Definition of Merchandising:
The word merchandising has become very popular in the garments trade of Bangladesh. And the job of merchandising has also taken a very popular dimension in the country. The concept of marketing & merchandising has somewhat merged under the cover of the phase merchandising.
“Merchandising means planning, development & presentation of a product for a target market in respect of prices, assortment, timing, styling etc.
The job of merchandisers has, of late become very difficult & complex due to a number of reasons:
- Frequent fashion change.
- Complex channels of distribution & sales.
- Growing complexity of line & product development.
- Increasing emphasis on quick response relationship between buyer-vendor-customer etc.
Apparel Merchandising
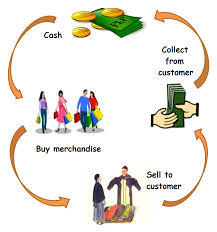
Merchandising -Merchandising involved with trade (buy & sale).
Apparel Merchandising – Apparel merchandising involved in garments trade (goods are bought and apparel sold).
Definition of Merchandising – Merchandising may be defined as: – Person who merchandises the goods, specifically for export purposes. Term Apparel Merchandising means:-
- Order confirmation by negotiation
- Buying raw materials and accessories
- Producing garments
- Maintaining required quality level
- Exporting the garments with in schedule time
From the above definitions, we can say that a person who involved in apparel merchandising needs a wide range of knowledge and skills to perform his/ her job successfully. The job itself is Technical and general as well.
MERCHANDISING:
Merchandising may be defined as-Person who merchandises the goods, specifically for export purposes. Element of marketing concerned especially with the sale of goods and services to customers. One aspect of merchandising is advertising, which aims to capture the interest of the segment of the population most likely to buy the product. Merchandising also involves product display; companies provide retailers with display and promotional materials and negotiate shelf space for their products. The development of sales strategies includes the determination of pricing, discounts, and special offers; the invention of sales pitches; and the identification of avenues for sales, including store-based retailing and alternative means such as direct-mail marketing, telemarketing, commercial Web sites, vending machines, and door-to-door sales.
Merchandising, as commonly used in Marketing also means the promotion of merchandise sales, as by coordinating production, marketing and developing advertising, display and sales strategies to increase retail sales. This includes disciplines in pricing and discounting, physical presentation of products and displays, and the decisions about which products should be presented to which customers at what time.
Merchandisers make sure that goods are available in the right stores, at the right time and at the right price. They work closely with buyers to forecast trends, plan stock levels and monitor how well goods are selling. Buyers select the product ranges, while merchandisers aim to maximize profits by deciding which lines will sell, how much to spend on stock, how much to buy and what price to sell at.
SKILLS & KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED FOR APPAREL MERCHANDISER:
Apparel Merchandiser should process the following basic knowledge and skills:
1. Good commend of English and good communication skills in English.
2. Good knowledge of Yarn, Fabric, Dyeing, Printing, Finishing, Dyes, Color Fastness, Garments production, etc.
3. Clear conception of the usual Potential Quality problems and garment manufacturing.
4. Good knowledge of the usual raw materials inspection systems and garments inspection system.
5. Knowledge of quota system and category countries, duty rate, custom regulation, shipping and banking documentation.
Roles & responsibility of merchandising:
Merchandisers generally perform a very hard responsibility. In order to satisfy customer by delivering specified goods of specified quality on designated date, he has to coordinate with all the concerned departments of manufacturing factory, supplier organization & the buyer. He needs to cut a balance between quality, lead time, delivery schedule & price of the merchandise. He also takes the responsibility of securing order, sourcing materials, follow-up of production, costing quality & delivery schedule under tight deadline.
When an export order is placed to a merchandiser, he has to schedule the following main functions to execute the export order perfectly in time (schedule):-
- Fabric requirement calculation (consumption, YPD).
- Accessories requirement, calculation (Example, Thread, button, interlining, label, poly bag and cartoon etc).
- Sourcing of fabrics.
- Sourcing of accessories.
- Production follow-up with fabric and accessories, be possible date of arrival of fabric and accessories in garment factory.
- Costing of garments.
- Garment analysis and production planning.
- Performa making, swatch making and distribution to the production unit and quality concern people.
- Pre-shipment inspection schedule.
- Shipment documents
- Have to prepare proper time and action plan
- Arranging shipping documents and final inspection.
EXECUTION PROCESS FOR A GARMENT EXPORT:
- Order inquiry from buyer to factory.
- Approval of order from Buyer, as per the costing given by the Merchandiser.
- Buyer Bank gives master L/C to the factory. Commercial dept deals with the follow up of L/C matters.
- B/B, L/C is given to the suppliers of accessories and fabric, etc.
- Fit sample sent to the Buyer for fit approval.
- Pre-Production sample submitted to Buyer with original accessories and fabric.
- Fabric and trims to be in housed on due time as per time and action plan.
- Pilot production to be started as per time and action plan. (Pilot production or initial production can consist of 100to 200 pcs.)
- Online inspection by buyers Q.C certifies the quality of the garments.
- Bulk production to be started, as per the time and action plan.
- In the main time commercial section, prepare the shipping documents
- Final inspection as per time and action plan (after final inspection ok).
- Goods are made ex factory.
- Goods handed over to the shipping line (Sea shipment)
- Goods will reach to buyer port.
- Cost of fabric is to USA $ mts.
MERCHANDISERS WORK USUALLY INVOLVES:
- Understanding quick response for an order proceed
- Planning the range of products to be sold, with the buying team
- Analyzing sales figures and trends
- Forecasting future sales and profits, using computer programmers
- Setting prices and sales targets
- Planning budgets and presenting sales forecasts to managers
- Negotiating prices with suppliers, placing orders and making sure that goods arrive on time
- Controlling stock levels, moving stock and making sure that best-selling products are always available
- Promoting or reducing the prices of slower-selling lines
- Visiting suppliers and stores to discuss how products are selling.
Most merchandisers specialize in a particular type of product, such as apparel merchandiser, Fashion merchandiser etc.
Merchandisers for large retail chains may be known as product managers and deal only with one or two product lines. In smaller companies they may be responsible for both buying and merchandising.
KEY OF APPAREL MERCHANDISING:
To be a merchandiser-
- Good business sense and an understanding of what customers or buyers want
- Good analytical and mathematical skills
- Decision making ability
- Good communication and negotiation skills
- Creative flair
- The ability to work well in a team
- Excellent organizational and planning skills
- The ability to work under pressure
- Good computer skills, especially in using spreadsheets.
Documentation of merchandising:
Production merchandising process starts once the order / fabric commitment is received and the product development department hands over the file to production merchandiser and ends when the goods reach the buyers. The entire cycle involves all activities directly or indirectly related to procuring of materials, planning and monitoring of the order.
1. Order confirmation document:
- Copy of master LC.
- Contract sheet:
- Contract no
- Style no
- Shipment date
- A.Q.L
- Order quantity & size Ratio
- Fabric description
- Labels & position
- Buyer’s comments & regarding approved sample.
- Proved trim card.
2 Import document:
- Performa invoice.
- Commercial invoice.
- Packing list.
- Utilization permission.
- PSI (Pre shipment Inspection) Certificate.
3. Documentation on received of the material at the factory:
- Inventory report.
- Swatches (on received fabric and accessories).
4. Documentation: Production oriented
- Production Plan.
- Daily production report.
- Daily quantity report.
- Daily production and inspection report
5. Export documentation:
- IC (Final Inspection certificate).
- BL (Bill of lading).
- AB (Airway bill).
- PL (Packing list)
- Certificate of origin.
PROCESS FLOW:
Production merchandising process starts once the order / fabric commitment is received and the product development department hands over the file to production merchandiser and ends when the goods reach the buyers. The entire cycle involves all activities directly or indirectly related to procuring of materials, planning and monitoring of the order.
MERCHAINDIING PROCESS:
Receipt of order beat:
Receipt of an order means final confirmation of the order from the buyer.
Since, this is the final confirmation it is done by means of a legal document
called a PO (purchase order) or an FC (fabric commitment).
Purchase order:
This is a legal document stating the quantity, delivery, price, style no, buyer, vendor details. On receipt of a PO it is very important that the merchandiser checks all details and confirms that they are correct like – quantity, delivery date, and price, style no, style description, color no & reference if mentioned, shipment mode, shipment port, vendor address, buyer address.
Fabric commitment:
Fabric commitment is a legal document confirming that the buyer will be buying the said quantity of a particular fabric. A garment style no need not be mentioned on this document as it is a commitment only for buying fabric. This kind of a legal document is used by the buyer when there are very probable chances of change in the style or the same fabric is being used in a number of styles and the buyer has still not decided on the quantity to be purchased in each of the styles. Hence in such a situation the buyer gives a block booking for fabric.
Once the order is received four different activities are started off simultaneously. These activities are – preparing a detailed T&A, Fabric Ordering, Trim Ordering, fit cycle and sample approvals.
T&A (Time & action):
Preparation of a detailed time and action (T&A) calendar is very essential in production merchandising. The reason being, large no of activities have to be followed up for each order and a merchandised may be handling large number of such orders and hence it is essential that all activities are listed. This minimizes the risk of missing out any of the activities. Hence while preparing a T&A one should list down as many activities as one can think of which are essential in smooth running of the order. A detailed discussion on T&A is done later in this module.
This T&A is prepared by the merchandiser in consultation with all the concerned departments such as – sourcing (fabrics & accessories), production, and quality assurance, logistics.
Once the T&A is finalized the same should be circulated to all concerned departments. Another important aspect of the T&A is fixing the responsibility. Along with finalizing the date by which a particular activity has to be completed, the merchandiser should also mention the name of person who is responsible to complete the activity by that time.
Fabric ordering:
This activity involves ordering of fabric with the mill. The important points to be taken care of during this activity are:
- Accurate computation of the requirement. This is essential to ensure that during bulk production the materials do not fall short nor are they in access and there are leftovers after the order is shipped. An accurate calculation of material requirement can be done if the BOM (bill of materials) as provided by the buyer in the specification sheet is studied thoroughly. Apart from just ensuring that the quantity is correct the BOM also helps in checking that all materials required in completion of the order are ordered and nothing has been missed out.
- Selecting the best vendor for the materials in terms of quality, price and delivery.
- The fabric order is places by the merchandiser by means of a purchase order. The purchase order should list down the following very clearly:
- Name & Reference no of the article
- Quality description of the article
- Quantity
- Price
- Delivery date
- Quality parameters as required by the buyer
- Payment terms
- Pilot yardage requirements if any
- The mill sends a PI (Performa invoice) confirming the details as mentioned in the PO. In case of any changes required in the PO the same are also mentioned in the PI. The mill also provides its bank details on the PI so that the factory can work out the payments.
- There can be various kinds of payment term agreements between the buying and the selling parties as below.
- Some % of payment in advance, the balance at sight. Example, 20% advance, 80% at sight. This means that 20% of the total value of goods is paid in advance, the balance 80% is pain once the goods are received by the buyer (factory). This payment can be done by means of DD (demand draft), check or TT (telegraphic transfer)
LC (letter of credit):
In this payment mode the banks of both parties are involved. The buying party (factory in case of fabric) opens up a LC with its bank and the same is transferred to the mills bank. On acceptance of the LC by the mills bank, this becomes a legal contract between the two parties. Once the goods are dispatched the mill submits the dispatch details (Invoice, packing list and Air way bill details) in its bank and gets the payment for the goods. The mills bank then approaches the factories bank and gets its payment from the same. The factories bank then gets the payment from the factory. The LC once made, a copy of the same should be called in by the merchandiser and studied to make sure all details as mentioned are correct.
The details to be looked at are:
- Name & Reference no of the article.
- Quality description of the article.
- Quantity
- Price
- Delivery date
- LC expiry date
Pilot Yardage:
Pilot yardage helps is ascertaining any problems that may come in the bulk yardage. The mill processes the first 100 – 200 yardage to ensure that the same meets the quality, color parameters as laid down by the customer. This helps the mill in taking corrective actions to eliminate any defects or problems. On the other hand the factory also requires yardage to complete all the pre-production processes such as sample approvals, size set etc. This pilot yardage helps the factory in making all the pre-production samples. Also the factory does fabric inspection and fabric shrinkage test to have an idea of how the bulk fabric will behave. At this stage if factory observes any problems in fabric behavior the same is immediately conveyed to the mill so that the mill can take corrective action.
- Next, prior to bulk fabric shipment the mill dispatches fabric shade bands, fabric inspection report and fabric test report.
Fabric inspection report:
This is generally a third part inspection done by buyer nominated inspection company like ITS, MTL etc. The most common and used method of inspection is the 4-point system. In this system every defect is given a point between 1 to 4 based on the nature of the defects. A maximum of 4 points per yards of fabric can be allocated. Fabric having more those 40 points per 100 square yards is considered to be reject. Different customers have different point levels depending upon how premium the brand is and also on the nature of the fabric. For example: a man made fiber should have lesser defects that a natural fiber and hence acceptable points level for polyester is kept lower that that of cotton.
Fabric shade band:
The mill segregates the fabric on the basis of shade and makes a shade band. In general a maximum of 3 shade bands are acceptable by customer, however this can again vary from customer to customer. The customer evaluates the different shades by means of a grey scale rating as acceptable.
Fabric test report (FPT – fabric performance test):
Yardage from bulk is sent to the nominated testing laboratory such as MTL, ITS for testing the physical and color parameters of the fabric as required by the customer. The testing laboratory also provides a wash care instruction for the fabric, which essentially means the best washing conditions for the fabric.
Fabric shrinkage report:
The mill tests 10% of the fabric to confirm that the fabric adheres to the specifications as laid down by the customer. For example if the customer accepts +/- 3% shrinkage, fabric having 5% shrinkage is rejected. The determining the shrinkage the fabric is tested as per the best washing conditions advised by the testing laboratory on the fabric test report.
- Once fabric passes through all the above tests and inspections it is shipped to factory. The factory again checks the fabric on 4-point system and also checks the shade bands and also does fabric shrinkage test to confirm that they adhere to the requirements of the buyer.
- With regards to fabric inspection the factory generally inspects 10% of the fabric, in case there is a problem the factory goes on to inspect 100% of the fabric.
For fabric shrinkage test:
Different procedures have to be adopted for ascertaining the shrinkages for a washed and a non-washed style.
- In case of a non-wash garment testing 10% of the fabric is sufficient to determine the shrinkage that needs to be included in the pattern. The fabric is washed based on the recommended wash care instructions in the FPT.
- In case of a washed garment, 100% fabric should be tested for shrinkage. The test is done as per the wash recipe. Once all rolls are tested, the rolls are segregated as per the shrinkages and different patterns are made to incorporate the shrinkages.
- Factory then also checks the fabric for shade banding, compares the same with the once sent by the mill and if found acceptable sends one sent out to log the same with customer. Once the buyer confirms that the shade bands are ok, the fabric is ready to be cut.
Trim ordering:
A similar process as done for the fabric is done for trims except for pilot trims. The factory can call in trims for sampling and these are called as PROMO TRIMS.
Sample approval:
While fabric and trim ordering is happening, simultaneously the sample approval procedure is also underway. The moment a style is selected it goes to the tech department for fitting. Here models wear the samples and they are evaluated in terms of fit, construction, measurement. The buyer then sends out comments, which are called as fit comments. In case another sample is requested the factory makes the same incorporating the comments and send again to buyer. This process is called fit cycle. Different customers have different no of fit cycles.
PP Sample:
Once the fit sample is approved the factory makes a PP (Pre-production) sample. This can be called by different names such as sealer sample, green tag sample etc. This sample is sent out the buyer for final approval and once approved becomes the final sample on the basis of which entire production is made and audited. This is the most important sample and one should take care that everything on this sample is correct as this then becomes the standard.
Size set:
Once PP sample is approved the nest step is to make a SIZE SET. All the fit samples and the PP samples are in the medium size, now the medium size is graded into the different sizes as per the purchase order. The basic purpose of size set is to ensure that grading between sizes is correct.
Pre production meeting:
In this meeting everybody concerned with the style sits together to make sure that everybody is on the same page and understands the product. Hence, this meeting has the merchandiser, production in-charge, cutting, finishing, fabric in-charge, line supervisor, pattern master, sample master etc. All tentative problems are discussed and solutions sought to execute the order smoothly.
Pilot run:
Once pre-production meeting is done the factory does PILOT RUN. Factory cuts 100 – 200 garments based on the order quantity. The pilot run is done on the assembly line and is aimed at ensuring that the operators of the assemble line understand the required quality levels. This is very essential since all samples prior to the pilot run (fit samples, PP & size set) are made in the sampling unit.
- Once Pilot run is approved the factory goes into bulk production. In line and interim inspections are preformed during the production process to ensure that the final product quality meets the required quality level.
- Once 80 – 90 % of the goods are packed a pre-final audit is done. This helps in taking corrective action if required before the final audit. Generally since the final audit happens very close to the shipment date, the pre-final gives factory a chance to amend problems if any.
- The last is the FINAL AUDIT. This is the last checkpoint before shipment. All aspects (packing, packaging, measurement, construction & visuals) are evaluated. Once the garments adhere to the required quality standards in all the parameters the shipment is passed and then the shipment is moved to thee logistic team.
- Now the merchandiser interacts with the logistic department, takes the shipment schedule and sends the same to the customer.