Card Holder
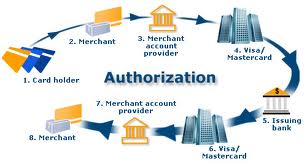
One of the participants in Credit Card transaction is the Cardholder who is solicited, screened and approved by the issuer. The letter establishes a line of credit for the customer and issues the credit card. The Cardholder uses the credit card either to purchase goods and services from a merchant or obtain a cash advance from a member for which the cardholder receives a monthly bill from the issuer.
Issuer
The second participant in Credit Card transactions is the Issuer. The Cardholder’s financial institution (usually called the issuing member or issuer) is a licensed member of Master Card/Visa. The Issuer:
- Issues the card to the approved cardholder
- Receives & pays for transactions from Master card and/or Visa
- Bills collect from the cardholder
The issuer also benefits from the services of a Third Party and /or association in processing information and payments.
Banks
Managing a credit card program is expensive and some small financial institutions prefer to offer credit cards to their customers without taking on the complications and responsibilities of becoming an issuing member.
These small financial institutions can contract to become an issuing agent of an issuing member. The issuing agent solicits cardholder applicants for the issuer generally through take-ones made available at its branches. The issuer, in turn, issues the card in its name has the cardholder relationship, makes all of the Credit decisions and completely manages the card program. It the agent Bank’s name appears on the card, and then the agent bank must be an affiliate/associate member of Master Card/Visa Int’l.
The issuer usually keeps most of the income from the cardholder account: the agent member may not receive small compensation for providing the application. While the issuing agent’s income from this arrangement is small, it does retain customers who might take their business elsewhere if a Credit Card Program were not available at their local financial institution. When the issuing agent’s name appears on the card it tends to preserve the financial institution-Card holder relationship.
Acquirer
The acquiring member or acquirer solicits and accepts merchants into its Credit Card Program. The acquire is a member of Master Card and /or Visa and holds a written agreement with the merchant to:
- Accept the merchant’s sales slips
- Provide the merchant with credit card authorization terminals, instruction and contracted support services
- Handle and process the credit card transactions
The acquirer usually charges the merchant a merchant discount for handling the transactions. The acquirer is licensed by Master card and /Visa and agrees to follow the operating rules and regulations of the two associations. Master Card/Visa provides various services to the acquirer, including authorization and settlement processing, interchange and resolution to member disputes. Many financial institutions are both issuers and acquirers: As issuers they maintain the cardholder relationship. As acquirers, they maintain the merchant relationship.
Merchant
The Merchant can be virtually any company, which meets the qualification standards of Master Card and/or Visa and an acquirer. Typical merchant business includes retail stores, restaurants, airlines, mail order companies, and health plans to name a few Master Card and Visa both require that the merchant be financially responsible and of good repute. The merchant has a written agreement with the acquirer to accept the Credit cards as payment and to abide by the terms of the agreement.
Operations of the Master Card International
Banks net a global Master card Tele communication networks. It is used primarily to send and receive authorization, clearing, and settlement transaction. Bank net provides the following benefits-
- Flexibility – through an adaptive and reactive routine network
- Reliability – through rerouting capabilities and back up facilities
- Efficiency – through peer-to-peer (PTP) architecture & packet switching protocol
- Expandability– without redesign
- Speed – average speed 2.1-second response time
How does the Bank Network?
Like other Telecommunication all data pass through a central switching center (a star network configuration). Through the world Master card has 16 switching center. Among those 7 switches are exits in US and rest of them exits in whole world. In Asia, 2 switches are in Bahrain & Singapore. Recent Master card is going to establish more switch .This network is very fast and expensive.
The Bank network offers several routes that information can travel along to arrive at any given distention. This is called a distributed network & also referred to as Peer-to- Peer (PTP) architecture. Compare to Star network it is cheaper.
- Network Layout
Member host computer system – is the gateway through which Master card merchants and card holder have access to the vast Master card payment system. To ensure good services to merchants and cardholders it is important to manage communication from host system to the Master card Interface Processor (MIP) efficiently.
- Master card Interface Processor (MIP)
Data enters the Bank net through MIP’s, which perform two general functions for the members:
- Provide member host access to Bank net, which lets bank authorization, as well as send and receive Inter Bank Network for Electronic Transfer (INET) files and a variety of reports.
- Provide processing support for member’s payment card software application.
MIPs are joined to the Bank network through Tele communication centers called ‘Nodes’ or ‘Switches’. Each node is like an intersection on the system, which access to at least two other nodes. Before entering the network, a member’s data enclosed in a packet by the sending MIP. When a packet reaches its destination, the receiving MIP arranges all the packets in sequences for processing.
- Member Host Connection
The connection from banks host computer system to a MIP depends on the number and types of the services provided to merchants and cardholder’s .The member host connection may involve one or more of the following options:
On-line – Banks host computer can be directly connected to an on- site MIP at bank business location. Bank can communicate to an off-site MIP using standard communication software and locally available Telecommunication access. Members who are in remote areas or do not have the transaction volume to warrant using on-site MIP may find MIP sharing a viable option.
Off- line – Bank can use Bank net PC file express a personal computer connection to the Master Card mainframe in St Louis, for sending and receiving bulk files over Telephone lines. Bank can use Computer-Assisted Telex Services (CATS), an authorization processing system offered to members who are not on-line.
- Applications
Master Card system applications are divided into two major categories: authorization which is primarily done On-line with immediate response time and bulk data processing such as Clearing and Settlement.
- Authorization
Authorization is the process by which a payment card transaction is either approved or declined by an issuer or its authorized agent or by Master card on behalf of the issuer. The authorization is required before the merchant completes the transaction. To facilitate authorization, the central site host computer maintains the member master and other organization support files. Payment and card transaction are approved or decline by an issuer in one of voice authorization or POS terminal authorization.
Standard authorization process is step-by-step procedure for authorization the use of Master card .For terminal authorization these seven steps process is complete in an average 2.1 seconds (MIP to MIP) if the issuer and acquirer are different parts of the world.
Step 1: The cardholder gives the card to the merchant
Step 2: The merchant starts the authorization process by either:
¨ Placing a call to the acquirer or its agent, or
¨ Entering the transaction in to the POS terminal
Step 3: The acquirer host computer system sends an authorization request message to the Banknet network through the acquirer MIP
Step 4: The Bank net network sends the authorization request message through the issuer MIP. The issuer MIP sends the authorization request to the issuer host computer
Step 5: The issuer host computer processes the authorization request and sends an authorization request response
Step 6: Bank net routs the response to the acquirer or its agent
Step 7: The acquirer or agents delivers the response to the merchant
Each day, millions of cross-border and local Master card transactions involving hundreds of millions of dollars, are “cleared” and “settled” via the Bank net Tele communications network using the Interbank Network for Electronic Transfer (INET). Clearing is the process of exchanging transactions details between an acquirer and an issuer to facilitate posting of a cardholder account, handle retrieval request and reconcile a member’s settlement position. Issuers, acquirer and INET play and assume the following responsibilities in the clearing process:
1. Acquirer
a) Checks data captured from merchant documents to ensure that format meets master card standards.
b) Stores records into issuing ICA member sequence and classify transactions by merchant to minimize the transaction and processing time and cost.
c) Creates a proper file with numerically stored records.
d) Balances the prepared data before transmissions in to Master card in St Louis, USA
e) Transmits data in the appropriate format.
f) Keeps a transmission log or a listing of each transmission.
g) Re-submits any items, batches or transmissions that have been declined for any reason by Master card.
2. INET (Interbank Network for Electronic Transfer)
a) Edits balances and distributes transaction data received from acquiring and issuing members.
b) For all transaction calculates each member’s daily net settlement figure, sends figures to each member and the member’s clearing bank and to master card net settlement bank.
c) Verifies and when necessary, adjusts batch amounts and fee calculations.
d) Rejects invalid records, batches or transmission and notifies sending members of rejection.
e) Updates acquirers interchange files to confirm that transmission have been received accepted.
f) Sorts and accepts incoming batches.
g) Produces and distributes outgoing inter change transmission files for each participating member.
3. Issuer
a) Edits and balances records received from INET.
b) Updates cardholder accounts and reconciles net settlement data.
Settlement
It is the process by which funds are exchanged between members for the net value of monetary transaction such as sales transactions, cash disbursement, merchandise credits and miscellaneous records. In this process Master card instructs the Master card settlement bank to transfer funds to those members in a credit position and to debit any members who are in a debit position. The bank through with the settlement process occurs is called the settlement bank.
International Settlement:
When acquirer and issuer are located in different countries the settlement amount is calculated is either US Dollar or in some cases local currency .For local currency the members settlement amount is determined in US Dollar & then converted to the local currency for payments. Funds transfer is subject to international two days standards.
Local Settlement:
Master card offers this service to accommodate members in the same country who need to clear all their transactions through INET and who desire to settle transaction with in the country in their local currency.
Members participating in local settlement process their domestic transaction through a local settlement bank at an agreed upon inter change rate(s). Master card credit and debit advisement are sent to a member designated local bank.
Security and Fraud
Security is the main feature in the card business. For the security purpose the following actions are involve.
1. Security Staff:
Job responsibilities can be divided in to the following parts:
A. Internal
- Conduct pre-employment investigating of prospective card department employee.
- Plan and supervise the manufacturing shipping, storing, embossing, encoding and mailing of cards.
- Plan and supervise the physical protection of card department and building including the related data processing and data communication facilities.
- Conduct investigations for other Master card members on request.
- Maintain liaison with the Master card security and risk management department on Network and relevant internal department.
- Train all personnel including employees with direct customer contract in fraud and awareness and detection.
B. Cardholder or Merchant Related
- Investigate prospective merchant (if applicable).
- Investigate cases of fraud involving the institution.
- Creates and implement cardholder and merchant education program (if applicable).
- Assists consumer civic and business groups in preparing and conducting fraud awareness programs.
2. Card and System Security:
- Make sure for the card production and processing the following criteria are required-
- Physical security of the premises
- Protection of cards during their production and issuance
- Merchant education and monitoring (if applicable)
- Early warning systems monitoring
- Fraud reporting and analysis
- Investigation of cards and merchant fraud
Card production Security
Card production security occur by the following two steps-
1. Plastic Procurement
Institution is responsible for obtaining cards from a plastics manufacturer. Master card periodically in the security Bulletin lists manufacturers, embowers and encodes that have been inspected and are in compliance with Master card minimum-security standards.
2. Card security features
To minimize fraudulent the following steps are occur-
a) Master Card Signature Panel: Signature panel helps to avoid fraudulent activities also provides authentication of the cardholder.
b) Identification of Card Source: The ordering member or affiliates ICA number the month and the year the order was placed and the manufacturer’s name placement of this information on the card is at the card designer’s discretion.
c) Expiration Date: No longer than two years from the issue date.
d) Master Card Embossed Characters: A special character, which is difficult to reproduce. This is appeared on the front of the cards.
e) Hologram: A three dimensional insignia created with a laser.
f) Indent Printing: Account number printed in reverse italic type on the card signature panel.
g) Two-Card Validation Codes: One of these 3 digits codes in printed on the signature panel following the account number and other is encoded on the magnetic stripe.