Naproxen
Definition: Naproxen (brand names: Aleve, Naprosyn, and many others) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve symptoms of arthritis (osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or juvenile arthritis) such as inflammation, swelling, stiffness, and joint pain. It is a nonselective COX inhibitor, usually sold as the sodium salt. It is available in both an immediate release and extended release formulation. Naproxen is generally safe for use by breastfeeding mothers.
There are two types of prescription naproxen: regular naproxen and naproxen sodium. Regular naproxen comes as an oral immediate-release tablet, an oral delayed-release tablet, and an oral suspension. Naproxen sodium comes as an oral immediate-release tablet and an oral extended-release tablet. Naproxen is also available in over-the-counter forms.
Naproxen can increase people’s risk of fatal heart attack or stroke, especially if they use it long term or take high doses, or if they have heart disease. Even people without heart disease or risk factors could have a stroke or heart attack while taking this medicine.
Do not use this medicine just before or after heart bypass surgery (coronary artery bypass graft, or CABG). Get emergency medical help if people have chest pain, weakness, shortness of breath, slurred speech, or problems with vision or balance.
Naproxen may also cause stomach or intestinal bleeding, which can be fatal. These conditions can occur without warning while people are using this medicine, especially in older adults.
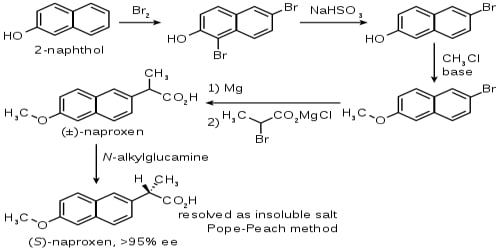
As an NSAID, naproxen exerts its anti-inflammatory action by reducing the production of inflammatory mediators called prostaglandins. It is extensively metabolized by the liver to inactive metabolites.
Uses and Dosages of Naproxen: Use naproxen exactly as directed on the label, or as prescribed by the doctor. Do not take this medicine in larger amounts or for longer than recommended. Use the lowest dose that is effective in treating the patient’s condition. Do not crush, chew, or break a naproxen tablet. Swallow it whole.

Naproxen’s medical uses are related to its mechanism of action as an anti-inflammatory compound. Prescription naproxen oral tablets are used to treat pain and inflammation in a variety of conditions. It’s approved to treat:
- rheumatoid arthritis
- osteoarthritis
- ankylosing spondylitis
- juvenile arthritis
- menstrual period pain
- tendonitis
- bursitis
- symptoms of gout.
Naproxen sodium is used as a “bridge therapy” in a medication-overuse headache to slowly take patients off of other medications.
Small amounts of naproxen are excreted in breast milk. However, adverse effects are uncommon in infants breastfed from mother taking naproxen.
The dose of this medicine will be different for different patients. Follow the doctor’s orders or the directions on the label. The amount of medicine that people take depends on the strength of the medicine.
Also, the number of doses you take each day, the time allowed between doses, and the length of time people take the medicine to depend on the medical problem for which they are using the medicine.
Dosage forms and strengths –
Generic: Naproxen
- Form: immediate-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 250 mg, 375 mg, 500 mg
- Form: delayed-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 375 mg, 500 mg
Generic: Naproxen sodium
- Form: immediate-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 275 mg, 550 mg
- Form: extended-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 375 mg, 500 mg, 750 mg
Brand: Naprosyn (naproxen)
- Form: immediate-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 250 mg, 375 mg, 500 mg
- Form: delayed-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 375 mg, 500 mg
Brand: Anaprox (naproxen sodium)
- Form: immediate-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 275 mg, 550 mg
Brand: Naprelan (naproxen sodium)
- Form: extended-release oral tablet
- Strengths: 375 mg, 500 mg, 750 mg

Effects of Naproxen: Common adverse effects include dizziness, drowsiness, headache, rash, bruising, and gastrointestinal upset. Heavy use is associated with an increased risk of end-stage renal disease and kidney failure. Get emergency medical help if people have signs of an allergic reaction to naproxen: sneezing, runny or stuffy nose; wheezing or trouble breathing; hives; swelling of people’s face, lips, tongue, or throat.
Common naproxen side effects may include:
- indigestion, heartburn, stomach pain, nausea;
- headache, dizziness, drowsiness;
- bruising, itching, rash;
- swelling; or
- ringing in patient’s ears.
A study found that high-dose naproxen induced near-complete suppression of platelet thromboxane throughout the dosing interval and appeared not to increase cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk, whereas other non-aspirin high-dose NSAID regimens had only transient effects on platelet COX-1 and were associated with a small but definite vascular hazard. Conversely, naproxen was associated with higher rates of upper gastrointestinal bleeding complications compared with other NSAIDs.
Information Source: