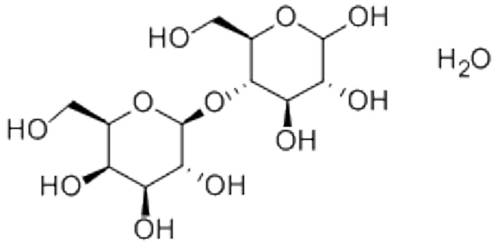
Classification of Matter is a sample of matter whose physical and chemical properties are the same throughout the sample because the matter has a constant composition. It is common to see substances changing from one state of matter to another.
Characteristics of matter
- It has mass and it takes up space
- Matter has the property of inertia
- It takes force to change the state of motion of matter
States of matter
Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. There are three different States (forms) of matter:
- Solid : Solids have definite volume and shape.
- Liquid : liquids have definite volume but no definite shape. Liquids take on the shape of their container.
- Gas : Gases has neither definite volume nor definite shape. They fill up whatever space they are put in.
The fourth state of matter is called plasma. Although this state is not common in earth and other planets most of the matter of the universe in the form of plasma. Plasma consists of high energy electrically charged particles and are some what like gases—they do not have definite volume or shape.
The state of matter depends on its temperature. At cold enough temperatures, almost all materials become solids. As they warm they can become liquids. At still higher temperatures they may become gases. At very high temperature they may become plasmas.
The kinetic theory of matter
According to kinetic theory of matter, all matter is made of tiny particles. These particles are in constant motion. The higher the temperature, the faster the motion. The motion and spacing of the particles determines the state of matter.
The particles of solid are packed very close together. Forces between the particles (intermolecular forces) hold them together in fixed arrangement. In solids, the particles move back and forth, but do not change positions.