Financial Performance Analysis of
Green Delta Insurance Company Limited
Insurance is a system of spreading the risk of one to the shoulders of many. It is a contract whereby the insurers, on receipt of a consideration known as premium, agree to indemnify the insured against losses arising out of certain specified unforeseen contingencies or perils insured against.
Insurance is not a new business in Bangladesh. Almost a century back, during British rule in India, some insurance companies started transacting business, both life and general, in Bengal. Insurance business gained momentum in East Pakistan during 1947-1971, when 49 insurance companies transacted both life and general insurance schemes. These companies were of various origins British, Australian, Indian, West Pakistani and local. Ten insurance companies had their head offices in East Pakistan, 27 in West Pakistan, and the rest elsewhere in the world. These were mostly limited liability companies. Some of these companies were specialized in dealing in a particular class of business, while others were composite companies that dealt in more than one class of business.
The government of Bangladesh nationalized insurance industry in 1972 by the Bangladesh Insurance (Nationalization) Order 1972. By virtue of this order, save and except postal life insurance and foreign life insurance companies, all 49 insurance companies and organizations transacting insurance business in the country were placed in the public sector under five corporations. These corporations were: the Jatiya Bima Corporation, Tista Bima Corporation, Karnafuli Bima Corporation, Rupsa Jiban Bima Corporation, and Surma Jiban Bima Corporation. The Jatiya Bima Corporation was an apex corporation only to supervise and control the activities of the other insurance corporations, which were responsible for underwriting. Tista and Karnafuli Bima Corporations were for general insurance and Rupsa and Surma for life insurance.
The basic idea behind the formation of four underwriting corporations, two in each main branch of life and general, was to encourage competition even under a nationalized system. But the burden of administrative expenses incurred in maintaining two corporations in each front of life and general and an apex institution at the top outweighed the advantages of limited competition.
Consequently, on 14 May 1973, a restructuring was made under the Insurance Corporations Act 1973. Following the Act, in place of five corporations the government formed two: the Sadharan Bima Corporation for general business, and Jiban Bima Corporation for life business.
After 1973, general insurance business became the sole responsibility of the Sadharan Bima Corporation. Life insurance business was carried out by the Jiban Bima Corporation, the American Life insurance Company, and the Postal Life Insurance Department until 1994, when a change was made in the structural arrangement to keep pace with the new economic trend of liberalization.
The Insurance Corporations Act 1973 was amended in 1984 to allow insurance companies in the private sector to operate side by side with Sadharan Bima Corporation and Jiban Bima Corporation. The Insurance Corporations Amendment Act 1984 allowed floating of insurance companies, both life and general, in the private sector subject to certain restrictions regarding business operations and reinsurance. Under the new act, all general insurance businesses emanating from the public sector were reserved for the state owned Sadharan Bima Corporation, which could also underwrite insurance business emanating from the private sector. The Act of 1984 made it a requirement for the private sector insurance companies to obtain 100% reinsurance protection from the Sadharan Bima Corporation. This virtually turned Sadharan Bima Corporation into a reinsurance organization, in addition to its usual activities as direct insurer. Sadharan Bima Corporation itself had the right to reinsure its surplus elsewhere outside the country but only after exhausting the retention capacity of the domestic market. Such restrictions aimed at preventing outflow of foreign exchange in the shape of reinsurance premium and developing a reinsurance market within Bangladesh.
The control over insurance companies including their functions relating to investments, taxation, and reporting is regulated mainly by the Insurance Act 1938 and the Finance Acts.
Objective of the report
The objective of the report can be viewed in two forms:
- General Objective
- Specific Objective
General Objective
This internship report is prepared primarily to fulfill the Bachelor of Business Administration (B.B.A) degree requirement under the Department of BRAC Business School, BRAC University.
Specific Objective
More specifically, this study entails the following aspects:
- To provide a brief overview of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited and their historical background.
- To analyze the Industry analysis of General Insurance Company in the last five years.(2008-2012)
- To Evaluate Stock Overpriced or underpriced
- To know the product and services of General Insurance company and those description
- To present my observation and suggestion to the Insurance Company.
Methodology
In order to generate this report only secondary data has been used. The source that have been used to gather and collect data is given below-
Secondary Sources
- Annual Report of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited, Reliance Insurance
Company Limited, Agrani Insurance Company Limited( 2008-2012)
- Brochures of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited
- Different written document of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited
- Website of DSE and Stock Bangladesh
- Newspaper
- Website of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited, Reliance Insurance Limited, Agrani Insurance Company Limited( 2008-2012)
Background and Overview of the Company:
Green Delta Insurance Company Limited (GDIC) is one of the leading private non life insurance companies in Bangladesh. GDIC was incorporated in December 14, 1985 as a public limited company, under the Companies Act 1913. Actual operations started on 1st January 1986, with a paid up capital of BDT 30.00 million. Now, Green Delta Insurance Company Ltd. is amassed about BDT 637.875 million with a credit rating of AA1 and ST1. GDIC holds the proud distinction of being the first ever company to raise its paid up capital to such a level. This is also the 1st Insurance Company in Bangladesh to have equity partnership with IFC. With a presence in the strategically important parts of the country, which includes 38 branches, Green Delta Insurance Company Ltd. has established its prominent presence with equity participation in Delta BRAC Housing Ltd., Progressive Life Insurance Co Ltd, United Hospital Ltd. FinExcel Ltd. and BD Venture Ltd. Green Delta Capital Ltd. and Green Delta Securities Ltd. are two of the direct subsidiaries. GDIC provides stock brokerage services through Green Delta Securities Ltd. (GDSL) and investment supports through Green Delta Capital Ltd. (GDCL).
Under the charismatic leadership of Mr. Nasir A Choudhury, Founder Managing Director and Advisor, Green Delta Insurance Company Ltd. has been leading the winds of change in the insurance industry of the country in terms of service standard, innovative products and legislative restructuring. After 28 years of glorious journey in the Insurance sector, Green Delta Insurance Company Limited has now become a big family of 14 respected board members, 600+ committed staff, numerous valued clients and thousands of esteemed shareholders. By now, Green Delta has been able to uphold the brand image as a prompt claim settler, superior service provider, and diversified product supplier – almost like a one stop solution provider in the non life insurance sector in the country.
Project part
Financial Performance analysis of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited
Summary:
- To analyze the Industry analysis of General Insurance Company in the last five years.(2008-2012)
The project consists with three different parts. They are given below
Project Part A: In the project part A the description of each of the insurance is given with the detail requirement of each of them so that after reading it anyone can get a overall idea of the product and services given by the GDIC.
Project Part B: In the project part B the industry analysis is given. For doing industry analysis three insurance companies have been chosen. Those are Green Delta Insurance Company Limited. Reliance Insurance Company Limited, Agrani Insurance Company Limited. After that, those profitability ratios, liquidity ratios and leveraged ratios have been analyzed with the findings and recommendations.
Project Part C: In the project part C the stock valuation of GDIC is given. For doing this the portfolio market return, risk free rate have been found out. After that, the beta, face value of stock, required rate of return, intrinsic value, growth rate of cash dividend of GDIC have been found out. Then, after doing the comparison of intrinsic value and market price of GDIC’s stock, whether the stock price of GDIC is overpriced or underpriced is found out. At the end the probable reason for overpriced or underpriced has been discussed.
Objective of the project
More specifically, this study entails the following aspects:
- Finding the recommendations to the GDIC on the basis of analyzing the financial ratios.
- To Evaluate Stock Overpriced or underpriced
- Finding the intrinsic value of the GDIC stock
- Finding the probable reason for overpriced or underpriced of stock
- To know the product and services of General Insurance company and those description
- To present my observation and suggestion to the Insurance Company.
Methodology
In order to generate the project part of this report only secondary data has been used. The source that have been used to gather and collect data is given below
Secondary Sources
- Annual Report of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited, Reliance Insurance Company Limited, Agrani Insurance Company Limited( 2008-2012)
- Brochures of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited
- Different website on financial ratios like Investopedia ,
- Website of Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE) and Stock Bangladesh
- Website of Green Delta Insurance Company Limited, Reliance Insurance Limited, Agrani Insurance Company Limited( 2008-2012)
Description and Requirement of Product and Services
Fire Insurance
Basic cover:
- Fire
- Lightning
- Explosion(domestic)
Damage during or immediately following
- Fire caused by – smoke, scorching,
- Falling walls, water used for extinguishing
- Fire, blowing up building for preventing
- Spread of fire.
- This coverage can be extended to include other perils by the additional premium;
- Riot, Strike
- Terrorism
- Storm, Flood
- Subsidence
- Landslide
- Aircraft damage
- Bursting or overflowing of tanks.
Exclusions
Fire due to
- Explosion except boiler used for domestic purpose
- Spontaneous combustion
- Earthquake fire
- Subterranean fire
- Own fermentation or heating
- Flood & Cyclone
Specific Exclusions
- Riot, Civil Commotion, War, Invasion, Act of Foreign Enemy, Civil War, Rebellion, Revolution, Insurrection etc.
- Radioactive Contamination
Basic Elements of Fire Rating from Tariff:
- Interest
- Construction
- Occupation
- Location
Burglary Insurance
Scope of Cover
Lost by burglary
- Housebreaking following upon an actual forcible and violent entry into or exit from the premises by the person or persons .
- Then the company will pay to the extent of such loss to the extent of the intrinsic value of the descriptive value of the insured.
Exclusions
- Theft by persons lawfully on the premises.
- Any legal liability,
- Loss or damage during the progress of or following upon fire or explosion.
- Earthquake, war, Riot, Civil war, Invasion etc.
Uncoverable property
- Deeds, bonds, stamp collections, bank or currency.
- Theft by persons lawfully on the premises.
- Any legal liability,
- Loss or damage during the progress of or following upon fire or explosion.
- Earthquake, war, Riot, Civil war, Invasion etc
Marine Insurance
- The oldest branch of insurance.
- Comprises: Cargo Insurance and Hull Insurance.
- Lloyd´s is the famous world´s Marine insurance market.
- Marine Insurance Act 1906.
Types of Marine Insurance
Hull Insurance
- Concerns the insurance of ships.
- Hull, machinery etc.
Cargo Insurance
- Plays an important role in domestic trade as well as international trade.
- Provides insurance cover in respect of loss of or damage to goods during transit by –rail, -road -sea -air
Types of Marine Policy
- Time Policy
- Voyage Policy
- Mixed Policy
Institute Cargo Clauses (C)
- a) Fire or explosion.
- b) Vessel or craft being stranded, grounded, sunk or capsized.
- c) Overturning or derailment of land conveyance.
- d) Collision or contract of vessel, craft or conveyance with any external object other than water.
- e) Discharge of cargo at a port of distress.
- f) General average sacrifice.
- g) Jettison.
Institute Cargo Clauses (B)
- Provides cover under ICC ( C )
- Additional risk
- a) Earthquake, volcanic eruption or lightning.
- b) Washing overboard.
- c) Entry of sea, lake or river water into vessel.
- d) Total loss of any package lost overboard or dropped whilst loading or unloading from vessel.
Extraneous Risks
Can be added on payment of extra premium to ICC (B)
- a) Theft, pilferage and / or non-delivery.
- b) Fresh water and rainwater damage.
- c) Hook and / or oil damage.
- d) Heating and sweating.
- e) Damage by mud, acid and other extraneous substances.
- f) Breakage.
- g) Leakage.
- h) Busting / tearing of bags
Institute Cargo Clauses
Provide cover for all risks of loss or damage.
- All risks means losses which are caused by accidental circumstances.
- Under ICC (C) and (B) the risks covered are specified.
Exclusions
- Loss caused by willful misconduct of the insured.
- Ordinary leakage, ordinary loss in weight or volume or ordinary wear and tear.
- Loss caused by inherent vice or nature of the subject matter.
- Loss caused by delay.
- Loss arising from insolvency or financial default of owners of the vessel.
- Loss or damage due to inadequate packing.
- War, riot, strike, lock-out, civil commotions and terrorism.
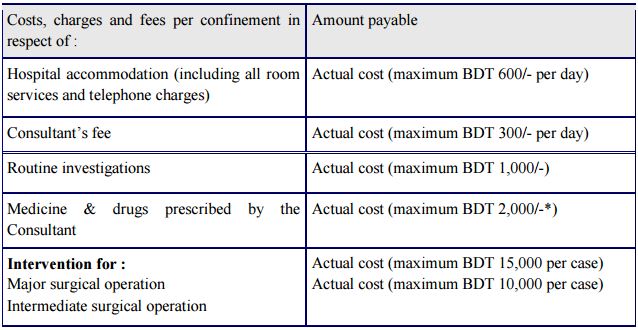
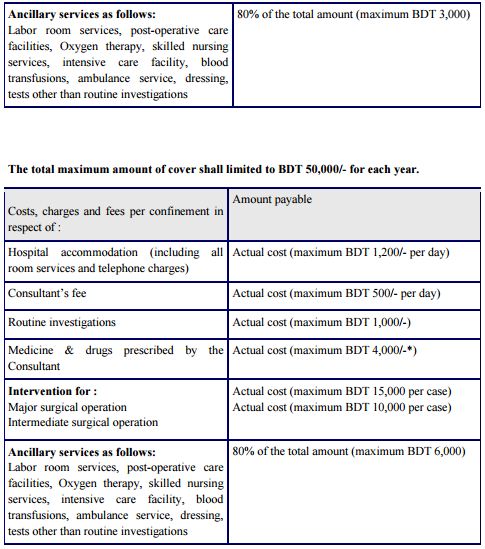
Health Insurance
- The health policy provides for reimbursement of hospitalization/domiciliary hospitalization expenses for illness/disease suffered or accidental injury sustained during the policy period.
- Under this scheme the expenses for treatment in a hospital for an illness or injury are insured.
- It does not cover for any expenses in respect of domiciliary or outdoor treatment.
Covers
- Hospitalization due to accident or illness.
- Ancillary services like ICU/CCU room, post-operative room, blood transfusion, special investigations, etc.
- Labor room services.
- Intensive care facility.
- Oxygen therapy.
- Skilled nursing services.
- Blood transfusions.
- Ambulance services.
- Dressing while in confinement and test other than the routine investigations.
Three plans
- Basic Plan
- Standard Plan
- Super Plan
The total maximum amount of cover shall limited to BDT 25,000/- for each year:
All Risk Insurance
Specially suitable for covering jewellery, valuables, curios, antiques and other works of art, paintings, watches, cameras and other similar articles.
Exclusions:
- Wear & Tear
- Repairing
- Breakage of glass of watches etc.
Personal Accident Insurance
- To provide compensation in the event of an accident causing death or injury
- The purpose of personal accident insurance is to pay fixed compensation for death or disablement resulting from accidental bodily injury.
- Personal accident and sickness policies are renewable annually and if a claim has occurred which could be of a recurring nature, the cover may be restricted at renewal or in severe cases renewal may not be offered
- It is against accident happening at anytime and anywhere including flying as a ticket holding passenger in an aircraft operated by an Air Transport organization providing scheduled air services.
Overseas Medical Insurance / Travel Insurance
Consequent upon an unforeseen event happening during the course of a journey away from the Usual Country of Residence, the Company will provide the Insured with immediate material assistance as specified under the Benefits set out in Sections (1) and (2) of this policy, provided that the event does not occur outside the Geographical Limits.
Exclusions:
The company will not be liable to provide any assistance which arises directly or indirectly from:
- Fraudulent acts by any Insured or any other person seeking to claim under this policy.
- Consequential loss of any kind.
- Extraordinary phenomena such as floods, earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, unusual cyclone storms, falling astral bodies or meteorites.
- Terrorism, civil unrest or riots.
- Actions by the armed forces, security forces or other organizations.
- Nuclear radioactivity.
- The participation by any Insured in:
- Competitions, rallies, or contests.
- Sports.
iii. Criminal conduct.
- Wagers or challenges.
- The deliberate act of the Insured.
- Illnesses or pathological states produced by voluntary consumption of alcohol, drugs, toxic, substance, narcotics, or medicines acquired without medical prescription.
- Any pre-existing medical condition, suicide or attempted suicide, mental illness, pregnancy or childbirth.
- Prostheses, glasses conduct lenses, hearing aids or artificial limbs.
- An aesthetic treatment a cure, a counter indication of traveling or of holidays, the impossibility of continuing in certain places with the advised preventive medical treatment, the voluntary interruption of pregnancy.
- Mental illnesses, depressions, any dental illness.
- Epidemics. Pregnancy complication.
- Aids, HIV
Loss of Profit Insurance
This cover in summary will cater for;
- Standing charges such as salaries
- Increased cost of working
Exclusions
- Loss of goodwill
- Failure to recover debts due to loss of records
- Depreciation of undamaged stock
Erection All Risk Policy (EAR)
An erection all risk policy is designed to cover the risks associated with the installation of machines/equipments or composite projects.
- The policy is normally designed to meet the requirements of those involved in the erection of a project either as a principal, contractor or sub-contractor.
- Risks associated with construction of Factory sheds, plants, warehouses, runways, bridges, dams, buildings, hangers, air-taxiways etc can be covered.
Scope of Cover- EAR Policy
- Location risks – Fire, Lightning, Theft, Burglary etc.
- Handling risks- Collision, failures of cranes or tackles, impact of falling objects.
iii. Testing & Commissioning Risks: Failure of safety devices, short Circuit, Explosion.
- Risk of Human Element: Carelessness, negligence, faults in erection, Strike & riot, Malicious damage, Terrorism.
- Acts of GOD: Flood, Storm, Tempest, Inundation, Landslide, Earthquake.
Exclusions:
- Loss due to faulty design, defective material, or casting and or bad workmanship.
- Loss or damage due to erection machinery and equipment due to mechanical/electrical breakdown.
- Loss or damage due to willful act or willful negligence
- Loss or damage due to war
- Loss or damage due to nuclear reaction
Contractors All Risk Policy
Coverage is extended to:
- Civil Engineering Contractors in the matter of works under construction.
- Covers projects like Buildings and Civil Engineering Projects such as office buildings, hospitals, schools, theatres, etc. factories, Power Plants, Roads and Railway facilities, airports, bridges, dams, tunnels, etc.
Exclusions:
- War Risks.
- Normal Wear & Tear.
- Rust, Corrosion, Erosion.
- Inventory Losses.
- Willful acts, Willful negligence.
- Consequential losses.
- Defective Material / Workmanship, Faulty Design.
Industrial All Risk policy
All industrial risks having overall Sum Insured of BDT 50 crores shall be under Industrial all risk policy.
Policy covers,
- Material damage only
- All risks/perils other than those which are specifically excluded.
Conditions
- 10% self insurance applicable.
- Additional 10% self insurance for more than one recoverable loss within past 3 years.
- Deductible of 10% loss but minimum 5 lac EE irrespective of perils.
- All project above 5 crore Sum insured to be surveyed.
Exclusions:
- Damage to the property caused by faulty or defective design materials or work manship, inherent vice, latent defect etc.
- Collapse or cracking of building
- Corrosion rust extremes or changes in temperature,
- Acts of fraud or dishonesty
- Mechanical or electrical break down or derangement of machinery or equipment.
- Bursting, overflowing, discharging or water tans apparatus or pipes when the premises are empty or disused.
- Any willful act or willful negligence on the part of the insured or any person acting on his behalf.
- Damage occasioned directly or indirectly in consequence of war, invasion act of foreign enemy, hostilities or warlike operations.
Professional Indemnity
Scope of cover:
- Any error/omission/negligence/on the part of the permanent employees and directors.
- Dishonest or fraudulent act or omission on the part of the permanent employees and directors.
Exclusions
- The insolvency of an insurance company.
- Libel or slander
- Loss of or damage to computer system and their records.
- Dishonest, fraudulent criminal or malicious act or omission of the insured.
- Terrorist activities
- Loss of or damage due to earthquake, volcanic eruption, flood, typhoid, hurricane, cyclone.
- Claims arising out of personal Liability, Employers liability, Product liability etc
Contractors Plant & Machinery Policy (CPM)
The policy provides a comprehensive cover against unforeseen and sudden physical damage to property by any cause not specifically excluded:
Hence covers:
- Location risks-Fire/lightning/theft/burglary
- Impact from falling objects-collision
- Risks of human element-Carelessness/fault material/riot/strike/malicious damage/terrorism
- Act of GOD: Storm/tempest/Hurricane flood/landslide etc.
Exclusions
- Electrical or mechanical breakdown.
- Explosion of any boiler or pressure vessel.
- Loss or damage due to wear and tear corrosion
- Loss of damage while in transit from one location to other.
- War perils, civil commotion, nuclear perils etc
Public Liability:
- Chemical exhaust or residue which is/are pollutant(s)
- Fumes as a result of R&D
- Testing on animals (rats etc.) – possible claim by Animal Rights activists.
Employer’s Liability:
- Liability on employer as a result of injury to employees during discharging their duty. This could be Vicarious Liability as well.
Worksmen Compensation
- Cover for employees for injuries which are work related.
Product Liability:
- Negligence
- Strict Liability
- Inability to recall
- Design Defects
- Product Withdrawal & Crisis Management Expense
- Emergency Medical Expenses for bodily injury in case of human clinical trials including trial related athletic activities.
- Employees who voluntarily participate should not be excluded.
- Vendor’s Extension
- Technical Collaborator’s Extension.
Project Part
Industry Analysis
Profitability or Return on Investment Ratios:
Profitability ratios provide information about management’s performance in using the resources of the small business. Many entrepreneurs decide to start their own businesses in order to earn a better return on their money than would be available through a bank or other low-risk investments. If profitability ratios demonstrate that this is not occurring—particularly once a small business has moved beyond the start-up phase—then entrepreneurs for whom a return on their money is the foremost concern may wish to sell the business and reinvest their money elsewhere. However, it is important to note that many factors can influence profitability ratios, including changes in price, volume, or expenses, as well as the purchase of assets or the borrowing of money. Some specific profitability ratios follow, along with the means of calculating them and their meaning to a small business owner or manager.
Net profitability:
Net Income/Net Sale
It measures the overall profitability of the company, or how much is being brought to the bottom line. Strong gross profitability combined with weak net profitability may indicate a problem with indirect operating expenses or non-operating items, such as interest expense. In general terms, net profitability shows the effectiveness of management. Though the optimal level depends on the type of business, the ratios can be compared for firms in the same industry.
Findings
From 2008 to 2009 GDIC had an increasing trend of net profitability. After that in 2010 it decreased slightly and then in 2011 was decreased in a huge percentage. Though from 2011 to 2012 it had an increasing trend it was not a well sign for GDIC because compared to Reliance the condition was not good. However, the performance of Reliance was far better than other two companies if we consider the consistency and the higher profitability. On the other hand, the condition of Agrani was not good at all as it had the lowest net profitability ratio than other two companies.. In 2012 the performance of Reliance was better in consideration of net profitability than other two companies. In 2009 and 2010 the performance of GDIC was good.
Recommendation:
After considering the scenario it could be recommended that GDIC has some problems with its indirect operating expenses or non-operating items, such as interest expense so it should be focused on it for the sake of effectiveness of the company.
Return on assets:
Net Income/Total Assets
Return on assets indicates how effectively the company is deploying its assets. A very low return on asset, or ROA, usually indicates inefficient management, whereas a high ROA means efficient management. However, this ratio can be distorted by depreciation or any unusual expenses.
ROA tells you what earnings were generated from invested capital (assets). ROA for public companies can vary substantially and will be highly dependent on the industry. This is why when using ROA as a comparative measure, it is best to compare it against a company’s previous ROA Numbers or the ROA of a similar company.
The assets of the company are comprised of both debt and equity. Both of these types of financing are used to fund the operations of the company. The ROA figure gives investors an idea of how effectively the company is converting the money it has to invest into net income.
The higher the ROA number, the better, because the company is earning more money on less investment.
Findings
From year 2008 to 2010 GDIC and Agrani has an increasing trend of ROA whereas Reliance has a decreasing trend of ROA. In those 3 years GDIC has higher ROA than other two companies. Besides, in 2011 GDIC’s has drastically decreased from 13.5% to 3.1%. Again in 2012 it was increased to 4.2%. However, Reliance has increased from year 2010 to 2011 and again it has a decreased trend from year 2011 to 2012. Also, in 2011 the ROA ratio of Agrani is decreased from 8.3% to 6.9% and in 2012 it was increased to 8.3%. By this it can be said that from year 2011 to 2012 GDIC’s condition in consideration ROA is bad compared to other two companies.
Recommendation:
For being efficient company GDIC should avoid depreciations and unusual expenses for getting higher ROA to improve the condition of company.
Return on investment 1:
Net Income/Owners’ Equity
It indicates how well the company is utilizing its equity investment. Due to leverage, this measure will generally be higher than return on assets. ROI is considered to be one of the best indicators of profitability. It is also a good figure to compare against competitors or an industry average. Experts suggest that companies usually need at least 10-14 percent ROI in order to fund future growth. If this ratio is too low, it can indicate poor management performance or a highly conservative business approach. On the other hand, a high ROI can mean that management is doing a good job, or that the firm is undercapitalized.
Findings
From year 2008 to 2010, GDIC had an increasing rate of return on investment; in 2010 it was very tremendous. Agrani also had an increasing figure. On the other hand, Reliance faced a bad situation because it had a decreasing rate. In the year 2011, the Agrani and GDIC’s ratio had been decreased which is a negative side. However in the year 2012 those companies ratio had been slightly increased. On the other hand, in 2011 the Reliance’s ROI had been increased little bit and in 2012 it was constant.
Recommendation:
So, it can be said that. Though 2012 has a growing rate but still it need to be improved because high ROI means good management of the company. Here, the return on the investment is not up to the mark so it should be increased.
Return on investment 2:
Dividends +/- Stock Price Change/Stock Price Paid
From the investor’s point of view, the calculation of ROI measures the gain (or loss) achieved by placing an investment over a period of time.
Findings
Here it can be found that, the return on investment of the three companies is not good. As, in 2012, 2011 and 2009 GDIC faced negative ROI. In year 2008 it was very good and in 2010 it has high ROI though it was less than the year 2008. In 2012 the condition of Agrani had a zero figure which was better than other two companies as other two companies had a negative figure and GDIC had the lowest percentage among other companies. In 2008, the condition of three companies was better compared to other four years.
Recommendation:
From the investors perspective it can be said that the ROI is not good enough of GDIC to invest here. So, for being in a good position GDIC should be focused on the issues by which they can increase their dividend and how they can increase their stock price by improving those qualities.
Earnings per share:
Net Income/Number of Shares Outstanding
EPS states a corporation’s profits on a per-share basis. It can be helpful in further comparison to the market price of the stock. EPS is the portion of the company’s distributable profit which is allocated to each outstanding equity share (common share). EPS is a very good indicator of the profitability of any organization, and it is one of the most widely used measures of profitability.
The earnings per share is a useful measure of profitability, and when compared with EPS of other similar companies, it gives a view of the comparative earning power of the companies. EPS when calculated over a number of years indicates whether the earning power of the company has improved or deteriorated. Investors usually look for companies with steadily increasing earnings per share.
Growth in EPS is an important measure of management performance because it shows how much money the company is making for its shareholders, not only due to changes in profit, but also after all the effects of issuance of new shares (this is especially important when the growth comes as a result of acquisition).
There is no rule of thumb to interpret earnings per share. The higher the EPS figure, the better it is. A higher EPS is the sign of higher earnings, strong financial position and, therefore, a reliable company to invest money. For a meaningful analysis, the analyst should calculate the EPS figure for a number of years and also compare it with the EPS figure of other companies in the same industry. A consistent improvement in the EPS figure year after year is the indication of continuous improvement in the earning power of the company.
Findings
GDIC has a higher EPS in the year 2008 but after that the condition of GDIC was falling but in year 2010 it was slightly increased but again it decrease in year 2011 and then in year 2012 it was slightly increased. In year 2012 GDIC’s EPS was best among three companies. In year 2011, 2010 and 2009 the reliance was best and in 2008 GDIC was best compared to other
Recommendation:
For getting higher EPS GDIC should focused on the issues by which the can increase their net income. They can increase it by reducing their cost and increase their revenues. Also they can take steps to reduce their tax payment. Higher the EPS means the condition of that company is better.
Current ratio:
Current Assets/Current Liabilities
It measures the ability of an entity to pay its near-term obligations. “Current” usually is defined as within one year. Though the ideal current ratio depends to some extent on the type of business, a general rule of thumb is that it should be at least 2:1. A lower current ratio means that the company may not be able to pay its bills on time, while a higher ratio means that the company has money in cash or safe investments that could be put to better use in the business.
The current ratio is an indication of a firm’s market liquidity and ability to meet creditor’s demands. If the current ratio is too high, then the company may not be efficiently using its current assets or its short-term financing facilities. This may also indicate problems in working capital management. Low values for the current or quick ratios (values less than 1) indicate that a firm may have difficulty meeting current obligations. Low values, however, do not indicate a critical problem. If an organization has good long-term prospects, it may be able to borrow against those prospects to meet current obligations. Some types of businesses usually operate with a current ratio less than one. For example, if inventory turns over much more rapidly than the accounts payable become due, then the current ratio will be less than one. This can allow a firm to operate with a low current ratio.
If all other things were equal, a creditor, who is expecting to be paid in the next 12 months, would consider a high current ratio to be better than a low current ratio, because a high current ratio means that the company is more likely to meet its liabilities which fall due in the next 12 months. One should view the relation between the operation cycle period and the current ratio Current ratio is a measure of liquidity of a company at a certain date. It must be analyzed in the context of the industry the company primarily relates to. The underlying trend of the ratio must also be monitored over a period of time.
Generally, companies would aim to maintain a current ratio of at least 1 to ensure that the value of their current assets cover at least the amount of their short term obligations. However, a current ratio of greater than 1 provides additional cushion against unforeseeable contingencies that may arise in the short term.
Businesses must analyze their working capital requirements and the level of risk they are willing to accept when determining the target current ratio for their organization. A current ratio that is higher than industry standards may suggest inefficient use of the resources tied up in working capital of the organization that may instead be put into more profitable uses elsewhere.
Conversely, a current ratio that is lower than industry norms may be a risky strategy that could entail liquidity problems for the company.
Current ratio must be analyzed over a period of time. Increase in current ratio over a period of time may suggest improved liquidity of the company or a more conservative approach to working capital management. A decreasing trend in the current ratio may suggest a deteriorating liquidity position of the business or a leaner working capital cycle of the company through the adoption of more efficient management practices. Time period analyses of the current ratio must also consider seasonal fluctuations.
Current ratio is the primary measure of a company’s liquidity. Minimum levels of current ratio are often defined in loan covenants to protect the interest of the lenders in the event of deteriorating financial position of the borrowers. Financial regulations of various countries also impose restrictions on financial institutions to lend credit facilities to potential borrowers that have a current ratio which is lower than the defined limits.
Findings
Here, if the condition among three companies is considered than GDIC’s condition is best among others. However, GDIC as individual is considered then the present condition of GDIC is not good as it can be noted that though from the year 2008 to 2010 the current ratio was increasing by the year, but from the year 2010 to 2012 this trend is decreasing which is not good for the company. Also, it can be said that GDIC wants to reduce its current asset to meet creditor’s demand and wants to invest those current asset in somewhere else where it could generate more profit. Also, the condition of other two companies is not bad. As those have to maintain a certain standard.
Recommendation:
As GDIC’s position is better than other two companies so GDIC should compete with itself as the current ratio trend of GDIC is year by year decreasing. It needs to sustain its growth and for that reason it should reduce its debt burden as well as should increase its current assets amount. Also, it can sustain its position to meet creditor’s demand as the ratio is not bad.
Recommendations
There are some recommendations given below for Green Delta Insurance Company Limited on the basis of the overall condition of it.
- GDIC can introduce more subsidiary companies like Green Delta Securities and Capital limited. By this their consolidated profit can be increased. For an example, they can introduce bank so that it can take large portion of their facility from their own bank. By this it can be benefited from getting facilities from its own bank .Besides, from bank it can earn profit also.
- GDIC can arrange seminars for the public and as well as for the employees so that the employees can get a proper knowledge how to deal with customer and how to increase their network and facility. Also, the perception of general people towards insurance can be changed in a good way and people can feel interest to do insurance.
- GDIC should focus on the investment on the employee like it can buy land for the employees and the employees can repay the land price on installment basis by his the employees can get accommodation facility in future and that will motivate them to work more dedicatedly for the company.
- GDIC should increase their online facility. By this it can give and take facilities by setting in the desk.
- GDIC should improve its technological facilities and it should reduce its paper pencil works. By this the cost and time can be minimized. Also, work will be easier by the advancement of technology.
- GDIC should downsize the employees for minimizing the cost because if the employees are not productive then it will increase the cost of the organization.
- “Employee Recruitment Process”- should be done in a fare process so that appropriate and talented employees are selected through the recruitment process and increase the productivity and quality of the service.
- The most important thing that has come to my mind concerning their promotional activities is that they should go for print or broad cast media for advertisement to make their customer aware about their range of services and make the strong place in the customers‟ mind.
- They should increase the number of Branches in all over the country with the permission of IDRA (Insurance Development and Regulatory Authority). Thus, the clients in every city can enjoy their insurance facility from their own city.
Conclusion
In present insurance is too much important to the business and individual sector. Most of the companies provide more or less same services. For this reason the competition is increasing day by day between the insurance companies. On the other hand some new insurance companies are going to start businesses in the competent market. BGIC need to develop their some productive sectors. In present, a company cannot establish properly without developing information technology. People search their desires requirement through Internet so, insurance companies need to develop Web address to increase both foreign and local investors. So we have discussed about both the problem and prospects of insurance business in Bangladesh. The progress of insurance business depends on the progress of economic condition. Insurance business also faces many problem. So if we develop economic condition as well as overcome the problems, it will help a lot to flourish this business in our country. So, GDIC should focus on those issues to develop its growth and faith from its customers. Green Delta is proud to be a company that helps people in time of trouble. GDIC is a company that can and does pull all steps when needed. Like the country we are young and have blended our youthful vigor with specialized knowledge and experience. The Board of Directors of GDIC includes veterans of insurance, trade & industry, doctors, chartered accountant, business professionals. Our management team comprises of qualified professionals trained from UK, Switzerland, Germany and many other advanced countries.