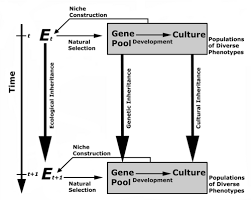
In Dual Inheritance Theory, culture is thought as information and conduct acquired through cultural learning. One in the theory’s central statements is that way of life evolves partly via a Darwinian selection practice, which dual gift of money theorists often summarize by analogy to genetic evolution. Dual inheritance theory, also called gene–culture coevolution as well as biocultural evolution, was developed in the 1970s and reveal how human behavior is a product of a couple of different and evolutionary processes: hereditary evolution and ethnic evolution.
Dual Inheritance Theory