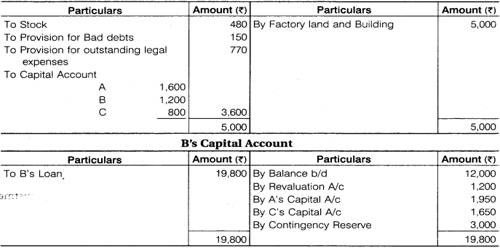
Working Capital is the difference between a company’s current assets, such as cash, accounts receivable, and inventories of raw materials and finished goods, and its current liabilities, such as accounts payable. Business organization requires adequate capital to establish business and operate their activities. The total capital of a business can be classified as fixed capital and working capital. It is considered the backbone of every business as it plays a very important role in the growth of the business. Net operating working capital is a measure of a company’s liquidity and refers to the difference between operating current assets and operating current liabilities. A company has negative working capital If the ratio of current assets to liabilities is less than one. Positive working capital indicates that a company can fund its current operations and invest in future activities and growth.
“Working Capital is considered the backbone of every business as it plays a very important role in the growth of the business. is a measure of a company’s liquidity, operational efficiency, and its short-term financial health.”
Working capital is a measure of a company’s liquidity, operational efficiency, and its short-term financial health. If a company’s current assets do not exceed its current liabilities, then it may have trouble growing or paying back creditors, or even go bankrupt. Fixed capital is required for the purchase of fixed assets like building, land, machinery, furniture, etc. That’s why financial managers give the utmost importance to working capital management for a healthy financial position of the firm. Fixed capital is invested for long period, therefore it is known as long-term capital. Similarly, the capital, which is needed for investing in current assets, is called working capital. The primary purpose of working capital management is to enable the company to maintain sufficient cash flow to meet its short-term operating costs and short-term debt obligations.
Generally, working capital refers to the current assets of a company that is changed from one form to another in the ordinary course of business, i.e. from cash to inventory, inventory to work in progress (WIP), WIP to finished goods, finished goods to receivables and from receivables to cash. The capital which is needed for the regular operation of the business is called working capital. Working capital is also called circulating capital or revolving capital or short-term capital. It is that part of a firm’s capital that is required to hold the current assets of the firm. Working capital is used for regular business activities like for the purchase of raw materials, for the payment of wages, payment of rent, and of other expenses. Examples of current assets are raw material, semi-finished goods, finished goods, debtors, bills receivable, prepaid expenses, cash at bank, and cash in hand. Working capital is kept in the form of cash, debtors, raw materials inventory, stock of finished goods, bills receivable, etc.