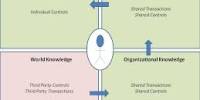
Workplace democracy is the application of democracy to the workplace in various forms (for example, voting systems, debates, democratic structuring, due process, adversarial process, and appeal systems). It refers to a system or approach in which employees have a say in organizational decision-making processes. It can be implemented in a variety of ways, depending on an organization’s size, culture, and other factors. It entails giving employees the right to shape policies, make decisions, and have a say in matters affecting their working environment.
Workplace democracy theory is closely related to political democracy theory, particularly in larger workplaces. Democratic workplace organization is frequently associated with trade unions, anarchist, and socialist movements (particularly libertarian socialist). Most unions have democratic structures, at least for choosing the leader, and these are sometimes viewed as the only democratic aspects of the workplace. However, not every workplace without a union lacks democracy, and not every workplace with a union always has a democratic way of resolving disputes.
Here are some key aspects and benefits associated with workplace democracy:
- Participation: Workplace democracy encourages employees to actively participate in decision-making processes that impact their work. This involvement can range from providing feedback and suggestions to having voting rights in key decisions.
- Empowerment: By giving employees a voice and involving them in decision-making, workplace democracy empowers them and recognizes their expertise and insights. This can lead to increased job satisfaction and motivation.
- Collaboration: Workplace democracy promotes collaboration and teamwork. When employees have the opportunity to contribute their ideas and opinions, it fosters a culture of open communication and cooperation among team members.
- Innovation: When employees have a say in decision-making, it can unlock their creativity and spur innovation. Diverse perspectives and ideas from different levels of the organization can lead to better problem-solving and the generation of new, innovative solutions.
- Transparency: Transparency in decision-making is emphasized in workplace democracy. It contributes to the creation of an environment in which information is freely shared and employees understand the rationale behind various decisions. This transparency has the potential to increase trust and strengthen the employer-employee relationship.
- Employee satisfaction and retention: Workplace democracy can help increase employee satisfaction. Employees are more likely to be engaged and committed to their work when they feel heard and valued. As a result, employee retention rates may improve.
Implementing workplace democracy necessitates a supportive organizational culture, open lines of communication, and a willingness to involve employees in decision-making. It may also include training and development initiatives to improve employees’ skills and knowledge so that they can participate more effectively. Overall, workplace democracy can result in a more inclusive and engaged workforce, fostering a positive work environment that benefits both employees and the organization.