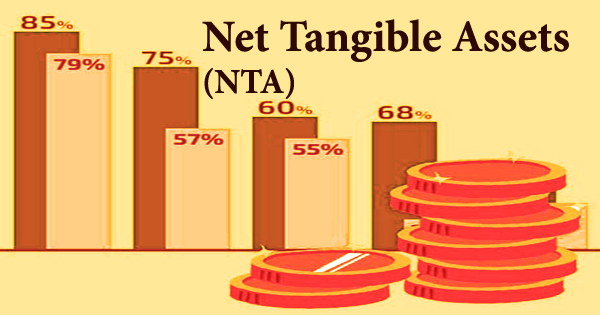
An investigation is the act of detail examination of activities so as to achieve certain objectives. Especially, an investigation is made in suspected places. An audit is the inspection, examination or verification of a person, organization, system, process, enterprise, project or product. On the other hand, an investigation is an inquiry, or the act of detail examination of activities so as to achieve certain objectives.
Dissimilarities between Auditing and Investigation – Following differences can be seen between auditing and investigation:
(1) Purpose
An audit is carried out for the purpose of ascertaining whether or not the balance sheet and profit and loss account show a true and fair view of the state of the company’s affairs and its profit or loss. The audit determines the true and fair view.
But an investigation aims at establishing a fact for some particular purpose i.e. to know the financial position of the concern or the earning capacity of the concern etc. It measures varies from business to business.
(2) On Behalf
An audit is carried out on behalf of the proprietor of the business, while an investigation may be conducted on behalf proprietors when they suspect any fraud in their business or on behalf of outside parties who wish to lend money or intend to purchase business or at the instance of the government on the request of the shareholders.
(3) Scope
An audit seeks to form an opinion on the financial statements. An audit includes only an examination of the accounts of a business whereas an investigation covers not only an examination of the accounts but also an inquiry into other relevant matters connected with the purpose for which it is undertaken. The investigation seeks to answer the questions, that are asked in the engagement letter.
(4) Use of Techniques
An audit is usually a test checking but an investigation is a much more thorough examination of the books of accounts. It goes into the depth of the problem and keeps on looking for far more definite evidence to arrive at the conclusion that it can firmly substantiate. Further, an investigation may be conducted even after the audit of the accounts.
(5) Period
An audit is related to only a year or six months while an investigation may cover several years.
(6) Statutory Obligation
Auditing is compulsory for every company. On the other hand, the investigation is discretionary. In the case of joint-stock companies, an audit is compulsory under the law while there is no such statutory obligation with regard to the investigation.
In Conclusion, auditing is performed by the auditor whereas an expert team does the performance of an investigation.
Information Source: