Grameenphone’s loyalty programs in telecommunication sector
based on customer insight & behavior
An internship is a temporary position with an emphasis on on-the-job training rather than merely employment, and it can be paid or unpaid. The report is a combination of three months internship program with Grameenphone.
The objective of this study is to acquire the knowledge about the loyalty program of Grameenphone and to do analysis based on customer insight and behavior. Grameenphone is a fast growing joint venture company in the telecommunication industry of Bangladesh. Considering the importance of customer satisfaction and longtime customer sustainability, this report was designed to assess the satisfaction level of Grameenphone‘s subscribers and to do the analysis of customer loyalty on grameenphone.
The first section, of this report includes a brief overview of Grameenphone‘s vision, mission values. It also provides the historical background of Grameenphone, and discusses about the products and services that Gameenphone offers. Moreover, a brief overview of telecommunication industry is given as well, where the ownership structure of Grameenphone is given. The second part of this report describes the divisions of grameenphone with main objectives and main tasks. The third part, of this report describes the job duties and responsibilities performed during my three month internship program at Grameenphone. Forth part is all about the industry analysis with the relative market share of the competitor company of grameenphone. In the fifth part of this report, there is a project part that includes the objective and methodology of project, along with the scopes and limitation. The facilities of Grameenphone STAR program are discussed very well and it is analyzed with the help of the results found through survey and interview. At the end, few findings on STAR program are given depending on the customer profession, motivation, desired offers and perception. Few recommendations are provided at the last part of this report for the improvement of STAR program, future expectation of this program segmentation based on customer demand along with varieties of suggestions.
Background of Grameenphone
Grameenphone Ltdis the market leader of the telecommunication industry in Bangladesh withmore than 50 million subscribers as of October 2014. It is a joint venture enterprise between Telenor and Grameen Telecom Corporation. Grameenphone got its operating license in November, 1996 and launched its service on March 1997. Its head quarter is situated in Bashundhara Residential Area.
The journey of Grameenphone started with the Village Phone program: a pioneering initiative to empower rural women of Bangladesh. The name ‗Grameenphone‘ translates to ―Rural phone‖. Starting its operations on March 26, 1997, the Independence Day of Bangladesh, Grameenphone has come a long way.
Grameenphone pioneered the then breakthrough initiative of mobile to mobile telephony and became the first and only operator to cover 98% of the country‘s people with network. Since its inception Grameenphone has built the largest cellular network in the country. Presently, nearly 99 percent of the country’s population is within the coverage area of the Grameenphone network.
Grameenphone has always been a pioneer in introducing new products and services in the local market. GP was the first company to introduce GSM technology in Bangladesh when it launched its services in March 1997.
It has now more than 1600 GP Service Desks across the country covering nearly all upazilas of all districts and 94 Grameenphone Centers in all the divisional cities.
History of Grameenphone
The plan of Bangladesh government to auction private cell phone licenses to private companies laid the foundation for Grameenphone‘s birth. So in October 10 1996, at the request of Dr. Muhammad Yunus (Grameen Bank‘s founder), a not-for-profit private company called Grameen Telecom was formed as private limited company. Grameen Telecom, in turn, created a for-profit company called Grameen Phone, found a foreign partner, put in a bid and received one of the four licenses. Hence GRAMEENPHONE Ltd. was born.Grameenphone was awarded the license to operate in Bangladesh in November 11, 1996 by the Ministry of Post and Telecommunications. Then, on the Independence Day of Bangladesh, Grameenphone launched its service with an effective and user-friendly mobile phone network. They started their operation from March 26, 1997 with only 72 employees.
They converted to public limited company on June 25; 1997.Grameenphone put a positive impact on the lifestyle of the people of Bangladesh.
Ownership of Grameenphone
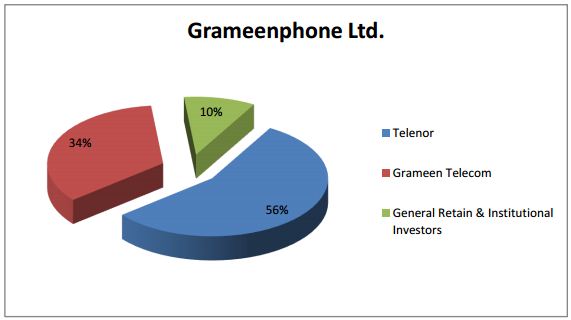
It is a joint venture enterprise between Telenor (55.8%), the largest telecommunications service provider in Norway with mobile phone operations in 13 other countries, and Grameen Telecom Corporation (34.2% ), a non-profit sister concern of the internationally acclaimed micro-credit pioneer Grameen Bank. The other 10% shares belong to general retail and institutional investors.
The technological know-how and managerial expertise of Telenor has been instrumental in setting up such an international standard mobile phone operation in Bangladesh. Being one of the pioneers in developing the GSM service in Europe, Telenor has also helped to transfer this knowledge to the local employees over the years.
Telenor Mobile Communication AS (TMC)
Telenor has more than 150 million mobile subscribers worldwide. It is ranked as the world‘s seventh largest mobile operator and has strong subscription growth, particularly in our Asian operations. It is listed on the Oslo Stock exchange with headquarters in Norway. It has placed itself as No. 1 on Dow Jones Sustainability Index 2008.
Telenor is emerging as one of the fastest growing providers of mobile communications services worldwide with ownership interests in 13 mobile operators across Europe and Asia.
Telenor is organized into three business areas; Mobile operations covering 13 countries, and Fixed-line and Broadcast services covering the Nordic region.
Grameen Telecom Corporation
Grameen Telecom Corporation, which owns 34.2% of the shares of GrameenPhone, is a notfor-profit company and works in close collaboration with Grameen Bank. The internationally reputed bank for the poor has the most extensive rural banking network and expertise in microfinance. It understands the economic needs of the rural population, in particular the women from the poorest households.
Grameen Telecom, with the help of Grameen Bank, administers the Village Phone Program, through which GrameenPhone provides its services to the fast growing rural customers. Grameen Telecom trains the operators, supplies them with handsets and handles all service related issues.
Grameen Telecom’s objectives are to provide easy access to GSM cellular services in rural Bangladesh, creating new opportunities for income generation through self- employment by providing villagers with access to modern information and communication based technologies.
Industry Analysis Part
Company competitive scenario
There are six mobile telephone operators in Bangladesh at the moment. Among them one is Government owned telephone operator: Bangladesh Telegraph and Telephone Board (BTTB) and the other five are privately owned companies namely ARE:
- Grameenphone Ltd.
- Axiata (Bangladesh) Limited
- Orascom Telecom Bangladesh Ltd.
- Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Ltd. (PBTL) and
- Airtel Bangladesh Ltd.
- Teletalk Bangladesh Limited
Grameenphone Limited
Grameenphone Limited, the number one and leading mobile phone company in the area of telecommunications in Bangladesh. Grameenphone Limited managed to grab 42.5% of the market share only by providing cost-effective & best service available in the market of mobile telecommunication. Grameenphone Limited has made its expansion not only in the urban areas, but also it stretched its network in the rural areas for the economic empowerment of the rural people. It has the largest network, the widest coverage, the biggest subscriber base and more value added services than any other mobile phone operators in Bangladesh.
Grameenphone Limited has a very strong competitive position in the telephone industry in the country.
Orascom Telecom Bangladesh Limited
With a market share of 25.5%, Banglalink is in the 2nd position in the cell phone industry. When Banglalink entered the Bangladesh telecom industry in February 2005, the scenario changed overnight with mobile telephony becoming an extremely useful and affordable communication tool for people across all segments. Banglalink was previously known as
Sheba Telecom which began operation in 1998. It was a joint venture between a Malaysian Conglomerate, Technology Resources Industries Berhad and a local firm named Integrated Services Ltd. (ISL). In 2005 Orascom Telecom Holding (OTH) acquired Sheba Telecom and gave a new trading name, ‗Banglalink‟. Within one year of operation, Banglalink became the fastest growing mobile operator of the country. This milestone was achieved with innovative and attractive products and services targeting the different market segments; aggressive improvement of network quality and dedicated customer care; and effective communication that emotionally connected customers with Banglalink.
Axiata (Bangladesh) Limited
Robi is the third largest mobile phone operator in Bangladesh in terms of revenue and subscribers (20.5 million as of October 2014). It has a market share of 21%. Axiata (Bangladesh) Limited is a dynamic and leading countrywide GSM communication solution provider. It is a joint venture company between Axiata Group Berhad, Malaysia and NTT DOCOMO INC, Japan. Axiata (Bangladesh) Limited, formerly known as Telekom Malaysia International (Bangladesh), commenced its operation in 1997 under the brand name Aktel among the pioneer GSM mobile telecommunications service providers in Bangladesh. In early 2008, Aktel slipped from the second position to the third after facing fierce competition from Banglalink. Aktel boasts of the widest international roaming service in the market, connecting 315 operators across 170 countries. It is the first operator in the country to introduce GPRS. Aktel uses GSM 900/1800 MHz standard and operates on allocated 12.8MHz frequency spectrum. Later, on 28th March, 2010 the company started its new journey with the brand name Robi.
Airtel Bangladesh Limited
AIRTEL Bangladesh Ltd. is a GSM-based cellular operator in Bangladesh. Airtel Bangladesh is the sixth mobile phone carrier to enter the Bangladesh market, and launched commercial operations on May 10, 2007. Market share of Airtel is 7.1%. Warid Telecom International LLC, an Abu Dhabi based consortium, sold a majority 70% stake in the company to India’s BhartiAirtel Limited for US$300 million. BhartiAirtel Limited will take management control brand from 20 December 2010. The Bangladesh Telecommunication Regulatory Commission approved the deal on Jan 4, 2010. Airtel Bangladesh had 8.75 million subscribers as of October 2014.
Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Limited
Citycell (Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Limited) is the first mobile communications company of Bangladesh. It is the only CDMA network operator in the country. As of 1 March, 2008, Citycell’s total mobile subscriber base is 1.56 million, up 137 per cent or 680,000 from two years ago, giving it the best growth rate of the company till date. Citycell is currently owned by Singtel with 45% stake and the rest 55% owned by Pacific Group and Far East Telecom.
By the end of 2007 Citycell had refurbished its old brand identity and introduced a new logo and corporate identity; the new logo is very reminiscent of the old logo. However the slogan has remained unchanged “Because we care”. Citycell had 1.37 million subscribers as of October 2014.
Teletalk Bangladesh Limited
TeleTalk (Teletalk Bangladesh Ltd) is a GSM based state-owned mobile phone company in Bangladesh. TeleTalk started operating on 29 December, 2004. It is a Public Limited Company of Bangladesh Government, the state-owned telephone operator. TeleTalk provide GPRS internet connectivity. Teletalk is the first operator in the country that gave BTTB (now BTCL) incoming facility to its subscribers. The mission statement of Tele Talk is “Desher Taka DesheyRakhun” (“Keep your Money in your Country”). TeleTalk is the 6th largest mobile phone operator in Bangladesh with 1.141 million subscribers as of October, 2014.
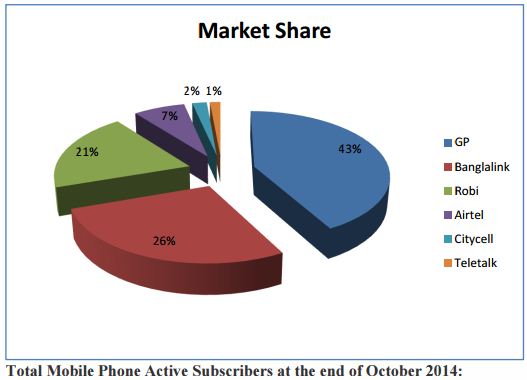
- Grameenphone Ltd. (GP): 5 core 2 lac 33 thousands
- Orascom Telecom Bangladesh Limited (Banglalink): 3 core
- RobiAxiata Limited (Robi): 2 core 46 lac 64 thousands
- Airtel Bangladesh Limited (Airtel): 81 lac 43 thousands
- Pacific Bangladesh Telecom Limited (Citycell): 13 lac 7 thousands
- Teletalk Bangladesh Ltd. (Teletalk): 12 lac 85 thousands
SWOT Analysis
STRENGTHS
- Good ownership structure- Grameenphone has the best ownership structure in the telecommunication industry in Bangladesh. Telenor is one of the largest companies, which is operating in different countries around the world. Again, in Bangladesh, Grameen Bank is one of the largest NGO, which has the sound communication all over the country.
- First Mover Advantage- Grameenphone is the first organization in Bangladesh, which has reached to the general people.
- High Brand Awareness- The branding activities have led Grameenphone to build a strong well- recognized brand. So the people are more familiar with Grameenphone than other companies.
- Wide Network coverage – Grameenphone has the widest network coverage and a large number of BTS station (Tower) all over Bangladesh. That‘s why the company can provide better connectivity in most of the area of the country. It has the best indoor coverage, 99% people coverage and 90% geographic coverage.
- Financial Soundness – Because of effective strategic planning, Grameenphone is able to earn a healthy amount of revenue, which gives them financial soundness.
- Rich Human Capital – All the stuff, which are related to Grameenphone are skilled and effective in their job responsibility. The reason behind this is the Human Resource Department of Grameenphone follows high standards to recruit new employees.
- Easy Access to the Widest Rural Network – It was easier for Grameenphone to reach the rural area of Bangladesh through the help already renowned Grameen Bank.
- Individualism: Although Grameenphone is closely affiliated with its multinational parent company, it has an independent brand identity in the market.
WEAKNESS:
Some of the weaknesses of Grameenphone are discussed below:
- High Call rates: Grameenphone has high call rates compared to other telecommunication companies in Bangladesh.
- Cultural Gap: Management team of Grameenphone has employees from different countries from different background and culture. This sometimes gives rise to cultural differences and communication barrier.
- Complicated Pricing Structure: Grameenphone has lots of products. The pricing and the billing procedures are different for each of the products and options. This creates confusion for the users and makes them reluctant to use the various product options.
- No Copyright: The GP brands are not protected by copyrights, which has led to the misuse of the branding attributes and bears the risk of such misusage in future as well.
- High Employee Turnover- Grameenphone‘s employee turnover is high which might indicate a low level of loyalty and dissatisfaction with the company.
OPPORTUNITIES
- Economic growth of Bangladesh – The economic growth of Bangladesh will increase the expansion of telecommunication industry more in the future.
- Focus on CSR program- companies and the general people are becoming more and more concerned about the environment, society and the country. More CSR activities by GP will be well appreciated and recognized by the people.
- New international Gateway- BTTB (Bnagladesh Telegraph & Telephone Board) has established new gateway to connect internationally which has made it easy for mobile phone operators to provide services of ISD call and international roaming.
- Huge need for telecom services- As the technology advances and people becomes more tech-savvy; the need for telecom services will continue to rise.
- Declining prices for handsets- the prices of handsets have decreased immensely which has enable the low income people to use mobile phones.
THREATS
- Unstable political Condition – the political condition of Bangladesh is very unstable.
- Increasing regulatory surveillance and government legislation: Constant observation of BTRC (Bangladesh telephone regulatory commission) sometimes corruption of BTRC makes business volatile.
- Threat from new entrant – GP is anticipating a possible threat from the new entrant BTTB. The state owned fixed-line monopoly BTTB has entered the market with extremely low tariffs. When BTTB will start operating at its full potential, it might destabilize the present competitive environment. However, BTTB currently poses very little threat to GP as they have just started their operation.
- Foreign exchange fluctuation- GP being a multinational company has high level of risk to fluctuation in the foreign currency. This poses a negative impact on the revenue and profit margin of the company.
PORTER’S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS FOR GRAMEENPHONE
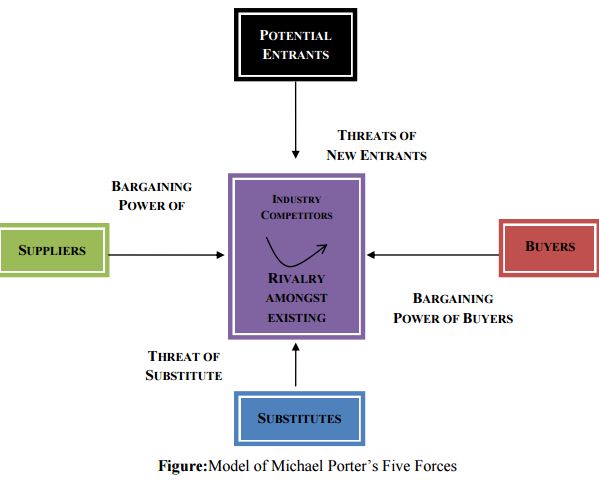
- Bargaining Power of Buyers is high since demand for their services are high and they have to abide by customer needs because customers can easily shift to other companies due to lower switching costs.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers is low due to low switching cost since there are a variety of suppliers in the industry supplying to these companies.
- Threat of New Entrants is high since new companies can easily enter the market as there are very limited barriers of entry.
- Threat of Substitute is high as there are a large number of competitors in the market such as Airtel, Banglalink, Robi and Citycell and customers can easily shift from one another due to the easiest switching costs.
- Rivalry amongst Existing Companies is definitely high as competition level is extremely high as all the companies are fighting.
Loyalty program
The authors state ―Loyalty programs are structured marketing efforts that reward, and therefore encourage, loyal buying behavior — behavior which is potentially beneficial to the firm (B. Sharp and A. Sharp 473-86). In Bangladesh, loyalty programs are revealing in large scale in banking, superstores, airline, consumer goods like jewelry, clothing etc. In Bangladesh, telecom sector witnessed massive development during the last decade, mainly due to the penetration of mobile telephony. With the change of technology, this industry is rapidly changing and near to saturation. Now the customers are more sensitive regarding the value offered by the companies. Reichheld and Sasser (1990) calculated the impact of customer retention on profitability: ―As a customer‘s relationship with the company lengthens, profits rise. And not just a little. Companies can boost profits by almost 100 percent by retaining just 5 per cent more of their customers‖ (p. 105). Fierce competition in the market is playing important role to undertake loyalty programs. Loyalty programs are initiated to satisfy and retain the valued customers as well as attract the new potential customers. The valued customer base gets retained and it generates sustainable profit.
Description of the Project
Origin of the Report
Internship program is the most important period for a BBA student. The duration of internship program is 3 months, which carries a best learning process to know about the organization and cope up the environment in such a way like professional employees. The experience that got by an intern during the internship period will make them more smart and professional in their future job sector. I started my internship at Grameenphone, Head Office, on 14th of September 2014 to 14th of December 2014.
Objectives of the Project
The initial objective of writing this report is to fulfill the partial requirement of the BBA degree. Grameenphone‘s loyalty program in telecommunication sector based on customer insight & behavior.
General Objective
The general objective of this report is to fulfill the requirement of internship report.
Specific objectives
- Know about the customer expectation of Grameenphone
- Know about the STAR program awareness
- Identify the segment of benefits which prefers by subscriber
- Addition new expectation from STAR Subscriber
Methodology
The report is descriptive in nature. To prepare a report gathering data is very important. The information was collected from both primary and secondary sources of data.
Primary data
- Personal observation
- Questionnaire survey
Secondary data
- Study on Annual Reports of Grameenphone
- Online data from Grameenphone website
- Study several article on Telecommunication industry of Bangladesh
Questionnaire Design
Questionnaire was prepared with both open and close ended questions. The target population was the subscribers who are using the service of Grameenphone. Total sample size of the customer was 20.
Scope of the Report
Telecommunication industry is the growing industry in Bangladesh. In this competitive world it is very tough to hold the market share in this industry, if the customer is not loyal by the service. So, it is very important to identify the customer expectation and design the loyalty program based on customer expectation and insight.
Benefit of the report
As a student, I have learned about the corporate companies and gathered vivid knowledge about telecommunication industry of Bangladesh specifically about Grameenphone STAR program. I also have learned the report writing, as a great deal of theory is included in this report.
Perception towards loyalty program
Loyalty programs are initiated to provide benefit to firms‘ valuable customers. The customers perceive value from the loyalty programs designed for them. It can be assumed that loyalty programs are perceived differently by different segment of customers and take part in encouraging loyalty. O‘Brien and Jones (1995, p.79-80) identify five elements which determine the value of loyalty program. These include cash value, choice of redemption options, inspirational value, relevance, and convenience. O‘Brien and Jones (1995) proposed that customers‘value perception is a necessary condition for developing brand loyalty through the loyalty program.
Effectiveness of loyalty program
Nunes and Drèze (2006) suggest that loyalty programs can serve different goals, such as retaining customers, increasing spending, and gaining customer insights. Well managed loyalty program can increase the customer retention rate by increasing the switching cost. Liu and Yang (2009) suggested, ―Companies executing loyalty program need to think beyond the design and management of the program itself, apply set of unique resources to maximize the appeal of a loyalty program to create a competitive advantage (106). So, companies should offer unique set of benefits to its‘ loyal customers so that the competitors cannot imitate and thus strengthen customer retention. Increased spending can lead to improved profitability. As a result, competitors cannot switch the customers to them. Loyalty programs create customer commitment which builds long term relationship with its customers.
Other mobile operators in loyalty program management
Other mobile operators are not practicing loyalty program in true sense. Banglalink introduced priyojon & ICON program where customers from all segments can earn and redeem points to enjoy discounts at shops, hotels and restaurants. Icon brand was introduced in 2010 to reward only premium business customers by providing various exclusive offers.
Robi gives discount offers to its‘ customers at various shopping outlets, restaurants, hotels, home decors, car decors, medical services, fitness clubs, fashion houses , beauty parlor, entertainment places, megashops, technological supports, transport facilities under the umbrella ―Reward Partners‖. Airtel is not even providing any such offers except basic telephony services.
.
Findings
- All groups of customer welcome loyalty program as a special subscriber of the company.
- Majority of the customers think loyalty program can make them stay loyal and emotionally attached with the company.
- Perception towards loyalty programs varies depending on the customer groups.
- Private Job holders expect invitations at events and discount offers are attractive to them.
- Public job holders expect privileges as special customer and like to get priority treatment at GPCs, customer careline.
- Businessmen expect privileges as well and likely to get invited.
- With the increase of tenure, when met all basic requirements from operator, very long term customers (generally GP subscribers) are staying with the company because the privileges are being offered to them as special customer and it is a means of ease of connectivity.
- Moderately long term customers (generally GP subscribers) usually indicated network coverage and ease of connectivity as the reason of their stay with the company.
- Short term users (usually Airtel users) who are using connection for shorter period of time are staying with the service because of features/VAS being offered to them.
- Noticeable subscribers of other operators are likely to become GP STAR.
- STAR subscribers spread positive word of mouth highly and are likely to recommend GP to others which prove they are happy with their status and operator.
- STAR subscribers are likely to upgrade their status (e.g. from silver to gold).
- STAR subscribers want loyalty programs occur frequently.
- Lifestyle offers do not play any role in customer loyalty.
- When the basic aspects of the core service meet satisfaction, loyalty programs add value to the creation of sustainable customer loyalty. So, loyalty programs act as compliment rather than main loyalty driver.
Recommendations
- Tailor loyalty programs according to the preference of customer base and make invitations accordingly.
- Valuable customer base also needs to be appreciated and thus make them remembered about their status.
- Youth is potential future prospect who are mostly using Airtel because of features.
This customer base will be very much profitable in the near future. GP should come out with the competitive features that can attract and thus switch this base to GP.
―Djuice‖ concept got very much popular because of the features and VAS they enjoyed by using that connection.
- GP should maintain its‘ strong network coverage, improve other aspects of telecom service and reveal new concepts and conduct loyalty programs simultaneously to increase the switching cost and create sustainable loyalty.
- GP STAR program should be conducted in such a manner that customers once attended an offer should be contacted on a regular basis through some other means and thus their newly grown expectation gets met.
- General customers need to know about GP STAR program. So, publicity through print or electronic media is required.
- Sample size should be increased while conducting surveys at GP STAR events.
- GP loyalty program should focus on arranging more events which promotes intimate environment where the valuable customers can meet & share ideas. This type of events (iftar, movie show, music show, dinner) make customers delight.
Conclusion
Loyalty program is an important initiative which is directed towards a customer base which is very much profitable. Different factors determining loyalty have been discussed in the project paper. I worked with several notions to come into a feasible decision. Loyalty program can create positive impact only when other aspects of telecom services are satisfactory to the customers. Careful management of the program with maintenance of other services can ensure satisfaction, retention and ultimately commitment by which we mean sustainable loyalty.