Business Objective and Strategies of Bank Asia Limited
Bank Asia has been launched by a group of successful entrepreneurs with recognized standing in the society. The management of the Bank consists of a team led by senior bankers with decades of experience in national and international markets. The senior management team is ably supported by a group of professionals many of whom have exposure in the international market.
It set milestone by acquiring the business operations of the Bank of Nova Scotia in Dhaka, first in the banking history of Bangladesh. It again repeated the performance by acquiring the Bangladesh operations of Muslim Commercial Bank Ltd. (MCB), a Pakistani bank.
In the year 2003 the Bank again came to the limelight with over subscription of the Initial Public Offering of the shares of the Bank, which was a record (55 times) in our capital market’s history and its shares commands respectable premium.
The asset and liability growth has been remarkable. Bank Asia has been actively participating in the local money market as well as foreign currency market without exposing the Bank to vulnerable positions. The Bank’s investment in Treasury Bills and other securities went up noticeably opening up opportunities for enhancing income in the context of a regime of gradual interest rate decline.
Bank Asia Limited started its service with a vision to serve people with modern and innovative banking products and services at affordable charge. Being parallel to the cutting edge technology the Bank is offering online banking with added delivery channels like ATM, Tele-banking, SMS and Net Banking. And as part of the bank’s commitment to provide all modern and value added banking service in keeping with the very best standard in a globalized world.
Mission Statement of BAL
- To assist in bringing high quality of service to customers and to participate in the growth and expansion of our national economy.
- To set high standards of integrity and bring total satisfaction to clients, shareholders and employees.
- To become the most sought after bank in the country, rendering technology driven.
- Innovative services by dedicated team of professionals.
Vision Statement of BAL
Bank Asia’s vision is to have a poverty free Bangladesh in course of a generation in the new millennium, reflecting the national dream. Our vision is to build a society where human dignity and human rights receive the highest consideration along with reduction of poverty.
Values of BAL
- Placing the interests of clients and customers first.
- A continuous quest for quality in everything the company does.
- Treating everyone with respect and dignity.
- Conduct that reflects the highest standards of integrity.
- Teamwork from the smallest unit to the enterprise as a whole.
Corporate Objective of BAL
- Highly personalized service
- Customer driven focus
- Total commitment to quality
- Outstanding products
- Contribute in the economy
- Commitment to its clients at each level
Corporate Slogan of BAL
“For a better tomorrow”
Product and Services, Schemes and Special Features
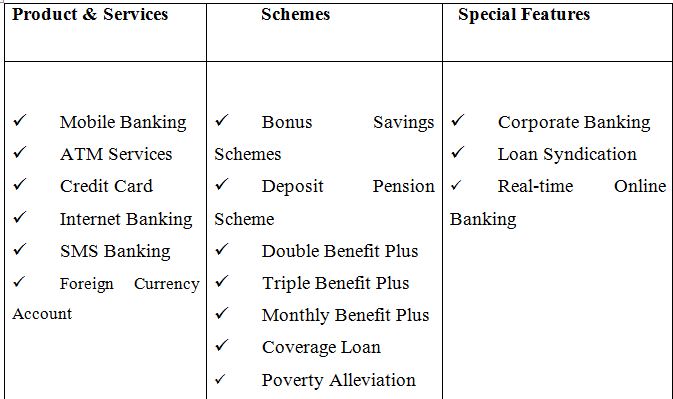
Table: Product and Services, Schemes and Special Features
Strategies
- To manage and operate the bank in the most efficient manner to enhance financial performance and to control cost of fund.
- To strive for customer satisfaction through quality and control and delivery of timely services.
- To identify customers credits and other banking needs and monitor their perceptions towards our performance in meeting these requirements.
- To review and update policies, procedure and practices to enhance the ability to expand better services to customers.
- To train and develop all employees and provide them adequate resources so that customers needs can be responsibly addressed.
- To promote organizational effectiveness by openly communicating company plans, policies, practices and procedures to all employees in a timely fashion.
- To cultivate a working environment that fosters motivation for improved performance.
- To increase direct contact with customers in order to cultivate a closure relation between the bank and its customers.
Trends of Branches Expansion
Bank Asia Ltd starts its journey not for very long. Till now it has only thirty three brunches. But Bank Asia Ltd had twenty nine brunches at end of year 2007.
The Bank had a tendency to open new branches every year; they had a average 20 growth of expansion. So Bank Asia Ltd had a very good branch expansion rate. The expansion rate was 21% during 2003 to 2004, 12% during 2004 to 2005, 26% during 2005 to 2006 and 21% during 2006 to 2007.
Number of Employees
Bank Asia Ltd creates new employment every year by opening new branches and expanding their existing departments. Bank Asia Ltd has a very good Growth rate of Employees the growth rate is increasing dramatically. The growth rate was 21%, 20%, 30% and 35% for the year 2004, 2005, 2006 and 2007 respectively.
HR Department of Bank Asia Limited
Each and every organization is composed of people. Acquiring their services, developing their skills, motivating them to high level of performance and ensuring that they continue to maintain their commitment to the organization are essential to achieve organizational objectives. Getting and keeping the desirable people is the most important thing for any organization. HR department of any organization ensure this things.
BAL invests extensively in its human resource development to build its employees capabilities. The goal is to empower staff and create a culture that encourages and rewards staff for their commitment, creativity and team work in order to respond rapidly to the ever changing customer needs and the market place.
Human resources Department of BAL is one of the most valued departments with the responsibilities of staffing, training and development, organization development, performance appraisals, rewarding, control and maintenance etc. With the start of BAL’s banking operation, the Human Resources Department (HRD) was not as strong and structured as it is now. The Human Resources Department of BAL consists of nine competent and experienced executives to carry out the whole responsibilities. The Human Resources Department of BAL stands in its Head Office at Purana Paltan under the direct supervision of the top management. The mission statement of HR Department is; “Employee of Choice, they will inculcate high performance culture where we will work with fun and pride”.
Now the BAL is trying to apply all sorts of modern HR activities related to their organization in order to achieve its mission.
The HRM Functions in BAL
HR department of BAL performs variety of activities Such as:
- Recruitment and Placement
- Training and Development
- Asserting Smooth Workflow in the Organization
Performance Appraisal System.
- Supervise the Employees
- Offer Attracting Compensation and Benefit Packages
- Maintain the Daily Attendance
- Provide Intrinsic Benefit
- Review the Salary Structure
- Review and Propose the upcoming Budget
- Perform the Administrative Activities for Smooth Functioning
- Create a Good Working Environment
- Implement the Disciplinary Action and so on.
The Structure of HR Department in BAL
In BAL enough to have a HR or personnel department, the personal director and his or her staff will play a key role in the designing and monitoring of human resources system. BAL is more likely to help design and implement HR system. A full-time specialist tends to emerge when organization have about one hundred employees. A standard structure of HR department in BAL is shown below:
Activities of HR Department in BAL
The activities performed by HR Department of BAL are given below:
- To control the administration of human resources of the bank.
- To access and collect compatible personnel who will be perfect for the bank.
- To take program and implement for developing human resources.
- To make appointment, promotion and appraising skill of officer and staff.
- To make service rules, correction, expansion administration rules, orders notice etc. for
- To maintain relationship with government and other institution.
- To access and grant retirement facilities at the time of retirement.
- To give general sip to the brilliant student of the university for appointing and finding skilled officer.
- To communicate with union scrutinizing their demands.
- To give loan for house building, by cycle, motorcycle and ensure their proper utilization.
- Developing relationship with administration proper implementation of labor law.
- To give medical facilities to the staff.
- To maintain relationship with retired or dead staffs and their families to know their condition.
- To maintain and grant leaves without regular leave.
- To coordinate and evaluate the branch office.
- To prepare and implementation policy about human resources and related activities.
- To control the activities the staff of the banks and take proper step to implement computer technology.
Human Resource Management System
Human Resource Management System (HRMS) applications consist of a broad set of business process and analytical capabilities spanning the employee life cycle, from hiring and on boarding, personnel and benefits administration, compensation, payroll, compliance, performance management, succession planning, and career development.
Importance of HRM Practices
The HRM is a foundational application suite used by companies of all sizes and in all industries. The need for an HRM practice is driven by several fundamental and potentially mission-critical business needs including:
- Managing personnel costs.
- Operating efficient business processes.
- Complying with regulations and managing legal exposures.
- Increasing the value of human capital.
Results Method Management by Objectives (MBO)
It aims to increase organizational performance by aligning goals and subordinate objectives throughout the organization. Ideally, employees get strong input to identify their objectives, time lines for completion, etc. MBO includes ongoing tracking and feedback in the process to reach objectives. Management by Objectives (MBO) was first outlined by Peter Drucker in 1954 in his book ‘The Practice of Management’. In the 90’s, Peter Drucker himself decreased the significance of this organization management method, when he said: “It’s just another tool. It is not the great cure for management inefficiency … Management by objectives work if you know the objectives, 90% of the time you don’t.”
Core Concepts
According to Drucker managers should “avoid the activity trap”, getting so involved in their day to day activities that they forget their main purpose or objective. Instead of just a few top management, all managers should:
Participate in the strategic planning process, in order to improve the implement ability of the plan and implement a range of performance systems, designed to help the organization stay on the right track.
Managerial Focus
MBO managers focus on the result, not the activity. They delegate tasks by “ negotiating a contract of goals’ with their subordinates without dictating a detailed roadmap for implementation .Management by objectives (MBO) is about setting yourself objectives and then breaking there down into more specific goals or key results
Main Principle
The principle behind Management by Objectives (MBO) is to make sure that everybody within the organization has a clear understanding of the aims, or objectives, of that organization, as well as awareness of their own roles and responsibilities in achieving those aims. The complete MBO system is to get managers and empowered employee acting to implement and achieve their plans. Which automatically achieved those of the organization.
Advantages
The MBO approach overcomes some of the problems that arise as a result of assuming that the employee traits needed for job success can be reliably identified and measured. Instead of assuming traits, the MBO method concentrates on actual outcomes. If the employee meets or exceeds the set objectives, then he or she has demonstrated an acceptable level of job performance .Employees are judged according to real outcomes and not on their potential for success, or on someone’s subjective opinion of their abilities. The guiding principle of the MBO approach is that direct results can be observed, whereas the traits and attributes of employees (which may or may not contribute to performance) must be guessed at or inferred. The MBO method recognizes the fact that it is difficult to neatly dissect all the complex and varied elements that go to make up employee performance. MBO advocates claim that the performance of employees cannot be broken up into so many constituent parts – as one might take apart an engine to study it. But put all the part together and the performance may be directly observed and measured.
Disadvantages
MBO methods of performance appraisal can give employees a satisfying sense of autonomy and achievement. But on the downside, they can lead to unrealistic expectations about what can and cannot be reasonably accomplished.
Supervisors and subordinates must have very good “reality checking” skills to use MBO appraisal methods. They will need these skills during the initial stage of objective setting, and for the purposes of self-auditing and self-monitoring. Unfortunately, research studies have shown repeatedly that human beings tend to lack the skills needed to do their own “reality checking”. Nor are these skills easily conveyed by training. Reality itself is an intensely personal experience, prone to all forms of perceptual bias.
One of the strengths of the MBO method is the clarity of purpose that flows from as also. It has become very apparent that the modern organization must be flexible to survive. Objectives, by their very nature, tend to impose certain rigidity.
Of course, the obvious answer is to make the objectives more fluid and yielding. But the penalty for fluidity is loss of clarity. Variable objectives may cause employee confusion. It is also possible that fluid objectives may be distorted to disguise or justify failures in performance.
Benefits of performance appraisals
Performance appraisals can be used to:
- Make employment decisions such as determining pay and promotions.
- Identify professional development needs.
- Identify factors in the work environment that help or hinder performance effectiveness.s
Motivation and Satisfaction
Performance appraisal can have a profound effect on levels of employee motivation and satisfaction – for better as well as for worse. Performance appraisal provides employees with recognition for their work efforts. The power of social recognition as an incentive has been long noted. In fact, there is evidence that human beings will even prefer negative recognition in preference to no recognition at all.
If nothing else, the existence of an appraisal program indicates to an employee that the organization is genuinely interested in their individual performance and development (Dewakar, 2008). This alone can have a positive influence on the individual’s sense of worth, commitment and belonging.
The strength and prevalence of this natural human desire for individual recognition should not be overlooked. Absenteeism and turnover rates in some organizations might be greatly reduced if more attention were paid to it. Regular performance appraisal, at least, is a good start.
Training and Development
Performance appraisal offers an excellent opportunity – perhaps the best that will ever occur – for a supervisor and subordinate to recognize and agree upon individual training and development needs.
During the discussion of an employee’s work performance, the presence or absence of work skills can become very obvious – even to those who habitually reject the idea of training for them Performance appraisal can make the need for training more pressing and relevant by linking it clearly to performance outcomes and future career aspirations. From the point of view of the organization as a whole, consolidated appraisal data can form a picture of the overall demand for training. This data may be analyzed by variable such as sex, department, etc. In this respect, performance appraisal can provide a regular and efficient training needs audit for the entire organization.
Recruitment and Induction
Appraisal data can be used to monitor the success of the organization’s recruitment and induction practices. For example, how well are the employees performing who were hired in the past two years? Appraisal data can also be used to monitor the effectiveness of changes in recruitment strategies. By following the yearly data related to new hires (and given sufficient numbers on which to base the analysis) it is possible to assess whether the general quality of the workforce is improving, staying steady, or declining.
Employee Evaluation
Though often understated or even denied, evaluation is a legitimate and major objective of performance appraisal. But the need to evaluate (i.e., to judge) is also an ongoing source of tension, since evaluation and development priorities appear to frequently clash. Yet at its most basic level, performance appraisal is the process of examining and evaluating the performance of an individual (Goel, 2008). Though organizations have a clear right – some would say a duty – to conduct such evaluations of performance, many still recoil from the idea. To them the explicit process of judgment can be dehumanizing and demoralizing and a source of anxiety and distress to employees.
It is been said by some that appraisal cannot serve the needs of evaluation and development at the same time; it must be one or the other. But there may be an acceptable middle ground, where the need to evaluate employees objectively, and the need to encourage and develop them, can be balanced.
Performance Appraisal System (PAS) of Bank Asia Limited
Performance appraisal system (PAS) is the tool for measuring the performance of an individual and identifies the gaps and plan future development in order to enable a better performance between the jobs and the incumbent.
It is an HR process for driving business outcomes. It is defining in advance what the employees must do as an individual to win in the market place and later on assessing the performance based on the extent to which the organization achieve result.
Performance appraisal system is quite structured that it can measure of assess both goal (What) and the management competencies (How).
Goals-Key Result Areas (KRA) is the specific major objectives to be set at the beginning of the year through consultation with the reporting manager or supervisor. These need to be aligned to the objectives of the function and consequently to overall objectives of the bank (BAL, 2010).
A management competency is a skill, ability or trait that predicts success to perform a job.
The Performance Appraisal needs to be implemented as per PAS format which will be circulated by HR at the beginning of the year. The BAL follows both rating and descriptive systems for the performance appraisal. Although, the appraisal system is non-participative, the employees are annually assessed by a joint consultation with their immediate supervisors and departmental heads. Rating is mainly done on the following factors-
- Knowledge of work
- Accuracy and Reliability
- Speed
- General Intelligence
- Sense of Responsibility and Duty
- Diligence
- Initiative and Self confidence
- Readiness to work for and with others.
- Indication key job responsibilities/ Targets/ Work plan of the employee for the year.
- Performance on the job.
- Knowledge level.
- Behavioral competence level.
The definition of rating in performance appraisal is given below for reference:
Performance Standard
- Excellent (4.5-5.0)
- Very Good (3.5-4.5)
- Good (2.5-3.5)
- Average (1.5-2.5)
- Below average(1.0-1.5)
Bank Asia consider the following term for Appraisal-
Excellent= 91-100, Very Good= 71-90, Good= 51-70, Average= 31-50 and Below Average= 0-30
Consider on the Job Performance and the results delivered by employee (Judge Quantity and Quality) – anyone of the following:
- A Strongest all around performer, Exceptionally Exceeded targets/ given what plan for above expectation.
- A Stronger all performer, Reasonably Exceeded or target/ given work plan above expectation.
- A Strong performer Met targets/ given work plan satisfactorily within expectation.
- A Reasonable performer, Closely Met target/ given work plan, but not fully satisfactory.
- Performance standard is Well Below, targets/ given work plan, needs serious tanning and serious efforts to improve.
Those who are rated in Excellent, Very Good, Good, Average and Below Average are eligible for incentive bonus or promotion.