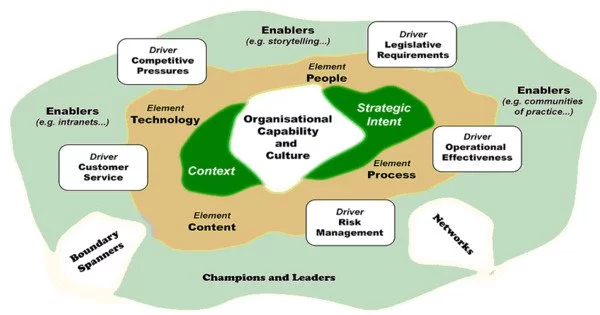
The term “knowledge ecosystem” refers to the interconnected network of people, organizations, resources, and technologies that generate, share, and use knowledge collectively. A knowledge ecosystem is a knowledge management approach that claims to foster the dynamic evolution of knowledge interactions between entities in order to improve decision-making and innovation via improved evolutionary networks of collaboration. It includes a diverse set of elements and dynamics that contribute to the creation, dissemination, and application of knowledge across multiple domains.
Knowledge digital ecosystems advocate that knowledge strategies should focus more on enabling self-organization in response to changing environments, as opposed to purely directive management efforts that attempt to manage or direct outcomes. The degree of “fitness” of a knowledge ecosystem is defined by the suitability of knowledge to the problems encountered. Articles on such ecological approaches frequently include elements of complex adaptive systems theory. The Canadian government is one of the known implementation considerations of the knowledge ecosystem.
Here are some key components and concepts associated with a knowledge ecosystem:
- Knowledge Creation: This is the process of discovering new facts and insights. It can happen as a result of research, innovation, and creative thinking. Universities, research institutions, and think tanks are frequently central players in the creation of knowledge.
- Knowledge Sharing: Knowledge is frequently shared through a variety of channels, including academic publications, conferences, seminars, and online platforms. Social networks and collaborative tools are becoming increasingly important for knowledge sharing.
- Knowledge Transfer: This entails applying knowledge gained in one context to another. It is frequently observed in the translation of research findings into practical applications, such as technology or policy development.
- Information and Communication Technologies (ICT): Digital tools and platforms play a crucial role in modern knowledge ecosystems. The internet, cloud computing, and social media have revolutionized how knowledge is created, shared, and accessed.
- Human Capital: The individuals involved in a knowledge ecosystem are critical. Researchers, educators, innovators, and experts contribute their expertise and skills to the generation and dissemination of knowledge.
- Organizations: Academic institutions, research organizations, government agencies, and private companies all play roles in knowledge ecosystems. They provide resources, funding, and infrastructure for knowledge-related activities.
- Policy and Regulation: Government policies, intellectual property laws, and regulations can significantly impact how knowledge is created and shared. Balancing incentives for innovation with the need for open access is an ongoing challenge.
- Cultural and Social Factors: The culture of knowledge sharing and collaboration in a particular community or organization can greatly influence the effectiveness of a knowledge ecosystem. Trust, cooperation, and a willingness to share are essential.
- Open Access and Open Science: Movements toward open access publishing and open science aim to make knowledge more widely accessible and transparent. This can enhance the efficiency and inclusivity of knowledge ecosystems.
Knowledge ecosystems have the potential to have a significant economic impact. Innovation and knowledge-based industries help to drive economic growth and competitiveness. It is critical to ensure the long-term viability of knowledge ecosystems. This includes funding, infrastructure, and policies that promote continuous knowledge generation and sharing. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are changing the way knowledge is generated and applied. They have the potential to transform numerous aspects of knowledge ecosystems.
In summary, a knowledge ecosystem is a complex and dynamic network where knowledge is created, shared, and applied. It involves various stakeholders and is influenced by technological, social, economic, and cultural factors. Understanding and nurturing knowledge ecosystems is vital for the advancement of society, innovation, and problem-solving in diverse fields.