WET PROCESSING TECHNOLOGY
Introduction
Textiles have such an important bearing on our daily lives that everyone needs to know something about them. From earliest times, people have used textiles of various types for covering, warmth, personal adornment, and even to display personal wealth. Today, textiles are still used for these purposes and everyone is an ultimate consumer.
A textile or cloth is a flexible material consisting of a network of natural or artificial fibres often referred to as thread or yarn. Yarn is produced by spinning raw fibres of wool, flax, cotton, or other material to produce long strands. Textiles are formed by weaving, knitting, crocheting, knotting, or pressing fibres together (felt).
The words fabric and cloth are used in textile assembly trades (such as tailoring and dressmaking) as synonyms for textile. However, there are subtle differences in these terms in specialized usage. Textile refers to any material made of interlacing fibres. Fabric refers to any material made through weaving, knitting, spreading, crocheting, or bonding that may be used in production of further goods (garments, etc.). Cloth may be used synonymously with fabric but often refers to a finished piece of fabric used for a specific purpose (e.g., table cloth).
Textiles have an assortment of uses, the most common of which are for clothing and containers such as bags and baskets. In the household, they are used in carpeting, upholstered furnishings, window shades, towels, covering for tables, beds, and other flat surfaces, and in art. In the workplace, they are used in industrial and scientific processes such as filtering. Miscellaneous uses include flags, backpacks, tents, nets, cleaning devices such as handkerchiefs and rags, transportation devices such as balloons, kites, sails, and parachutes, in addition to strengthening in composite materials such as fiberglass and industrial geotextiles. Children can learn using textiles to make collages, sew, quilt, and toys. Textiles used for industrial purposes, and chosen for characteristics other than their appearance, are commonly referred to as technical textiles. Technical textiles include textile structures for automotive applications, medical textiles (e.g. implants), geotextiles (reinforcement of embankments), agrotextiles (textiles for crop protection), protective clothing (e.g. against heat and radiation for fire fighter clothing, against molten metals for welders, stab protection, and bullet proof vests). In all these applications stringent performance requirements must be met. Woven of threads coated with zinc oxide nanowires, laboratory fabric has been shown capable of “self-powering nanosystems” using vibrations created by everyday actions like wind or body movements.
From fiber to fabric Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd is truly integrated undertaking has the capability to offer a complete product range for the export textile markets. The goal of Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. is to become the preferred partner for sourcing high quality fabrics and clothing from Bangladesh with highly advanced technology and an emphasis on developing local human resources. Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. has the potential to make an important contribution to the nation’s growing readymade garments export sector. The rational behind the existing structure and future expansion of Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. is to capture value-added at each stage of the textile manufacturing process. Despite Bangladesh’s lack of indigenous cotton production capability, Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. has leveraged Bangladesh’s labor cost advantage and export competitiveness to the maximum
Machine Description of Knitting Section:
Serial no | Name | Origin | Needles | Type | M/C dia | Gauge | Feeder | |
1. | JUINN LONG | Taiwan | 1440T | S/J | 19’’ | 24G | 57F | |
2. | JUINN LONG | Taiwan | 1584T | S/J | 21’’ | 24 | 63F | |
3. | JUINN LONG | Taiwan | 1740T | S/J | 28” | 24 | 69F | |
4. | JUINN LONG | Taiwan | 1740T | S/J | 23” | 24 | 69F | |
5. | JUINN LONG | Taiwan | 2400T | S/J | 32” | 24 | 96F | |
6. | JUINN LONG | Taiwan | 2712T | Ly S/J | 36” | 24 | 108F | |
7. | SAMJUNG | Korea | 1658T | Rib | 22” | 24 | 66F | |
8. | SUNG CHANG | Korea | 1996T | Rib | 23” | 24 | 69F | |
9. | SUNG CHANG | Korea | 1996T | Rib | 21” | 24 | 63F | |
10. | FALMAC | Singapore | 1696T | Rib | 30” | 18 | 48F | |
11. | FALMAC | Singapore | 1696T | Rib | 30” | 18 | 48F | |
Production Planning Sequences and Operation
Basic technological concept :
The fundamental structure unit of a knitted fabric is the loop. Any circular knitted fabric is composed of row after row of intermeshed loops. Different types of fabric are made of different method of intermeshing the loop. The gross dimension of knitted fabric is simply a relation of average shape and size of individual loop. There are several key variables in the production which affect the average shape and size of the loop. After knitting the grease fabric is dyed to required shade and finished to required weight and width.
Classification of knitting:
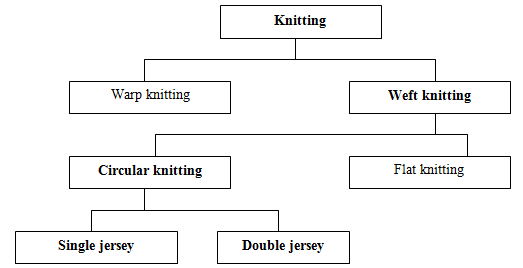
Warp knitting :
A method of making a fabric by normal knitting means is which the loop made from each warp thread is formed substantially along the length of the fabric. Characterized by the fact that each warp thread is feed more or less in the line with the direction in which the fabric is produced.
Weft knitting
A method of making a fabric by normal knitting means is which the loop made from each weft thread formed substantially along the length of the fabric. Characterized by the fact that each warp thread is feed more or less in the line with the direction in which the fabric is produced.
Single jersey
A fabric in which all the loops of the Wales are intermeshed in one direction is called single jersey. Only cylinder is used to make single jersey fabric. End Products of Single Jersey Circular Knitting Machine:
1. Single Jersey Plain
2. Single Lacoste
3. Double Lacoste
4. Single pique
5. Double pique
6. Terry
7. Heavy Jersey
Double jersey
A fabric in which all the loops of the alternate wale/Wales are intermeshed in one direction and all the loops of the other wales knitted t the same course are intermeshed in the other direction is called the double jersey. Dial and cylinder are used to make this type of fabric.
Methods of increasing production
By the following methods the production of knitted fabric can be increased –
A. By increasing m/c speed:
Higher the m/c speed faster the movement of needle and ultimately production will be increased but it has to make sure that excess tension is not imposed on yarn because of this high speed.
B. By increasing the number of feeder:
If the number of feeder is increased in the circumference of cylinder, then the number of courses will be increased in one revolution at a time.
C. By using machine of higher gauge:
The more the machine gauge, the more the production is. So by using machine of higher gauge production can be increased.
E. By imposing other developments:
a) Using creel-feeding system.
b) Applying yarn supply through plastic tube that eliminates the possibilities of yarn damage.
c) Using yarn feed control device.
d) Using auto lint removal.
Relationship between knitting parameter
1. Stitch length increase with decrease of GSM.
2. If stitch length increase then fabric width increase and Wales per inch decrease.
3. If machine gauge increase then fabric width decrease.
4. If yarn count increase (courser) then fabric width increase.
5. If shrinkage increases then fabric width decrease but GSM and Wales/inch increase.
6. for finer gauge, finer count yarn should use
7. Grey GSM should be less than finish GSM
Considerable points to produce knitted fabrics
When a buyer orders for fabric then they mention some points related to production and quality. Before production of knitted fabric, these factors are needed to consider. Those are as follows-
– Type of Fabric or design of Fabric.
– Finished G.S.M.
– Yarn count
– Types of yarn (combed or carded)
– Diameter of the fabric.
– Stitch length
– Color depth.
Effect of stitch length on color depth
If the depth of color of the fabric is high loop length should be higher because in case of fabric with higher loop length is less compact. In dark shade dye take up% is high so GSM is adjusted then. Similarly in case of light shade loop length should be relatively smaller
Factors that should be change in case of fabric design on quality change
a) Cam setting
b) Set of needle
c) Size of Stitch Length
Key accessories used in Circular knitting
- Yarn feeder guide
- Needle
- Sinker
- Cam
- Cylinder
- VDQ pulley
- Pattern wheel
- Sinker cam cap
- Sinker trick ring
- Dial
- Needle retaining spring
- Cam box
- cam plate
- Inventor
- Belt
Quality control equipment
- Yarn tension meter
- Stitch length meter
- Magnifying glass
- GSM cutter etc
Difference between S/J and double jersey m/c:
| Single jersey m/c | Double jersey m/c |
| 1.One set needle is used. | 1. Two set needle are used. |
| 2.Has sinker. | 2. Has no sinker. |
| 3. Inside of m/c is vacuum. | 3. Inside is not vacuum. |
| 4. Has sinker box. | 4. Has no sinker box. |
| 5. Has sinker ring. | 5. Has no sinker ring. |
| 6.Ex:- S/J | 6.Ex:-Rib,Interlock etc. |
m. Feeder ring
vii. Cam box
viii. Wheel
Relation between m/c dia & Number of feeder of this m/c:
Number of feeder =m/c dia
Positive feed system:
If needle gets required thread without stretch for loop formation, it is called positive feed system.
Negative feed system:
If needle drawls the thread for loop formation called negative feed system.
Negative feed system is best. Because
i. Easy mechanism.
ii. No slippage.
iii. Maximum 4 course length variation.
iv. To adjust loop length variation.
v. No possibility of thread breakage.
vi. Wide range yarn feeding.
V.D.Q:
V.D.Q means Variable dia for quality.
Function: To control fabric G.S.M.
Faults & their causes in Knitting
1. Hole Mark
Causes:
Holes are the results of yarn breakage or yarn cracks.
During loop formation the yarn breaks in the rejoin of the needle hook.
If the yarn count is not correct on regarding structure, gauge, course and density.
Badly knot or splicing.
Yarn feeder badly set.
Remedies:
Yarn strength must be sufficient to withstand the stretch as well as uniform.
Use proper count of yarn.
Correctly set of yarn feeder.
Knot should be given properly
2. Needle Mark
Causes:
When a needle breaks down then needle mark comes along the fabrics.
If a needle or needle hook is slightly bends then needle mark comes on the fabrics.
Remedies:
Needle should be straight as well as from broken latch.
3. Sinker Mark
Causes:
When sinker corrode due to abrasion then some times can not hold a new loop as a result sinker mark comes.
If sinker head bend then sinker mark comes.
Remedies:
X Sinker should be changed. tension variating prod the needle laow G.S.M fabric production.
Remedies:
Maintain same Yarn tension during production.
Use good conditioned needles.
5. Drop Stitches
Causes
Defective needle.
If yarn is not properly fed during loop formation i.e. not properly laid on to the needle hook.
Take-down mechanism too loose.
Insufficient yarn tension.
Badly set yarn feeder.
Remedies:
- Needle should be straight & well.
- Proper feeding of yarn during loop formation.
- Correct take up of the fabric & correct fabric tension.
- Yarn tension should be properly.
6. Oil stain
Causes:
When oil lick through the needle trick then it pass on the fabrics and make a line.
Remedies:
Ensure that oil does not pass on the fabrics.
7. Rust stain
f any rust on the machine parts.
Remedies:
If any rust on the machine parts then clean it.
Proper maintenance as well as proper oiling.
8. Pin hole
Causes:
Due to break down or bend of the latch, pin hole may come in the fabric.
Remedies:
Change the needle.
9. Grease stain
Causes:
Improper greasing
Excess greasing
Remedies:
Proper greasing as well as proper maintenance
10. Cloth fall- out
Causes:
Cloth fall- out can occur after a drop stitch especially when an empty needle with an empty needle with closed latch runs into the yarn feeder and remove the yarn out of the hook of the following needles.
Remedies:
Make sure all the latches of needle are closed with feeding yarn after a drop stitch.
11 . Barre: A fault in weft knitted fabric appearing as light or dark course wise (width wise)
stripe(s).
Causes:
This fault comes from yarn fault.
If different micro near value of fiber content in yarn.
Different lusture, dye affinity of fiber content in yarn.
During spinning different similar classes of fiber is mixed specially in carded yarn & these fibers have similar characteristics.
In draw fame different similar classes sliver is mixed and make one sliver.
Remedies:
We can use this fabric in white color.
12. Fly:
Causes:
In knitting section too much lint is flying to and fro that are created from yarn due to low twist as well as yarn friction. This lint may adhere or attaches to the fabric surface tightly during knit fabric production.
Remedies:
Blowing air for cleaning and different parts after a certain period of time.
By cleaning the floor continuously.
By using ducting system for cleaning too much lint in the floor.
Over all ensure that lint does not attach to the fabric.
13.Yarn contamination
Causes:
If yarn contains foreign fiber then it remains in the fabric even after finishing,
If lot, count mixing occurs.
Remedies:
By avoiding lot, count mixing.
Fault less spinning.
14. Yarn Faults:
X Neps. Slubs. Yarn count, Thick/Thin place in yarn, Hairiness.
Comparison between machine dia and grey dia.
Formula:
Grey dia =(1.2-1.4)machine dia
Introduction: Generally grey dia is (1.2-1.4)times higher than machine dia.
Machine Parameter:
Machine no: 08
Machine dia: 32²
Fabric type:Fleece
Fabric dia: ?
- Procedure: Measure the dia of grey fabric by measuring tape.
And we get 40.5²
- Grey dia = 1.265 Machine dia
Result: Grey dia is 1.26 times of machine dia.
Determination of the lycra percentage of weft knitted fabric.
Introduction: Lycra percentage means how much lycra is used with 100gm fabric.
Procedure:
1. At first we will have to take one cotton yarn package and its related lycra package.
2. Then we will have to weigh both package by electronic balance and note down it.
3. Then this both package is set on respective place and then run the machine again.
4. Run the machine for certain times(hours) before the total yarn gets finished.(approximately 8hrs or 1 shift).
5. Then again take those selected packages and weigh once again.
6. Calculate the consumption of both lycra and cotton yarn package.
7. Then add both both consumption weight of lycra and cotton yarn package.
8. Divide the consumption of lycra by total consumption weight of lycra and cotton.Then multiply the result by 100.
9. Now we get lycra percentage in the produced fabric.
Calculation:
Machine no:17
Produced fabric: Full feeder lycra single jersey:
Yarn count: 34s
Weight of cotton yarn package at start = 780gm
Weight of cotton yarn package at end = 180gm
Weight of lycra yarn package at start =140gm
Weight of lycra yarn package at end =120gm
So, amount of cotton yarn used = (780-180)gm
=600gm
Amount of lycra yarn used = (140-120)gm
=20gm
Amount of total yarn used =(600+200)gm
=620gm
Lycra percentage
=3.23%
Result: Lycra percentage on produced fabric is 4.54%
Again,
Calculation:
Machine no:09
Produced fabric: Full feeder lycra single jersey:
Yarn count: 40s
Weight of cotton yarn package at start = 460gm
Weight of cotton yarn package at end = 60gm
Weight of lycra yarn package at start =260gm
Weight of lycra yarn package at end =240gm
So, amount of cotton yarn used = (460-60)gm
=420gm
Amount of lycra yarn used = (260-240)gm
=20gm
Amount of total yarn used =(420+20)gm
=440gm
Lycra percentage
=4.54%
Result: Lycra percentage on produced fabric is 4.54%
So from above two experiments in is transparent that lycra percentage increase with the increase
Of count of cotton yarn.
Determination of the extensibility of lycra.
- Procedure:
- Measure the length of lycra from package to needle butt.
- Then measure the length of lycra at relaxed state.
- Subtract the length of lycra at extensible position from the length of lycra at relaxed state.
- Then divide the length of extension by the extensible length of lycra and then multiply by 100 to get lycra extensibility.
Calculation of extensibility:
Length of lycra from package to needle butt=61.5
And length at relaxed state =9.5
Length of extension =52
Lycra extensibility =(52/61.5 )
=84.55%
Remarks: Lycra extensibility is 84.55%.
Conversion of interlock to rib and rib to interlock:
By the following ways we can convert rib to interlock and interlock to rib:-
By changing time gaiting of needle through moving or rotating dial or cylinder for a length of about distance between two needle.
For rib structure needle is set side by side of cylinder and dial. And for interlock structure the needle remain face to face.
The cylinder is adjusted by moving screw up and down.
Cam box of both dial and cylinder will have to be changed.
check and conform actual count of yarn:
By following way we can check and confirm actual count of yarn:
Machine name: Wrap Reel electronic.
Company Name: SDL ATLAS(Brand)
SL:751H0003
And Electronic Balance
Function: To measure the actual count of yarn
Formula:
Here , L = Length of the yarn in yards
W= Weight of yarn in lb.
W= weight unit 1lb.
l= length unit (840yds).
Procedure:
® At first we will have to take 100m of yarn from the package whose count will have to be checked. It is done by wrap reel machine.
® Then its weight is measured by electronic balance.
® By putting this value in the formula we can calculate the count
Example:
We took a cotton yarn package whose count is 34s.
For getting sure we took 100m of yarn by wrap reel machine and then measure its weight on electronic balance. And we got 178gm.
So, its actual count is
= 33.06s
Remarks: So the actual count is 33.06s.
VDQ pulley and its function:
VDQ pulley means variable diameter quality pulley. It is very important part of knitting machine.
Function:
- Control yarn supply
- Control yarn tension
- Control stitch length
- Finally control G.S.M
Changing of stitch length by VDQ pulley:
There is a nut or screw under or over the pulley. After losing the nut we can change the diameter controlling parts. If we rotate ‘+’ direction diameter will increase and stitch length will increase. If we rotate ‘-‘ direction diameter will decrease and stitch length will decrease.
Relationship between grey dia, grey stitch & grey G.S.M:
Grey dia is proportional to grey stitch
Or, grey dia ∞grey stitch
And grey G.S.M is inversely proportional to stitch length
Or grey G.S.M∞
Tightness factor:
It is a measure of how much of the fabric is covered by yarn and indicates how open and closed a fabric is called tightness factor.
It is the ratio of the area covered by the yarn in one loop to the area occupied by that loop.
Tightness factor where l is loop length in cm
Tightness factor range from 11(for slack fabric) to 19 (for tight fabric) and an average of 15 is preferable which is optimum in general.
If loop length in mm then k-value is always between 1to 2 and the average 1.5
What types of precaution will take when we will produce grey Milange and white fabric:
At first yarn count must be checked
Two machines are separated by net so that grey Milan dust or fibres can not contaminate the white fabric or can not be introduced into the white fabric as fly.
Calculation of machine efficiency or production efficiency:
Date: 20-06-12
Introduction:
The machine which is used to produce single jersey fabric is called single jersey machine.
Machine Parameters:
Jiunn long machine co. ltd.(made in Taiwan)
Model no.:JLS-02
Machine No.:081105(13)
Needles: 2544T
Diameter: 34²
Feeder: 96
Gauge: 24
Yarn count:30s
GSM: 150
Stitch length: 2.70mm
R.P.M: 18.5
Operator Name: Md. Sumon and Humayun Ahmad.
Production .0000946×
12.33Kg/hour
73.98Kg/6hours
Production has obtained:
Weight of 1st roll=20,62Kg
Weight of 2nd roll=21.12Kg
Weight or 3rd roll=25.70Kg
Total weight=67.44Kg
Efficiency:
Efficiency=
=91%
Describe the oiling system of circular knitting machine:
Oiling:
Oiling is the process of supply oil in different parts of machine. Oiling is very important for smooth running of machine . It is compared with blood circulation of human body.
Types of oiling:
In general oiling is done in two ways:
i. Pulsonic oiling system
ii. Uniwave oiling system
Pulsonic oiling system:
It is electrically driven oiling system . In this system of oiling , motor is used. It is modern type of oiling system and in modern system. Maintenance of personic oiling system is difficult and skilled personnel is required to maintain personic oiling system.
Uniwave oiling system:
- It is conventional oiling system
- Motor is not required in this system.
- Oil is supply through compressed air.
- Easy to maintain.
- Less skilled personnel can maintain this type of oiling system
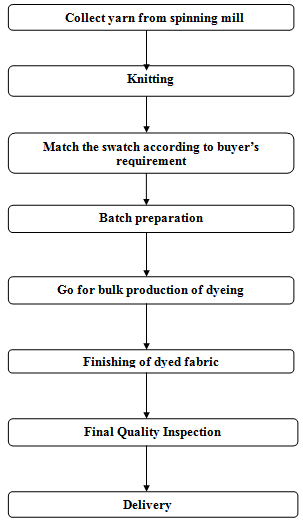
6. Working Procedure of dyeing lab:
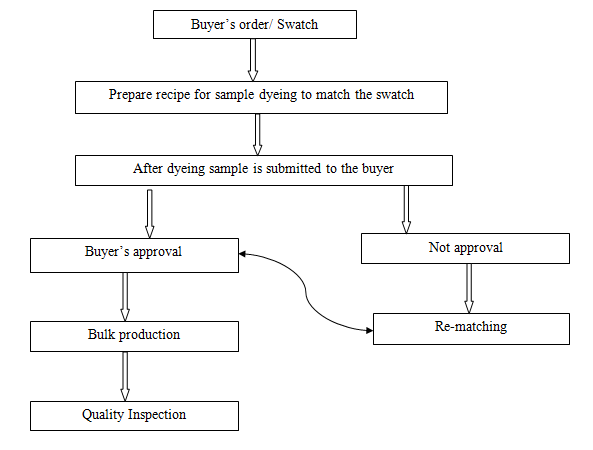

Process sequence of Batch preparation

Dyeing section at Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd.(INCTL)
At INCTL the following dyeing process were run during our internship:
- Whitening
- Normal dyeing
- Turkish color dyeing
- PC/CVC dyeing
- Topping
- Strippin
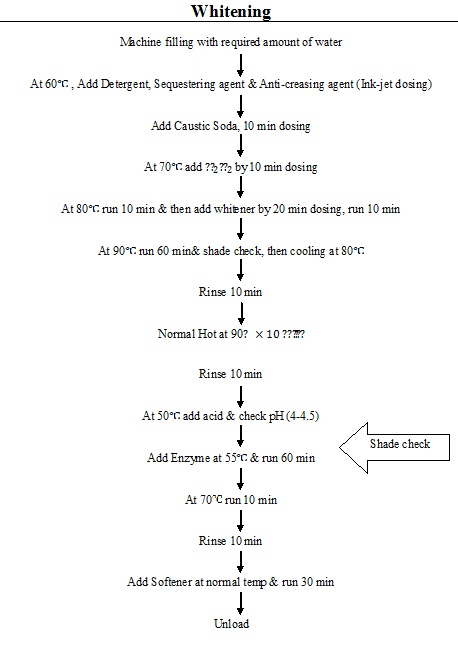
Flow chart of Pre-treatment (Scouring/Bleaching) process of cotton at INCTL
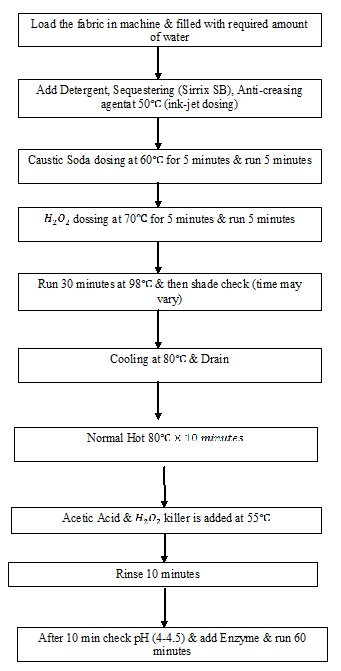
Dyeing Process Flow Chart:
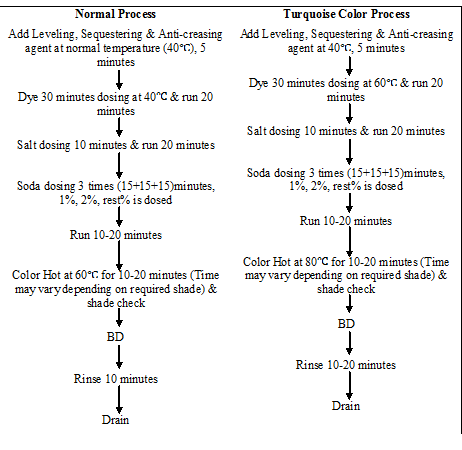
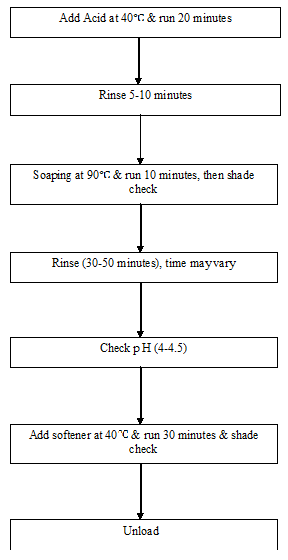
After-treatment (Acid, Soaping, Softener) process flow chart:
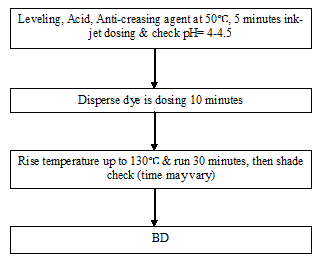
Process Flow Chart of P-C Blends at INCTL:
Polyester part dyeing:
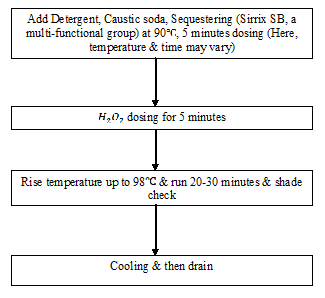
 Pre-treatment:
Pre-treatment:
Cotton part dyeing:
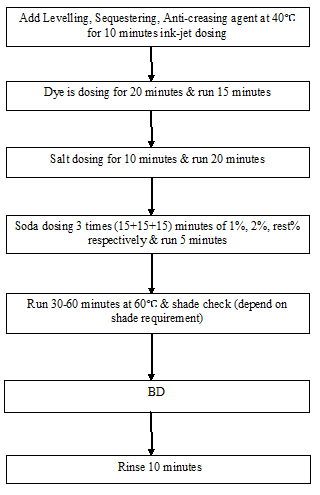
After-treatment:
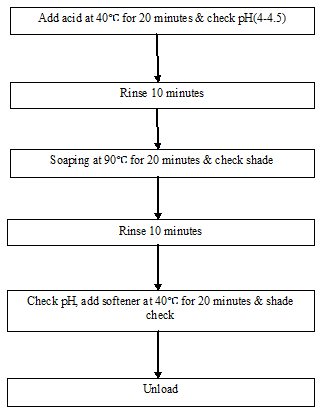
Finishing Operation Sequences:
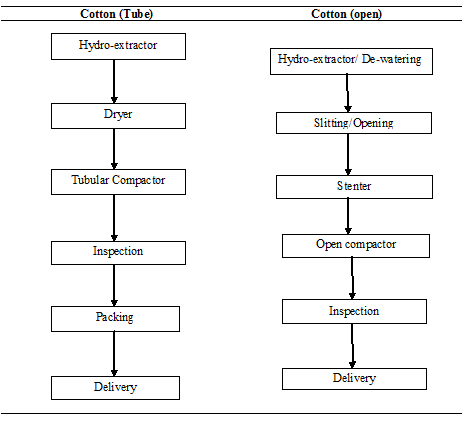
Chapter: 7
Quality Assurance System
Quality Control:
Mainly this factory follows ISO Standard. But testing Standard depends on buyer requirements.
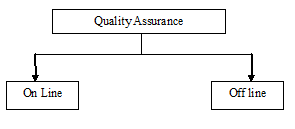
On Line Test:
1. GSM of the Fabric
2. Exact Diameter and Width
3. Grey Fabric Inspection (4 point)
4. Shade Check
5. Bias and Bowing
6. Visual appearance (Enzyme performance)
7. Stripe
Off Line Test:
All the Off Line tests for finished fabrics can be grouped as follows-
- Physical Tests, and
- Chemical Tests.

Quality Control Flow Chart
List of Equipments:
- Computer
- Light box
- Electric Heater
- Sample Dyeing M/C
- Electrical Balance
- pH meter
- G S M Cutter
- Washing M/ C
- Shrinkage & Spirality measurement instrument
Finished Fabric dia:
In Knit, dyeing finishing, finished diameter is Very important factor. It should be kept as the buyer requirements. Simply a measuring tape measures it. Finished diameter is controlled at compacting m/c.
GSM Test:
G S M is the most important factor. There is a G S M Cutter. The Sample cut by this weighted in the electronic balance. The reading (in gm) from the balance multiplied by 100 to get Value of GSM.
Rubbing Fastness test:
Purpose:
The fastness test to rubbing is used on a variety of fabrics to evaluate the transfer of surface from the test fabric when it applied surface friction or rubbed against a rough surface.
Rubbing fastness test is determined by Crock meter. The test fabric is clamped in the plate of the crock meter. A standard fabric is used for rubbing the test sample. `0 cycles are given manually by a handle. Then the standard fabric is assessed with the help of the grey scale. The scale is graded from 1 to 5, being the Poorest and 5 being and 5 being the best.
Pilling Test:
Generally, pilling test is applicable for fabric with synthetic fabric. This test is carried out in pilling box. A Sample of 10cm 10cm is sewn round a rubber tube. Then the tube in the Pilling box and the door of it is closed. Then the meter is set for 14400 cycles. After the cycle is completed, the fabric is assessed by a special grey scale. The grey scale is provided Pilling box.
Light fastness test:
Purpose:
Light fastness is the test design to evaluate the laundering fastness test of dyeing, Pigment which re to be made in comparison of result obtained on many test pieces treated under light.
Method: ISO-105 C06
Apparatus:
- Light fastness tester & blue scale
- Scale
- Scissor
- Hard paper
Procedure:
At first, we took the blue woolen cloth & test sample. The blue woolen clothes were dyed with acid blue, 104,109 etc. Then we cut the woolen cloth & sample according to template. The blue woolen cloth is cut to make standard & sample is cut to test light fastness. Then we put the holder of woolen cloth and sample in the set of machine and set the time, which was 24 hrs. After completing the process we get the slandered test result. Then we compared with the standard rating.
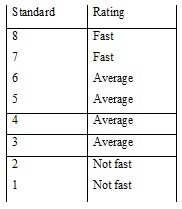
Result:
The test result of light fastness test is equivalent to the class of standard 6.So we can say that the color fastness of dyed fabric is average.
Chemical Test:
- Shrinkage and Spirality or Twisting
- Fastness to wash
- Fastness to Perspiration
Wash fastness Test:
Purpose:
The resistant of color of my dyed or printed material to washing is known as Wash fastness.
The test fabric is sewn with multifibre such that two multifibre strip remain at the both side of the test fabric.
Then they are washed with the recipe:
5 gm fabric + 100 cc water + 0.5% detergent + 0.10 % sodium perborate + 25 Steel balls.
Washes with: 60º c x 30 min
Then the multifibre is detached from the test fabric. It is dried and wash fastness is assessed by grey scale.
Color Fastness to Perspiration:
Purpose:
To assess the degree of change of shade or cross staining due to Perspiration.
Method: ISO ISO-105C06
Reagent: Alkaline Solution:
* L Histadine monohydrochloride monohydrate 0.5 g/l
* NaCl
* Di – Sodium Orthophosphate dehydrate 0.5 g/l
* ( Dilute the Solutions in one liter distill water)
* 8 ± 0.05 with 0.1 mol/ltr. (0/1N) NaOH.
Procedure: (Alkaline Perspiration)
* Keep the specimen in contact with S.D.C multifibre stripe
* Allow the Specimen to soak for 30 min
* Place the specimen glass slide and lightly scrap of with a glass rod.
* Place the specimen indicator for hrs at 37º C. Then remove from incubator open out keep sometime in open air.
* Repeat the same process with another specimen using the acid solution.
Assessment: Assess the change in color of each specimen and the staining of the multifibre strip using the grey scale.
Report: Record the change in color of each specimen and & the staining of the individual components of the multifibre adjacent fabric separately for both the acid alkaline test.
Check:
Purpose: To fulfill the buyer requirements to keep the pH of the fabric as Per standard.
Method: ISO-105C06
Procedure:
* Take 3 Pieces of 2 gm sample
* Take 100ml of distilled water (pH – 5.5 to 7.5) in three Conical Flack.
* Shake them for 1 hrs in normal temperature.
* Finally measures the pH by average them.
* Standard pH range for colored fabric 6 to 8
Shrinkage and Spirality Test:
Shrinkage and Spirality both are very important for control the quality of fabric. Buyer considers + 5% allowance for both Shrinkage and spirality.The scale is 50 cm long.
Instrument:
- Washing m/c
- Measurement tape
- Scissors etc.
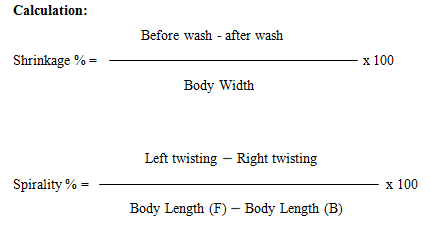
Quality Control:
Mainly this factory follows ISO-105C06 Standard. But testing Standard depends on buyer requirements.
Remarks:
Quality Control is the most important department in every Textile industry. It is strongly recommended that the Quality should be maintained as exactly the buyer’s requirements.
R & D (Research & Development)
R & D fabrication:
- Sampling order receiving from Merchandiser.
- Selection of yarn.
- Knitting parameters setting.
- Finishing parameters setting (Samples + Production).
- Samples inspection according to four point system.
- Testing of samples.
- Checking parameters at every stage (Knitting, Dyeing & Finishing).
Process flow of R& D:
Maintenance
The term maintenance has the following meanings:
- Any activity – such as tests, measurements, replacements, adjustments and repairs — intended to retain or restore a functional unit in or to a specified state in which the unit can perform its required functions.
- For material — all action taken to retain material in a serviceable condition or to restore it to serviceability. It includes inspection, testing, servicing, classification as to serviceability, repair, rebuilding, and reclamation.
- For material — all supply and repair action taken to keep a force in condition to carry out its mission.
- For material — the routine recurring work required to keep a facility (plant, building, structure, ground facility, utility system, or other real property) in such condition that it may be continuously used, at its original or designed capacity and efficiency for its intended purpose.
Objects of maintenance
i. To keep the factory plants, equipments, machine tool etc in an optimum working condition.
ii. To ensure specified accuracy of products and time schedule to delivery to customers.
iii. To keep the down time of machines to the minimum.
iv. To keep the production cycle within the stipulated range.
v. To modify the machine tools to meet the need for production.
vi. To improve productivity of existing machines and to avoid sinking of additional capital.
vii. To reduce the maintenance costs as far as possible thereby leading to reduction in factory overheads.
- To prolong the useful life of the factory plant and machinery by retaining their acceptable level of accuracy of performance.
Function of maintenance
1.Inspection or check ups
2.Lubrications
3.Planning & Scheduling
5.Training of maintenance personnel
6.Storage of spare parts
7.Records & analysis
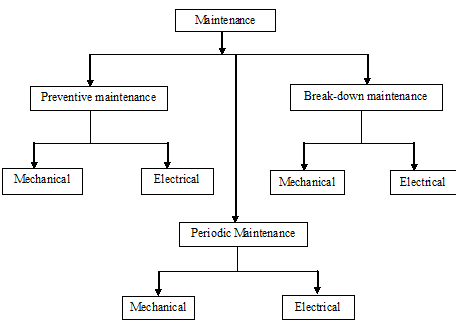
Types of maintenance at INCT
Preventive maintenance
Preventive maintenance refers to only a part of good maintenance program. It consists of routine actions taken in a planned manner to prevent breakdown & to ensure operational accuracy is economically & practically possible to do so.
Preventive maintenance, where equipment is maintained before break down occurs. This type of maintenance has many different variations and is subject of various researches to determine best and most efficient way to maintain equipment. Recent studies have shown that Preventive maintenance is effective in preventing age related failures of the equipment. For random failure patterns which amount to 80% of the failure patterns, condition monitoring proves to be effective.
Breakdown maintenance
Breakdown maintenance practice allows a machine to run without much routine attention fill it actually breakdown.
Periodic Maintenance
Maintenance of different machines is prepared by expert engineer of maintenance department for a period of time. Normally in case of dyeing machine maintenance after 30 days complete checking of different important parts are done.
Flowchart of maintenance
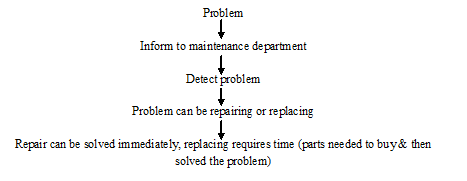
Advantages of maintenance
a) Reduction in production down time.
b) Lesser overtime pay for maintenance personnel.
c) Lesser number of stands by equipments is needed.
d) Less expenditure on repair.
e) Due to planned spare parts replacement, lesser spare parts are needed to keep reserve in store.
f) Greater safety to the employees because of reduced breakdown.
g) To get optimum production & optimum quality.
Requirements for good maintenance
a) Good supervision & administration of maintenance department.
b) Proper control of maintenance work.
c) Correct clear & detailed instruction should be given to the maintenance crew & to the operators.
d) A good lubrication program should be followed.
e) Proper maintenance record should be maintained.
f) Adequate stock of spares should always be kept.
g) Surrounding should be dust free & clean with proper ventilation & illumination.
h) Manufacturers of machine tools should be consulted when required.
i) Maintenance department should remain in contact with planning & purchasing department for deciding the type of machine tools to be purchased.
Planning of maintenance work
Following steps are involves planning of maintenance work:
1. Anticipation of maintenance work.
2. Determination of the best method to perform the work.
3. Scheduling of maintenance work to conform to production plans.
4. Arranging the required material.
5. Allocation of work to the individuals.
6. Instruction the individuals about schedules & methods.
7. Follow up & checking of work.
8. Evaluation of the work & performance.
Scheduling of work to specific time periods
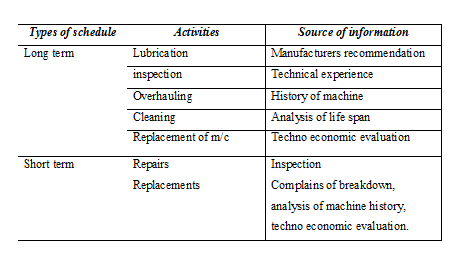
Evaluation of maintenance performance

Maintenance Tools & Equipments
Combination Tools/Spanner
Function: Tightening & loosening of nuts & bolts.
Socket Ratchet Set:
Function: Tightening & loosening of nuts & bolts.
Slide Range:
Function: Tightening & loosening of nuts & bolts.
Pipe Threat Cutting Tools:
Function: To cut the threat in pipe.
Bearing Puller:
Function: To assist the opening of bearing from shaft.
Pipe Range
Function: Tightening & loosening of pipe joint.
Pipe Cutting Tools
Function: For Pipe cutting.
Hole Punch
Function: Punching the hole.
Divider
Function: For circle marking on metal &wood.
Easy Opener
Function: To open the broken head bolts.
External Threat Die
Function: For external Threat cutting.
Heavy Scissor
Function: Cutting of gasket & steel sheet.
Oil Can
Function: Oiling of moving parts.
Srill M/C
Function: For drilling.
Grease Gum
Function: Greasing of moving parts.
Grinding M/C
Function: For grinding& cutting of mild steel.
Welding M/C
Function: For welding.
Spirit Leveler
Function: For perfect leveling.
File
Function: For smooth the metal surface.
Hammer
Function: For scaling & right angling.
Hacksaw Blade
Function: For metal cutting
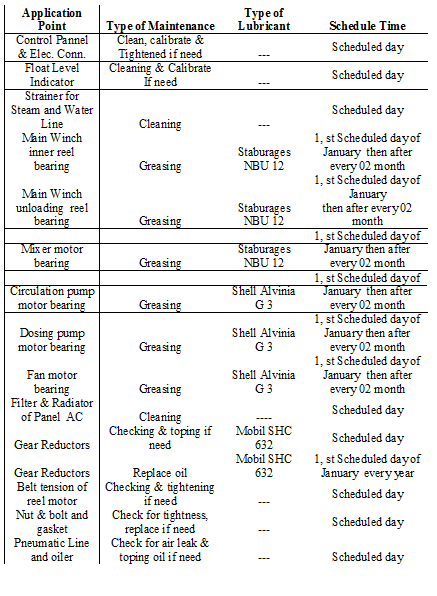
Yearly Maintenance Schedule for DILMINLER DYEING M/C
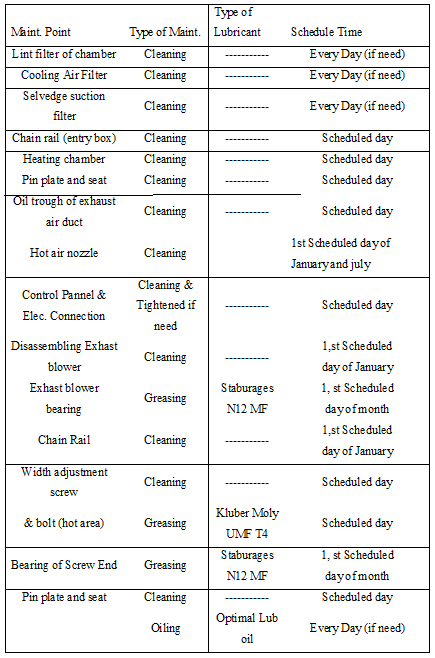
 9.13 Yearly Maintenance Schedule for STENTER M/C
9.13 Yearly Maintenance Schedule for STENTER M/C
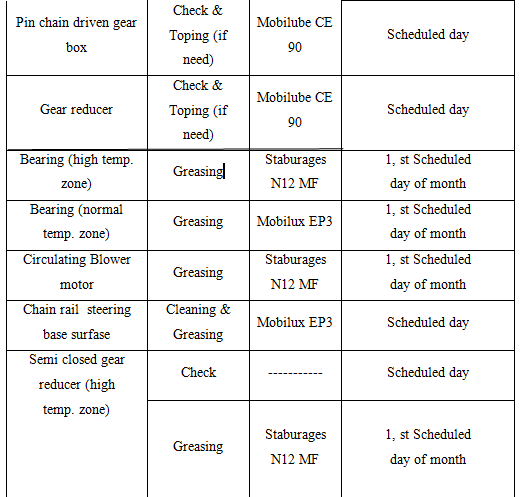
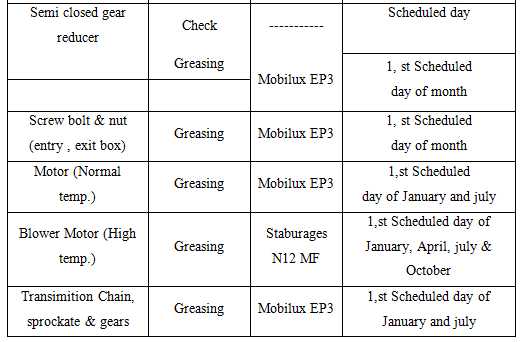
9.14 Maintenance of Generator (CATERPILLAR)
Oil change: After 2000 hr
Oil filter: after 2000 hr
Tefit adjust: 1000 hr
Air filter: 1000 hr
Maintenance of water pump:
Bearing, seal, capling, pump bearing, shaft etc portion.
Maintenance of Compressor (GARNDER DENVER)
Oil change: after 2500 hr
Air filter change: after 2500 hr
Oil separator change: after 6500 hr
Remarks:
Maintenance of machine is very essential to prolong the machine life and good maintenance is important for economical consideration.
In this industry maintenance program is done by expert maintenance team. So very few times production are stopped due to machine problem.
Utility Service
Utility Available and Source at INCTL
Electricity : Generator
Gas : TITAS
Water : Pumps
Compressed air : compressor
Steam : Boiler
Electricity
The main utility electricity is supplied from Generator. The total power is then distributed as per requirements of different section like knitting, Dyeing, Finishing, WPT, EPT and Garments.
Generator House:
No of generator: 03

10.3 GAS
Mainly gas is delivered from TITAS. It is mainly used for steam production. Generally 0.35 m3 gas is required to produce 1kw electricity. The price of 1m3 gas is 5.25 tk.
10.4 Water
Pump section
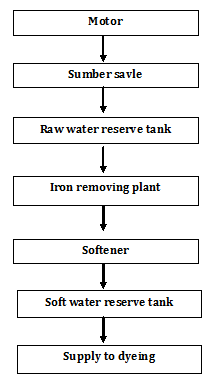
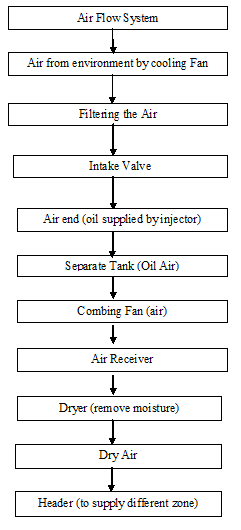
10.5 COMPRESSOR
Compressor is mainly used to deliver compressed air to different section as required. In KKDL Ltd 2 compressors are used to produce and deliver compressed air to different section.
10.5.1 Process Flow Chart
10.5.2 Compressor house
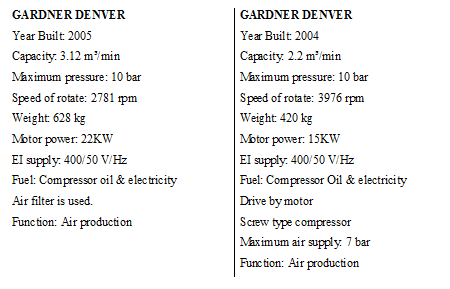
10.6 BOILER
Boiler is mainly used to produce and deliver steam to different section as required. In KKDL, there are 2 boilers to produce and deliver steam to different section.

10.6.1 Boiler Section at INCTL:
| MERCHMAR (Fire tube boiler)Fuel type: Natural gasElectricity supply: 415 V 50 Hz 3 PH Manufacture: 30-07-01 Origin: England Capacity: 11200 PPH Year Manufacture: 2001 Working pressure: 1034/150 N/mm²/PSI Design pressure: 1069/155 N/mm²/PSI Test pressure: 1604/233 N/mm²/PSI | HURST (Fire tube boiler)Year of manufacturing: 2006Origin: China Capacity: 10350 PSI Fuel: Natural Gas Steam LBs/hr = 10350 Maximum W.P. P.S.I. = 150 |
Store & Inventory Control
Inventory control:
Inventory control is a planned approach of determining what to order, when to order and how much to order to stock so that costs associated with buying and storing are optimal without interrupting production and sales.
Inventory Control reduces costly inventory errors, improves customer service, and will increase the value of our business. Wasp’s inventory software and inventory tracking systems are easy to use and implement without the cost or complexity of larger inventory tracking systems.
Inventory control is concerned with minimizing the total cost of inventory. In the U.K. the term often used is stock control. The three main factors in inventory control decision making process are:
- The cost of holding the stock (e.g., based on the interest rate).
- The cost of placing an order (e.g., for row material stocks) or the set-up cost of production.
- The cost of shortage, i.e., what is lost if the stock is insufficient to meet all demand.
The third element is the most difficult to measure and is often handled by establishing a “service level” policy, e. g, certain percentage of demand will be met from stock without delay.
An inventory control system is a process for managing and locating objects or materials. In common usage, the term may also refer to just the software components.
Objectives or importance of inventory control:
- 1. Financial objectives:
Hence the goal to keep inventory cost within the limits of funds available.
- 2. Property protection objectives:
These are twofold objectives in terms of end results to be achieved namely-
- To safe an important asset again theft, preventable waste, ensures able damage or unauthorized use.
- To make certain that the value of this asset is correct in the company’s book.
- 3. Operating objectives:
- To obtain the best overall balance between product & inventory carrying costs on one hand &customer service to the other.
- To minimize losses from price declines.
Functions of inventory control:
i. To develop policies, plans & standards to achieve inventory control objectives.
ii. To build up a logical & workable plan for doing the job satisfactory.
iii. To develop methods that will bring defined result economically.
iv. To provide necessary physical facilities.
v. To maintain overall control by checking result & adopting corrective action.
Types of inventory:-
1) Production inventories:
Items which are converted to final product by processing e.g. –raw materials.
2) In process inventories:
Semi-finished products at various stages of production.
3) Finished goods inventories:
Complete products ready for dispatch.
4) Miscellaneous inventories:
Scarp, Surplus & obsolete items.
Advantages of inventory control:
A well planned and properly administered system of inventory control will give the following benefits:
i. Improvement of customer frictions.
ii. Improvement of labor and community relations.
iii. Increase in the effectiveness of key personnel’s.
iv. Reduction in manufacturing cost.
Procedure for inventory control:
Control of incoming material:
When the goods from the supplies arrive at the factory gate. This form is filled up by the man at the gate. This form is known as stores Receipt Voucher (S.R.V). Here mentions the goods received date. Suppliers name, together with information regarding rejected or returnable goods.
Then the incoming materials go through the inspection the inspector will sign the S.R Voucher or the authorizes the store keeper to accept the goods. From the stores the S.R. Voucher will move to the accounts section which will in due course of time match it with the suppliers invoice before making any money payment.
Control of stores issue:
The material is issued from the stores against a particular numbers. On the basis of materials requisition note duly signed by the authorized person, usually it is raised in triplicate. One copy is retained in the authorized person’s office, one in the store & in the third copy moves from the stores to the central stock control department.
Where concerned persons will make necessary adjustment in their stock ledger & then to the costing department. Sometimes surplus material from the production departments are returned to stores under a note.
Perpetual inventory control:
To control the physical location & movement of the inventory. We usually use the perpetual inventory record. It usually shows the maximum & minimum limit of inventory receipts , issues & balance on any given date & quality etc. One of the simplest types of perpetual inventory control card is a bin card. It very easily facilitates the physical checking of the stores.
The type of inventory carried in INCTL as follows-
- Gray fabric : Own knitted or imported
- Dyes and chemicals: Local or Imported
- Spare parts : Local or Imported
- Packing materials : Local or Imported
- Finished fabrics : Good or Rejected
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS):
MSDS indicate above materials properties, chemical reaction, using method
Which are dangerous or not etc. It also indicates how the materials should be kept.
- Sulfuric acid (H2SO4)
- Hydrochloride acid (HCl)
- Caustic Soda (NaOH)
- Acetic acid (CH3COOH)
- Hydrogen peroxide ()
- Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl)
- Oxalic acid (COOH-COOH)
- Soda ash (Na2CO3) etc.
Stock position:
The materials which are stock in store room. From store room materials (dyes & chemicals) are taken when necessary.
Update:
Dyes must be stock, otherwise dyeing process will be hampered due to lack of dyes & chemicals.
For more production stock should be more & for less production stock should be less. Normally, May, June & July, these 3 months order is not available.
Store of dangerous chemicals:
Dangerous chemical: Caustic soda, Acetic acid, Hydrogen peroxide, Hydrose etc.
Keep:
- Cold places
- Used hand gloves
- Use eye protected glass
- Use gum boot
Store of Enzyme:
It should always keep in A.C. room.
Arrange dyes:
Arranging each color separately in a order (Red, Yellow, Black, Orange etc.)
Separate Spoon & pot:
Separate spoon & pot must be used for separate dyes & chemical. It has the following importance:
- Avoid unwanted mixture between two different dyes & chemicals.
- To avoid uneven shade.
- To ensure uniformly dyeing.
Safety measure to be taken during weighing & handling dyes:
- Hand gloves
- Eye glass
- Gum boot etc.
Rack:
There are some racks where dyes & chemicals are kept.
Life-time:
Life time means expire date. It is very important for dyes. If dyes life time is over then the dyes will give uneven shade.
Cost Analysis
Introduction:
Costing is a process by which the setting price of a product is calculated. It is a very important task for a factory which runs for business purposes.And it is also strictly followed in the Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. Costing of the products considering the raw materials expenditure, salary and wages of officers and workers, distributions and advertisement expenses etc. all direct and indirect expenses is done in this factory. It is determined by a troop of accountants with advice and consultancy of executive director.
Costing Of the Product:
The following points are considered for costing any dyed product in Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd.
- Total dyes & chemical cost
- Total utility cost
- Salary
- Payment
- Transport cost
- Entertainment cost
- Miscellaneous cost
- Government cash incentive
Price of the Product:
Generally price of product is determined by the required profit adding to the total expenses.
So,
Price of products= (Direct expenses + Indirect expenses + Factory Overhead) + Required profit
Knitting Charge of Different Fabrics:
| Fabric name | Charge per kg(Tk) |
| 09 |
| 30 |
| 16 |
| 16 |
| 16 |
| 16 |
| 17 |
| 30 |
| 25 |
| 22-25 |
Dyeing Charge of Different Fabrics:
Name of fabric process | Charge per kg(Tk) |
| 35 |
| 30 |
| 85 |
| 75 |
| 110 |
| 95 |
| 25 |
| 45 |
| 115 |
Costing of the Product:
Let price of yarn is $ 3.00/ kg.
Process loss of yarn for knitting (10%) = $0.30
Knitting fabric cost = $3.30
Cost of dyes & chemicals = $2.50
Process loss for dyeing (12%) = $0.30
Dyed fabric cost = $ 6.10
Packing cost = $0.05
Production cost of fabric=$6.15
Fabric price (with 25% margin) =$7.79
Fabric consumption/ doz. =
(Body length + Sleeve length) x Chest length x 2 x GSM x12 /10000000
Garments specification:
Body length=78 cm
Sleeve length=33 cm
Chest length=62 cm
GSM=210
Fabric consumption/ doz. = {(78+33) x62x2x210x12}/ 10000000
= 3.469 kg
Fabric consumption/doze (with 10% wastage) = 3.816 kg
Body fabric cost / doz. =$(7.79x 3.816)
= $29.73
Cost of collar& cuff/doz = $ 4.00
Cost of Trims=$ 2.25
Cost of Trims (with 5% Process loss) = $2.36
Production Cost of Garments/ doz=$36.09
Garments Price/doz (with 25% Profit) =$45.12
Remarks:
Costing is very important for a productive factory. Without proper costing all production curriculums will go to vain. Because a factory cannot reach to its goal without achieving good profit and good profit is not possible without skillful costing. In Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd.There are some skillful personnel to do this job.
Marketing Activities
MARKETING ACTIVITIES:
Consumers of Product:
Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. is a 100% export oriented industry. All the goods produced in this industry are exported into various foreign countries.
Product Label:
Product label differs from buyer to buyer. The product labels are prepared according to the fabric criteria & the buyer requirements.
Package Size & Label Market:
Package size & label differs from buyer to buyer. The Package size & label are prepared according to the buyer requirements.
Importing Countries:
There are some countries which are importing goods from Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. Which are given below?
• Belgium
• Netharland
• Germany
• Sweden
• Japan
Manpower of Marketing:
Marketing plays a vital role in the field of displaying / showing the goods criteria of the products to the buyer & to communicate with the buyer. There are about 15 people in the marketing section of the industry.
Marketing Strategy:
Marketing strategy is a very important factors to sale the products to the buyer. If the marketing strategy is not so developed, it will be very hard to reach the goal. In case of garments marketing the dealings with the buyer is a very important factor.
Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. mainly senior marketing officers, merchandiser & higher officials deal with the buyer. There are some fixed buyers of the industry. The buyers give their orders continuously all over the year. The marketing officers & the merchandisers communicate with the buying houses to collect the orders.
By both side understanding the rate & the order quantity are fixed. A well defined marketing strategy has the following characteristics:
- Good quality
- Low price or competitive price
- Prompt service
- Good commitment r Good business communication
Duties & Responsibilities of Marketing Officer:
Job summery:
i) Market search
ii) Market development
iii) Customer’s motivation
iv) Production follow up
v) Technical assistance of customer
Dealing with the buyer & convince the buyer is the main duty of marketing officer. A marketing officer also has some other duties. The main duties & responsibilities of a marketing officer are given bellow
To prepare cost sheet by dealing with the buyer.
- To take different steps by discussing with the high officials & merchandisers To maintain a regular & good relationship between commercial officer & merchandisers
- To maintain a communication with the buyers and buying houses
- Communicate with better criteria of the products
Garment merchandising is an intricate and detail oriented job. If it can be done properly .can be very rewarding. On the country, if it is done with lack of knowledge. Insufficient skill and thoroughness, it can be destructive.
In the Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd, very skilled and experienced personnel run the merchandising section. After receiving an order, the merchandiser with the help of pattern master calculates the total consumption of fabric. Then according to the cost detail sheet and the price mentioned by the buyer costing is done. After the price is negotiated with the buyer order is placed to the suppliers of raw material and accessories.
The manufacturing factory as per the requirement suppliers the fabric and a ledger is maintained regularly to assess the production status. The accessories such as label, button, zipper, sewing thread, packing materials are collected from outside [sometime mentioned by the buyer] through back-to-back L/Cs. The merchandising department also looks for the sources for procuring yarns to produce fabric. Merchandising section monitors the production status regularly and ensures time delivery of the shipment.
Remarks:
MASCO INDUSTRIES Ltd has a well learned marketing & merchandising team. They always communicate with the buyers. Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. has some fixed buyers. The marketing section also looks the quality & quantity buyers.
MARKETING ACTIVITIES
Introduction:
INCT is 100% export oriented industry. All the goods produced in this industry are exported into various foreign countries.
Product label differs from buyer to buyer. The product labels are prepared according to the fabric criteria & the buyer requirements.
Recent Buyer of INCTL:
- H & M
- ZXY
- TAG & HAPPA FASHION
- IMPRESS PRENATAL
- TEEN AGE
- ARTSANA
- GDS
- AWG
- MERCHANTEX
- BILLA AG
- IMPRESS CONFORMA
- CENTERLINE
- IMPRESS OLIMPIAS
- IMPRESS GARTICO
- BROVA
- DESIGN TEX
- PROM TEX
- DIKIES and so on.
Marketing Strategy
Marketing Strategy is a very important factors to sale the products to the buyer. If the marketing strategy is not so developed, it will be very hard to reach the goal. In case of garments marketing the dealings with the buyer is very important factor.
INCT mainly senior marketing officers, merchandiser & higher officials deal with the buyer. There are some fixed buyers of the industry.yhe buyers give their orders continuously all over the year. The marketing officers & the merchandisers communicate with the buying house to collect the orders.
By both side understanding the rate & the order Quantity are fixes.
A well define marketing strategy has the following characteristics:
- Good quality
- Low price or competitive price
- Prompt service
- Good commitment
- Good business communication
Remarks:
INCT has a well learned marketing & merchandising team. They always communicate with the buyers. INCT has some fixed buyers. The marketing section also looks the quality & quantity buyers.
Water Treatment and Disposal system
14.1 Water Treatment Plant (WPT)
Water for a textile plant may come from various sources. But this water can not be used directly in textile processing because it contains various salts. These salts are mainly the carbonates (CO32-), Hydrogen carbonates or bi-carbonates (HCO3–), Sulphates (SO42-) and Chlorides (Cl–) of Calcium (Ca2+), and Magnesium (Mg2+). These are called hardness in the water. These must be removed though water treatment plant.
14.2 Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
The effluent generated from different sections of a textile industry must be treated before they are discharged to the environment. Various chemicals and physical means are introduced for this purpose.
Capacity : 40m3/ hr
Cost : Tk. 2.5 / m3

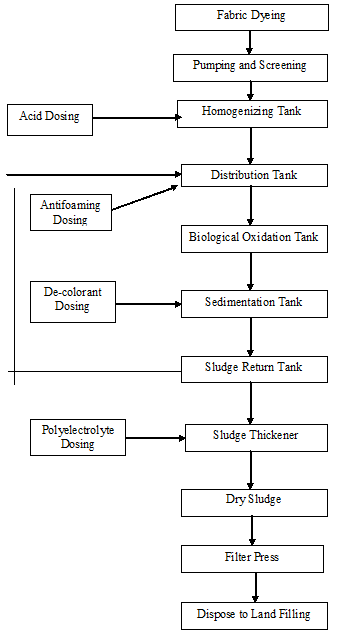
14.3 Process Flow chart of Biological Effluent Treatment Plant
14.4 Function of different Unit of Biological Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
Screening unit
It works like a filter. By filtering waste water, it removes threads, pieces of fabrics, small metal pieces etc. In this unit a rotating brush is used for clean the pores if screen. The brush rotates periodically.
Storage and Homogenization tank
Different waste water from varies process is stored and makes a homogeneous mixture by mixing different concentration of waste water.
Neutralization tank:
Neutralization of waste water is performed by dosing 98% H2SO4 as required to control the PH of waste water PH range 6.5 to 7.5.
Distribution tank:
It distributes the water to the biological oxidation tank. Continuous aeration is supplied here. Antifoam is dosed here to control the foaming in the oxidation tank.
Biological oxidation tank:
It is the heat of E T P. The entire harmful chemicals are damaged here by breaking their bonds. This is done by bacteria. To ensure the proper function work and growth of bacteria, few conditions must be maintained.
- Temperature : 35º to 37º C
- (Maximum) : 6.5
- Dissolved oxygen : 4 PPM
Sedimentation Tank / Biological feeding tank:
Treated water is overflowed here from oxidation tank. Decolourent is used here to destroy the color of waste water.
Settling tank / Sedimentation Basin:
A tank or basin in which waste water is held for a period of time, during which the heavier solids settle to the bottom and the lighter material will floats to the water surface. In this tank sludge is immersed and the harmless water is discharge to ponds, Land, river etc.
Sludge Thickener:
Sludge taken here from clarifier. Polyelectrolyte is dosed coagulate the sludge. After one hour of polyelectrolyte dosing aeration is stopped and fresh water discharge to drain when sludge is taken. The thickened sludge is transferred to the sludge thickener bed.
Sludge Thickener bed:
Here sludge is dried which is used as good fertilizer as well as fuel of brick field. Sludge is dried under the sunlight.
Required Chemical for Biological ETP:
H2SO4:
Function: Neutralize the waste water controlling the PH. It is auto dispensed in the neutralization tank.
Polyelectrolyte:
Function: Used for sedimentation / sludge coagulation and also killing bacteria.
Antifoaming Agent:
Function: Used for reduction / controlling foam. It is used auto / manually in the distribution tank.
De-colorant:
Function: Used for removing color. It is used auto / manually in the sedimentation feeding tank.
Sodium Hypochlorite:
Function: It is used to kill the harmful bacteria. It is used in the biological oxidation tank.
Product Quality Checked:
- Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD)
- Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD)
- Total suspended solids
- Total dissolved solids
- Color
- etc.
Remarks
Waste water from processing industries e g. Dyeing , Printing , Finishing and washing causes great harmful effect on our environmental, As a result agricultural land loses its fertility, natural water becomes polluted aquatic life is destructive and crops are damages.
So, it is important to control ETP plan.
CONCLUSION
There is large difference between the theoretical knowledge and practical experiences. This is truer in case of the study of Textile Technology. Industrial attachment or Industrial training is an essential part for textile education because it minimizes the gap between theoretical and practical knowledge. This industrial training increases our thought a lot about textile technology. It also helps us to know a lot about industrial production process, machineries, and industrial management and made us suitable for industrial life. Besides it gives us the first opportunity to work in industry. So we can say industrial attachment prepare us for the expected destiny of practical life.
We have completed our industrial attachment from Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd. During our eight weeks long industrial training at Impress-Newtex Composite Textiles Ltd we got the impression that this factory is one of the modern export oriented composite knit garments industry of our country. This factory does not compromise in case of quality. So, they have established on-line and off-line quality control of each product. Besides, they also use the good quality yarn, dyes and chemicals in their production process. Due to this, it has earned a “very good reputation” in foreign market for its quality product over many other export oriented textile mills. It has very well educated and technically experienced manpower to get rid of any defect in production process. It has also a good organizational hierarchy.
There are some suggestions from us within our limited knowledge
SOME SUGGESTIONS:
- Knitting production needs to increase as well as technical persons need to be employed there.
- More skilled labor should be used in a project and the overall efficiency will increase.
- Dyeing floor should keep always neat and clean. It kept wet after unloading the fabric from the dyeing machine. Water must be swept time to time.
- During the transport of the fabric and during the loading of the machine, fabrics get soiled due to their drawing over the floor. This makes the fabric/part of the fabric dirty. It may require more scouring/bleaching agent or may create stain.
- Due to the pressure of higher production sometimes machine operators do not maintain accurate time according to the actual process so that less quality product is produced and may reject. So our suggestion is to increase machine and reduce the pressure on the operator.
- Should increase understanding between the top level personal and floor level personal.
- Finishing section need to be enlarged well as more technical persons need to be employed there.
- The machine stoppage time should be analyzed and minimized. The maintenance should be carried out when the machine is out of action (Wherever possible) and routine maintenance should be carried out regularly.
- In knitting and finishing section, every worker should use mask to make protect them from fly. Otherwise the exhaust air system should be more effective.
- Workers are not interested to wear their gown & hand gloves.
- Some workers do not want to maintain the proper time and temperature of dosing of dyes and chemicals; proper rinsing, soaping or proper dyeing procedure.
- Proper follow-up required at knitting, dyeing & finishing section by the key personnel.
- In the Laboratory, there is no technical person; a textile engineer (B.Sc) may be employed here.
- There is shortage of proper light in the dyeing and finishing floor, specially, when smoke is produced from dryer and Stenter. Proper lighting should be provided in the floor.
- Knitting and finishing floor is jammed with fabrics, so it should have to be neat and clean.
- The person at the top level of a department must take good care of the trainees & he should provide all kinds of support to them.
Limitations of the report:
- Because of secrecy act, the data on costing and marketing activities have not been supplied.
- We had a very limited time. In spite of our willing to study more it was not possible to do so
- Some points in different chapters are not included as these were not available.
- It is not possible to hold the whole thing of a textile industry in such a small frame as this report. So, try our hard to summarize all the information that we are provided.