Combined leverage is the leverage that refers to high profits due to fixed costs. The combination of operating leverage and financial leverage is called total leverage or combined leverage. It includes fixed operating expenses with fixed financial expenses. Operating leverage measures operating risk whereas financial leverage measures financial risks. It indicates leverage benefits and risks which are in a fixed quantity. Total leverage or combined leverage measures the total risk of the business. It measures the total risk of a firm. If operating leverage is greater than financial leverage then the firm should try to reduce it to maintain the level of risk vice versa. With the help of it, we can find out the effects of fixed operating cost and fixed financial charges on operating profit and earnings per share respectively.
Combined leverage shows the total risks associated with the firm. With the help of it, we can find out the effects of fixed operating cost and fixed financial charges on operating profit and earnings per shares respectively.
This leverage shows the relationship between a change in sales and the corresponding variation in taxable income. Operating leverage is measured by the percentage change in earnings before interest and tax due to percentage change in sales whereas financial leverage is measured by the percentage change in earnings per share due to percentage change in earnings before interest and tax. If the management feels that a certain percentage change in sales would result in a percentage change to the taxable income they would like to know the level or degree of change and hence they adopt this leverage. It is a combination of financial and operating leverage.

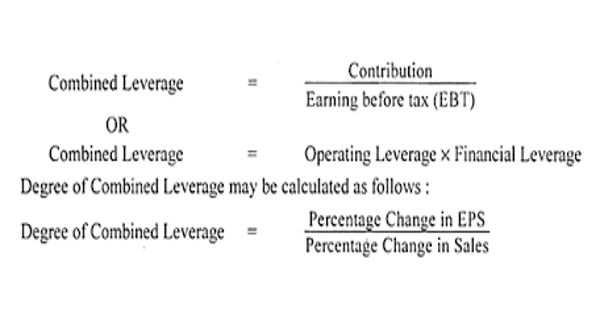
Formula:
If one income statement:
Combined Leverage = contribution margin / earnings before tax (EBT)
OR
If two income statements:
Degree of Combined Leverage =% change in earnings before tax (EPS) / % change in sales
OR
Degree of Combined Leverage (DCL) = DOL*DFL
Where,
DCL = Degree of Combined Leverage
DOL = Degree of Operating Leverage
DFL = Degree of Financial Leverage
Thus, the degree of leverage is adopted to forecast the future study of sales levels and resultant increase/decrease in taxable income. It indicates leverage benefits and risks which are in a fixed quantity. This decree establishes the relationship between contribution and taxable income. If operating leverage is greater than financial leverage then the firm should try to reduce it to maintain the level of risk vice versa.
Information Source: