on the fixed assets is charged on straight line basis at the following rates:
Furniture and Fixture 10% p.a
Office equipment 20% p.a
Motor vehicles 20% p.a
Other decoration 12% p.a
Fixed assets after deducting accumulated depreciation were in 2003 Tk. 61,369,226, in 2004 Tk. 83,971,729 and in 2005 Tk. 110,616,082. It is because of the expansion of branches during that period.
- Total assets of the bank consists of –
- Cash in hand and with Bangladesh Bank and Sonali Bank.
- Balance with other banks and financial institution.
- Money at call and short notice.
- Loan and Advances.
- Fixed assets (Furniture and Fixture, Office equipment, Motor vehicles, Office Renovation and Leasehold Land)
- Other Assets
Total Assets of the bank was Tk. 7,858,833,009 in 2003 and Tk.12, 085,815,830 in 2004- a 53.786% increment. The value of total assets stood at Tk. 14,807,905,231 in 2003-a 88.42% increase. It shows the advancement of the bank responding the market.
The Total Deposit of the bank was-
2006
2005
2004
Tk. 12,704,902,083
Tk. 9,042,183,740
Tk. 4,483,256,901
The pictorial graph and the subsequent numerical figure show that the deposit collection was more than double than that of 2003. In 2005, total deposit was increased by 40.5% than the deposit of accumulated in 2004. So it is vivid from the viewpoint of deposit collection the performance of the bank in 2004 was far better than 2005.
- LONG-TERM DEBT:
Here, the long term debt represents the borrowing from other banks, financial institutions and agents. The illustration depicts that the long term debt of the bank significantly decreased in 2005. The year wise actual long term debt was as follows:
2006
2005
2004
Tk. 660,000,000
Tk. 1,430,000,000
Tk. 2,340,000,000
- LOANS AND ADVANCES:
Loans and advances of the bank constitute different purpose loans (repair and maintenance of dwelling house, customer durable loan scheme, car loan, term loan, loans against Trust Receipt etc), cash credit (cash credit, cash collateral) and overdraft (normal overdraft, secured overdraft).The total loans, cash credits and overdrafts for the three years was as follows-
2006
2005
2004
Tk. 9,383,459,513
Tk. 6,690,408,551
Tk. 4,327,826,794
The graphical and numerical presentation depicts that loans and advances increased by 54.6% in 2004 and 116.82% in 2005 (taking 2003 as the base year). The growth level of loan and advances is about the same rate both in 2004 and 2005.
- INVESTMENT:
Investment includes investment in government securities and investment in shares. The numerical figure of investment appears as follows:
2006
2005
2004
Tk. 2,447,953,778
Tk. 3,220,777,070
Tk. 1,896,920,200
Overall investment increased by 69.79% in 2004 being a total of Tk 3,220,777,070. But in 2005 the value of investment decreased by Tk 772,823,292 or 24% in comparison with that of 2004.
ANALYSIS OF THE PROFIT AND LOSS ACCOUNT:
The profitability of any business concern can be understood by analyzing the Profit And Loss Account of that concern. Profit And Loss Account shows the revenue generated, corresponding expenditure and the resulting profit or loss. Analysis of the Profit And Loss Account of the Trust Bank Ltd. exhibits the following summarized information:
Particulars 2006
2005
2004
Gross Income 1444597936
1046361480
535499256
Gross Expenditure 1218311568
829977294
467354988
Profit before Tax 226286368
216384186
68144268
Profit after Tax 121286368
216384186
68144268
Tax paid 105000000
—-
—-
- OPERATING INCOME:
In this competitive market this bank earned Tk. 1,444,597,936 in 2005 which is 38.06% greater than the gross income of 2004. It clearly indicates that this is a growing organization and will continue its success in the coming years.
- OPERATING EXPENDITURE
Here the ratio of expenditure in 2005 has decreased than that of previous year. But the percentage of expenditure has increased @ 46.79% in 2005 which is more than the percentage increase in the Gross revenue.
- PROFIT BEFORE TAX:
The Actual Profit before Tax of the bank was as under:
2006
2005
2004
Tk. 296,261,558
Tk. 216,384,186
Tk. 68,114,268
From the information mentioned above a comment can be made that Year-2004 was its “Golden Age”. But in 2005 it also increased its “profit before tax” and gained a honorable position in the banking sector.
The Actual Profit after Tax of the bank was as under–
2006
2005
2004
Tk. 121,286,368
Tk. 216,384,186
Tk. 68,114,268
And the amount for the provision of tax was –
2006
2005
2004
Tk. 105,000,000
Tk. —————-
Tk. —————–
From the above mentioned statement, it is vivid that the net profit touches the peak in 2004 by accomplishing a stunning rise of 217.68%. But the journey of increasing profit can=me backward in 2005. The After Tax Net Profit went down by 43.95% in 2005 comparing the profit of 2004 the Provision for Tax played a significant role in this respect.
- TREND OF OTHER FINANCIAL STATEMENT ISSUES:
Sl No
Particulars
2006
2005
01
Total contingent liabilities & Commitments 4681077063
3123318980
02
Amount of classified loans during current year 121286368
216384186
03
Provisions kept against classified loans 58000000
41293255
04
Provision surplus/Deficit 2315796
–
05
Interest earning assets 13,401,393,133
11,380,077,637
06
Non-interest earning assets 1,406,512,098
679,632,588
07
Incomes from investment 194,479,592
177,745,964
08
Earning per share 24.26
44.16
09
Net income per share 24.26
44.16
RATIO ANALYSIS:
SL no
Particulars
2006
2005
01
Capital Adequacy Ratio 12.49%
15.20%
02
Credit Deposit Ratio 76.65%
75.25%
03
Percentage of classified loans against total loans and advances 1.32%
1.47%
04
Cost of fund(Deposit cost & Administrative cost) 9.23%
9.30%
05
Return on Investment(ROI) 10.88%
23.01%
06
Return on Assets(ROA) 0.82%
1.79%
07
Price Earning Ratio N/A
N/A
Comment: Although the cost of fund went down in 2005 by 0.07%, the profitability of the bank was declining. Return on Investment went down significantly by 12.13% and the Return on Assets also went down by more than half i.e. 0.97%. Moreover,
there was a shortage of capital adequacy in 2005 as the ratio fell down from 15.20% to 12.49%, although the Credit in response to Deposit increased by a little bit, by
1.40%. So it can be said that investment was not efficiently made. Concentration should also be given to the Capital, Deposit and Credit Management.
PERFORMANCE OF THE BANK: DHANMONDI BRANCH:
Trust Bank Limited started its journey at Dhanmondi, Dhaka in 2003 recognizing its location at Bangladesh Rifles (BDR) Gate no 04, Peelkhana, Satmosjid Road, Dhanmondi, Dhaka. Currently the Dhanmondi branch conducts its operation under the management of Mr.Md.Mozakkerul Islam, the AVP and Manager of the branch with a staff of 31 (including 4 office help). The ratio between women and men personnel is above 2:1 i.e. among 27 employees 19 are women and the rest are men. The women empowerment in that way is obviously praiseworthy.
PROFITABILITY ANALYSIS:
To evaluate the performance of the branch, analyzing its profitability is a stepping stone. Profitability analysis consists of the analysis of Income, Expenditure and the
resulting profit or loss. A summary of the provisional income, expenditure and profit/loss of the bank for the last five months (January, 2006 to May, 2006) appears as follows:
Statement of Provisional Profitability (Adjusted)
Particulars
31st January
Up to 28th February
Up to 31st
March
Up to 30th April
Up to 31st May
Provisional Income 10597103.59
20774974.75
33323897.69
45336624.17
58801147.00
Provisional Expenditure 8558480.55
16882793.48
25541389.18
34626096.65
44730172.36
Provisional Profit/Loss
2038623.04
3892181.27
7782508.51
10710527.52
14070975.23
Statement of Profitability of the year 2006
Particulars 2006 Income 1607,71,042,16 Expenditure 1192,42,832,66 Profit/Loss 415,28,209,5 Comparison of Income Statement :
Here a comparison is shown of the Income between the year 2004, 2005,and 2006:
Comparison of Statement of Income
Particulars 2004 2005 2006 Income 1046361480 1444597936 16077104216 Changes 100% 96.04% 118.42% From the above table and graph, it is found that in the year 2006, the overall income of the branch is satisfactory in comparison to the year 2004 and 2005.It implies in the year 2006, the bank was done good business.
CONTENTS OF INCOME
Heads of Accounts Year 2006 Interest Received 1,409,98,548 Interest on Branch Account 85,79,453 Commission, Exchange & Brokerage 92,58,404 Other Income 19,34,635 Source: Income Statement of Trust Bank Limited for the year 2006
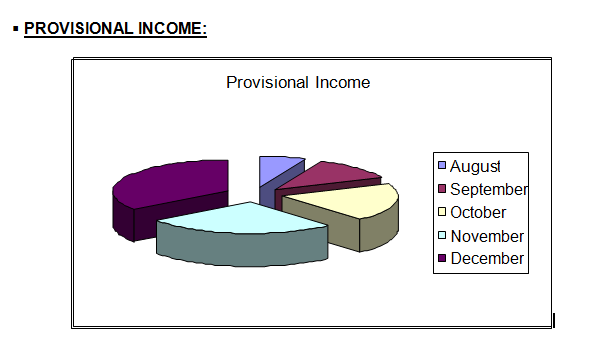
-
- § The absolute income of the branch for that period was as follows:
Statement of Income (Individual Month Wise)
Particulars
January
February
March
April
May
Provisional Income 10597103.59
10177871.16
12548922.94
12012726.48
13464523.42
Changes 100.00%
96.04%
118.42%
113.36%
127.06%
From the above table and graph, it is found that except in February, the overall income of the branch is satisfactory in spite some downfall in April. In February, the
income went down by 3.96%. Proper concentration should be given to the consistency of income.
Statement of Provisional Income
Heads Of Accounts
31st January
28th February
31st March
30th April
31st May
Interest Received 10185277
19636282
31503687
4,25,26,689
54832265
Interest On Branch Account 624986
1187357
1920207
24,65,838
3009681
Interest On Loans & Advances 95499589
18428672
29550757
4,00,12,893
51755940
Commission, Exchange & Brokerage 347410
821744
1352016
21,80,018
3133628
Exchange Gain 2295
4707
12474
21,495
28825
Expenditure Paid On Deposits 7469588
14648079
22161041
3,00,49,990
38970982
Salary & Allowances And Others 516376
1081226
1645756
22,66,724
2857367
- § PROVISIONAL EXPENDITURE:
Statement of Expenditure (Individual Month Wise)
Particulars January
February
March
April
May
Provisional Expenditure 8558480.55
8324312.93
8658595.70
9084707.47
10104075.71
Changes 100.00%
97.26%
101.17%
106.14%
118.06%
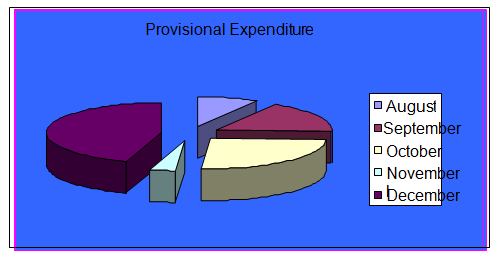
-
Comparison of Expenditure Statement:
Here a comparison is shown of the Expenditure between the year 2004, 2005 and 2006:
Comparison of Statement of Expenditure
Particulars 2004 2005 2006 Expenditure 1218311568 829977294 1192,42,832,66 Changes 100.00% 97.26% 101.17 From the Table above, it is found that operating expenditure increased highly in May. The rise in expenditure is somewhat inconsistent with the previous months. Care should be imparted on the minimization of the operating expenditure.
Contents on Expenditure
Heads of Accounts Year 2006 Interest Paid on Deposit 1,040,76,702 Salary and Allowances 79,89,902 Rent, Taxes, Insurance, etc 27,45,756 Legal Expense 19,250 Postage, Stamp, Telex, etc 5,15,155 Depreciation and Amortization 21,15,313 Repair and Maintenance 1,23,385 Stationeries, Printing, Advertising, etc 4,21,187 Other Expenses 12,36,179 § PROVISIONAL PROFIT/LOSS:
Profit is rise of 381.75% of the year 2006 in comparison of the year 2004-05. The overall profit or loss of the branch is good in the year 2006, which shows that the bank is done good business in this year.
Comment: From the above Table some conclusions can be drawn about the budgetary achievement of Dhanmondi Branch.
- Growth of export and import of the branch has been improved but deposits, advances and profit has been declined.
- In response to budget deposits, advances, export and import target have not been achieved.
- On the whole, the performance of the branch is satisfactory.
CHAPTER FOUR:
OVERALL FINDINGS:
Findings:
- Trust Bank Ltd. is the pioneer of private sector banking business.
- The customer service is very much impressive than of other financial Institutions. Although, I have no idea about other branches of TBL, But in particular, TBL Dhanmondi branch is a good example of better Customer service.
- The decision undertaken by the management is sometimes self centered i.e. the market competitiveness is often ignored to give priority on their own capability and resources.
- The marketing strategy adopted by the bank is effective but not efficient. General people take time to index Trust Bank; Most of the time they disregard it with the Mutual Trust Bank.
- The management have hardly overcome the notion-“A bank of armed forces at cantonment” i.e. the banking concept is yet to be universalized.
- Top management guides to its subordinates when needed but the specialization of the personnel on a particular task is not ensured. It has been found that executives are transferred from one branch to another without ensuring other executives being acquainted with the task.
- Computerization is speeding up the performance of the organization but the software used by the TBBL-“FLORA” is not updated & so fast. It is easy to handle but contains some flaws.
- The profit earned by the bank in the previous periods is satisfactory but the deposit mobilization and accumulation is not as targeted.
- The expansion process of the bank has little match with the modern pace of globalization. Despite being stoned in 1999, the bank has only 27 hands now.
- The products offered by the TBBL are very limited in range comparing to the contemporary banks. The clients can hardly find the best alternative of particular products.
- Special schemes like consumer credit scheme, monthly saving scheme,
Western Union Money Transfer etc. are very popular.
- The overall performance is good.
CHAPTER FIVE:
Problems and Recommendations:
Problems:
- Not enough of computers.
- Less interest payment by Trust Bank Limited than others in some accounts.
- Still the bank is not fully computerized. So, manual registers are used in some cases.
- There is no color printer in this branch.
- On line banking is not introduced in Trust Bank Limited.
Recommendations:
- Giving better customer service, Full computerization of all activities, Supply of new PC’s in place of old one, sufficient numbers of PC needed for proper working.
- Interior decoration should be introduced for clients comfort.
- The management should impart more imphasis on the advertisement of the bank in different electronic and printing media. The Basic goal of the advertisement should be firstly to make people know and understand that the bank is universal one and permits any one’s access.
- Full computerization of the branch will less the time consumption of manual process. So, that the employees will able to perform well at the end.
- The spread out mechanism of the bank should be faster and progressive as well. Being established in 1999, the bank has established only twenty seven branches in eight(8) years. The mode of extension is much slower than other contemporary and equivalent banks.
- On line banking should be introduced to compete with multinational banks.
- The management should care for the personnel more. At the recruitment stage, it should go for the best candidate and after selection the personnel should be allowed with proper opprtunity to be expert on particular task bestowed on them.
- More products of varied interests should be introduced for the diversified client group.
- To enhance the image of the bank and to assume social responsibility, the bank should engage itself to various social programs like Scholarship to poor but meritorious students, Empowerment of the children in abject poverty, Compaign against dowry and other social evil etc.
CHAPTER SIX:
Conclusion:
Trust Bank limited pursues decentralized management polices and gives adequate work freedom to the employees. This results in less pressure for the workers and acts as a motivational tool for them, which gives them, increased encouragement and inspiration to move up the ladder of success. The profit earned by the bank is used to the welfare activities of the Trust. The economic service of the bank is open to all caste and class of people. The bank is formatting and accomplishing various welfare projects and activities for the socio economic infrastructural development of the country and the active participation to the up gradation of the comparative feeble class of the society, in stead of accumulating profit. It has also been linked with many foreign banks to facilitate the foreign currency transfer by the members of armed forces working in the UN and emigrant Bangladeshi. The report is aimed at studying and understanding the various services offered by TBL to its clients. In addition, the report also studies how Trust Bank Limited has maintained growth in its general banking business by maintaining and enhancing its relationship with its clients. The success of Trust Bank limited is largely credited to its friendly, co-operative approach, understanding the special banking needs of each and every client and concern for the benefits and welfare. From the beginning, the prime objective of Trust Bank limited was to increase capitalization, to maintain disciplined growth and high corporate ethics standard and enhance the health of the share holders. Its customer service is very much impressive than of other financial institutions. Their effective strategy, time demand offerings, up to date rules and regulations to cope with international market and their friendship customer services easily impress the clients. So, now Trust Bank limited is in leading position in Financial Institutional sectors in Bangladesh. The financial performance of the bank in recent years is pretty well. Moreover, any laxity in operational ground can considerably be compensated through the cordial services provided by a staff of talented officers or employees.
APPENDIX:
Bibliography:
- Ø Annual Report for the year (2001,2002,2003,2004,2005,2006) of Trust Bank Limited
- Ø Term papers of TBL Training manuals
- Ø Transaction in foreign Exchange
- Ø Principles & Practice (By M.R. Sinha.)
- Ø Guidelines for Foreign Exchange Transactions.
- Ø General Banking Operation manual
- Ø ICC Customs & Practice for Documentary Credits
- Ø Trade secretes – Dhaka Chamber of Commerce & Industry
- Ø Comparative Banking – Lecture sheet
- Ø Foster, 2006, Financial Statement Analysis, 2nd Edition, Prentic Hall
- Ø Cateora & Graham, 2006, International Marketing, 12th Edition, McGraw Hill
- Ø Philip Kotler,2004-05, Principles of Marketing, International Edition, Prentice Hall,
- Ø Auditor’s Report for the year ended December31,2006
- Ø Daily Affairs Statement for the year of 2006
- Ø Income, Expenditure & Profit/Loss statement of the year 2006
www.trustbankbd.com