Plastic Industry in Bangladesh
4.1 Location
The plastic industry is clustered in the IslamBagh area of old Dhaka. There is no official registration of these firms; there total number is not certain. According to estimates by a number of entrepreneurs the total number of firms could exceed 3000. But the industry has now expanded to outside the capital. It has been learnt that, some new plastic industries has been recently established in Chittagong, Bogra, Comilla and many other parts of the country, mainly to cater the needs of the local markets.
Production Process: Plastic chips comprised the principle raw material used in the production of plastic products. Plastic chips used in Bangladesh, are of two types
1. High Quality Imported Chips
2. Locally produced from waste Plastic
A die is usually designed by the entrepreneurs and manufactured by a local engineering workshop. The die is then used in a molding machine to produce plastic products. After molding, products are checked and finishing is done using a pair of scissors and other simple tools. The final stage of production consists of coloring and packaging of products.
4.2 Sales and Revenues
The Table shows that output sales vary according to season. Average sales of manufacturing units during the peak period are about 2.5 times higher than the off peak period. About 43% of the total output was sold on credit compared to 58% of raw materials bought on credit. Credit sales were made to retail and wholesale shops. As seen in Table credit is repaid within 2-4 weeks depending on the type of units and was about 3 weeks on average. The period of which credit is outstanding was shorter for firms with lower sales. Average interest paid on credit sales by the retailers and wholesalers was about 9% with little variation observed by the type of unit. There is also little variation in the rate of interest between the peak and non-peak season. During the non-peak season manufacturers are willing to sell their products on credit to retailer and wholesalers. However such willingness only prevailed for some selective products for which demand declines during the non peak season.
Table 4.1: Sales Output
| Product Type | Monthly peak Taka | Monthly off-peak Taka | Annual Total Taka | Cash Sales % | Credit sales % | Total |
| 2. Toys and Games 3. Furniture & Fixture | 18,650
16,000
| 5,900
8,500
| 134,900
154,500
| 60%
50%
| 40%
50%
| 100%
100%
|
Source: Plastic Household products manufacturing, 1999.
4.3 Permanent Assets
Assets including own premises, advances paid for rental premises, machinery and equipment ancillary equipment and fixtures and fittings. The principal fixed assets of enterprises in this industry are machinery and equipment, since premises are in most cases rented. Apart from those the inventory of raw materials and finished goods is also important.
Most of the industries are located in a kutcha (temporary structure) while some have semi-pucca and a very few have pucca (permanent structure). The average area of the premises is 172 square feet. The actual area varies from 135 square feet to 200 square f
eet
depending on the type of unit. A large number of manufacturing units use kutcaha premises compared to raw materials manufacturers.
Machinery and equipment are simple. The main machine used is a hand molding machine. Ancillary machinery and equipment are hand cutter, die, measuring and weighting equipment, scissors and other simple tools. Coloring brushes are used for coloring and making designs on products. Machinery and equipment are locally produced and available in local markets. A typical enterprise has a few other assets such as wooden shelves, tables for the molding machine and an electric fan.
4.4 Financing the Industry
The important financial aspects of the industry are as follows:
- Financing of Fixed Assets
- Credit Purchases of Raw materials (Inputs)
- Credit Sales of Output
Plastic product manufacturing especially by small firms has grown rapidly with increased urbanization and population growth. These enterprises are initiated by the entrepreneurs themselves without any institutional support or formal finance. Investment was financed from the owner’s savings; fund’s borrowed from friends and relatives involving no visible payment, and from funds obtained from professional money lenders at interest rates of up to 100%. Operating costs were met from internal cash generation and trade credit. The output of this industry is often sold out on credit, depending on the relationship of the entrepreneurs with retailers and wholesalers.
The role of money lenders in the financing fixed assets had been significant in this industry, even though the 100% rate of interest charged was about 6 times higher than that prevailing in the formal financial sector. The main reasons which promoted the entrepreneurs to use such high cost finance are described below:
- Easy access to the money lenders
- Adequate Repayment Schedule (over 20 weeks)
- Confidence in the ability to repay since the investment is considered as involving very little risk and hence able to absorb the high cast of borrowing.
The confidence reflects their earlier experience in similar activities. The role of money lenders was insignificant in financing operating costs because trade credit for purchase inputs was easily available at much lower interest rates which did not exceeded 33%.
About 43 percent of output is sold on credit while 58% of inputs is bought on credit. Entrepreneurs find credit sales of output very risky. Credit sales are based only on the good relationship between the entrepreneurs and the retailers or wholesalers with whom they deal further, because of the shortage of operating capital, entrepreneurs prefer not to sale on credit.
Financing of fixed Assets mainly involves raising capital for following reasons:
- To procure machinery and equipment
- To pay a rental advance of the premises at the time of set-up
- For financing of additional machinery and equipment and new premises for expansion.
As all most all the entrepreneurs in this industry had experience in similar businesses that had good knowledge about machinery. The following table shows the types of Machinery and equipment in use and they are value according to different types of production units. Enterprises producing raw materials incurred an average machinery cost of Tk.30,600. The machinery cost for the units producing finished products varied from Tk.10,530 to Tk.15,700.
4.5 Effects of Seasonality
The demand for plastic products increases during the winter season, when there are a number of fares in the city. Extra people are employed to handle the increased level of production and sales. The duration of peak period varies from 4-7 months (October to March) depending on the type of product. It can be mentioned here that the demand for toys and house hold goods continues at a reasonably uniform level during the off-peak season.
Findings & Analysis
5.1 Analysis of collected data
5.1.1 Ratio of Entrepreneurs
The entrepreneurs in plastic industry are by and large male. All the owners surveyed was male. The environment and procedures prohibit any female intrusion, although there are some female workers. If we ignore the sampling error we can say that 100% owners are male. So it is evident that female are not comfortable in this business.
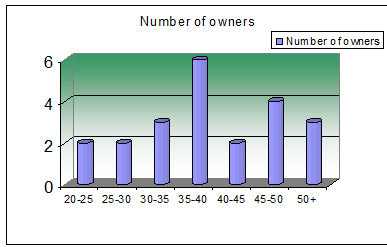
5.1.2 Age variation
This industry needs a healthy mount of initial investment. So, very young entrepreneurs are found rarely. Most owners of the plastic industries show a trend to engage in the industry in their late 30s and early 40s.
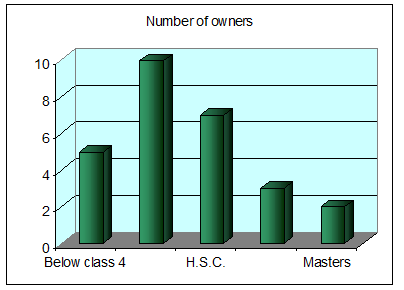
5.1.3 Educational Qualification
Largely the entrepreneurs seem to lack much educational background. Generally educational qualification is not of much importance in this industry. Most of the owners are only High-school passed.
5.1.4 Forms of Ownership
All of the plastic industry units are either sole-proprietorships or partnerships. Family owned partnerships are also prevalent.
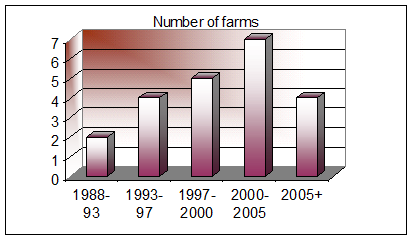
5.1.5 Starting Period of the Business
Although plastic industry came to Bangladesh in the 1980s the trend for that business in a large scale is relatively much more recent. More than 90% of the industry units that we surveyed started operating in 1990s, majority of them were within 6 years.
5.1.6 Latest occupation prior to starting the business
Although plastic industry came to Bangladesh in the 1980s the trend for that business in a large scale is relatively much more recent. More than 90% of the industry units that we surveyed started operating in 1990s, majority of them were within 6 years.
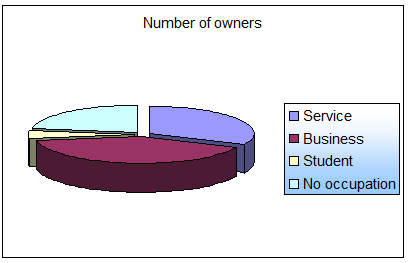
5.1.7 Business Experience
About 70% of the owners, that is 16 out of 22 owners surveyed, said that they were previously engaged in another job before turning to this profession. Most of the previously employed owners had a business.
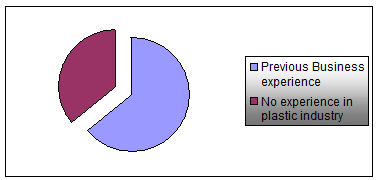
5.1.8 Family Members
Of the 40% owners who said that they were previously engaged in some business and some the others a total of 32% had previous business experience in this industry, some from family business and some from occupational background.
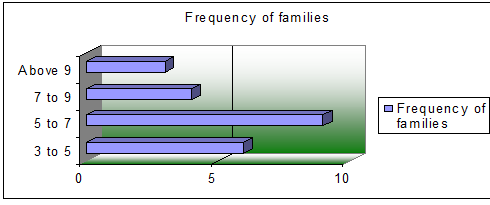
Many of the owners of the industries live with a joined family of more members. In 60% cases the owner is the only earning member of the family.
5.1.9 Reasons for Starting the Business
Most of the owners pointed financial self-sufficiency as the key reason for starting the business. 70% of the respondents identified financial incipiency as the primary reason while 23% said failure to find employment as the reason. There were few cases where added social status and others were also a reason.
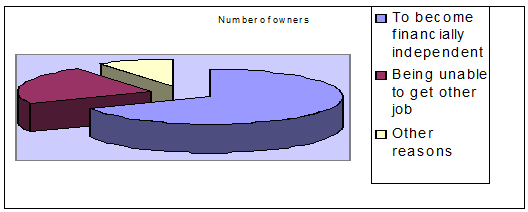
5.1.10 Capital invested primarily
Most of the owners pointed financial self-sufficiency as the key reason for starting the business. 70% of the respondents identified financial incipiency as the primary reason while 23% said failure to find employment as the reason. There were few cases where added social status and others were also a reason.
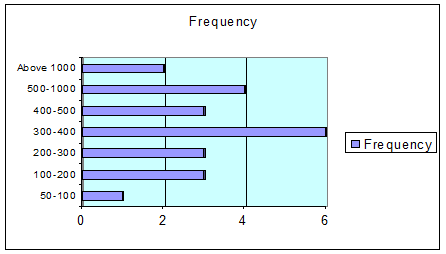
5.1.11 Sources of Initial Capital
The amount of capital invested in the industry varied a great deal, mainly with the product type. The manufactures of PVC pipe had invested a lot more than the utensil manufacturer and they also had more return on investment. The total investment of the whole industry varied from Tk. 50000 to more than Tk. 20 lakh.
Almost all the owners said that the capital was acquired from own or family sources. Some said that they themselves invested the full amount of capital. On the other hand there were cases where the full amount was bear by some family member.
5.1.12 Current Capital
While some said that capital has increased. In some cases the amount of capital has increased by quite a significant margin, whereas in other cases the increase has been insignificant. Some others have also claimed that the amount of capital has decreased due to losses.
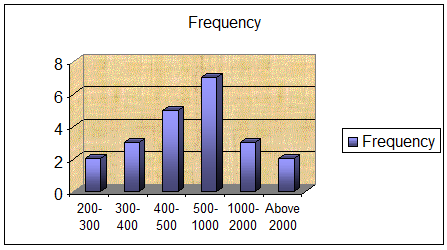
5.1.13 Peak and Low Business Season
While some said that capital has increased. In some cases the amount of capital has increased by quite a significant margin, whereas in other cases the increase has been insignificant. Some others have also claimed that the amount of capital has decreased due to losses.
Here different types of industry show different peak seasons according to their production and sales volume. The P.V.C. pipe industries show rapid sales in the winter season. In the dry season pipes are required by the farmers for the irrigation of lands. They show a depressed sale volume in the rainy season because in this season not many construction works are underway
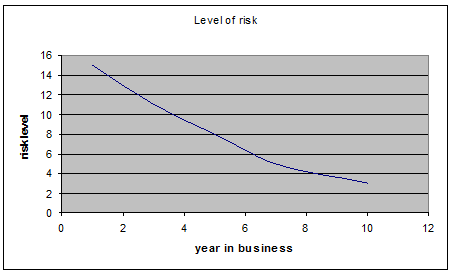
5.1.14 Risk Factors in the Business
In any business undertaking or entrepreneurial activities, there always exist certain risk factors. These factors may be negligible or they may be high, but they do persist. The owners of the businesses interviewed asserted that all the businesses at the starting point included a high degree of risk; with only a few exceptions saying moderate risk. More than 90% said high initial risk. As the business progressed the risk degrees were lessened.
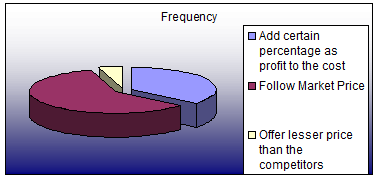
5.1.15 Pricing
Most of the firms practice cost-plus or mark up pricing to determine the price of their products. Many others just follow the current market price or the on-going pricing.
5.2 Major Challenges
The plastic product manufacturing was quite profitable in the past years. Recently, the industry has faced a number of problems. From the interview of several entrepreneurs the major problems can be summarized by the following –
1. The first challenge for the entrepreneur is keep up with the imported products. As many companies are importing low price products from India, Singapore, Thailand and so on.
2. Government help is not sufficient. Starting the business needs lots of paper work and formalities if done properly. So many of the entrepreneurs do their business without proper documents.
3. Unstable political condition hampers the production a lot. It also decrease the supply of raw materials.
4. As this industry was profitable, many entrepreneurs has come up and set new industries. This has caused an intense competition in the sector. For this reason the price of end products has decreased 300-400%. While the technology has not improved that much.
5. Sometimes there is a crisis in the raw materials market. For this reason, the price of raw materials has increased almost 100% in the last 4 years.
6. The Industry was exporting some of its products in the North-Eastern India. But recently, some plastic industries have been established in that area to cater the local market. So the export has dried up. This is also affecting the industry.
7. There depression going on in our economy. As a result the people are not spending much. Especially in the villages, which is the largest market of most of the plastic goods, the farmers are not getting due price of their products. So indirectly the plastic industry is also faced with problems.
8. Electricity failure is affecting the industry very much, as the whole production process is based on electricity.
9. The Dhaka based producers are also facing competition from the producers of plastic hailing from other districts. For example, quite a few plastic industries have been established in the Chittagong, Bogra abd in Comilla districts.
10. As it is a manufacturing industry, the profit comes little later than service companies. So the entrepreneurs have to survive in the initial stages.
Recommendation
6.1 To the Government
- First of all Government should create a secluded industrial zone for plastic industries with gas and electricity and other supplies and transfer all the industries there.
- Government should provide loans according to their capital.
- Ensuring uninterrupted Electric Supply. It has been mentioned by the most of the respondents that the electricity problem of recent times is heavily affecting the industry. The government must solve this problem as soon as possible. Government should take steps to stabilize the economy and political condition
- Government has to minimize the bureaucracy and the harassment that the entrepreneurs have to go through to import raw materials.
- Government should remove taxation on the plastic sector for at least a five year period to give the growing industries a chance. In the case of PVC pipe manufacturers, the government has imposed VAT recently, which is affecting the industry very much. So the government should exempt VAT for all new PVC pipe industry for at least five years.
6.2 To the entrepreneurs
To overcome the challenges entrepreneurs need to take some steps. These are –
- As most of the workers are unskilled, there should be a training period for each worker so that they can learn and contribute more.
- Most of the small enterprises are not following the rules and regulations, which eventually hampers the business.
- Entrepreneurs should update the technologies for production. Use of computer should be increased to get more efficiency.
Conclusion
Entrepreneurs in our country seldom face many challenges because of corruption, inefficiency in government and unstable political condition. The plastic manufacturing industry assumes a very important position in manufacturing activities. It now possibly generates gainful employment of at least 1 lakh people in manufacturing activity. All this have been achieved without the help of the government or any of its institutions. The industry processes a great potential for expansion and can meet the demand for a large variety of domestic goods and children’s toys and games. It also has export potential. Therefore government intervention is necessary in terms of providing access to credit acquiring improved technology, training to produce and develop products and marketing services. As a developing country and a having market of 15 crore entrepreneurs should come forward to develop this industry.
Some more parts-
Challenges Faced by Entrepreneurs in Plastic Industry (Part-1)
Challenges Faced by Entrepreneurs in Plastic Industry (Part-2)