Modified duration is a useful measure of a bond’s price (the present value of its cash flows) sensitivity to interest rate changes. It is an extension of Macaulay duration. In other words, it depicts the impact of a 100-basis point (1%) change in interest rates on the price of a bond. Modified duration follows the idea that loan costs and bond costs move in inverse ways. As the bond world is more complicated than the stock world, it is significant for the financial backer to know the altered term of the bond.
Duration is a measure of a bond’s interest rate risk or the danger of a bond’s price falling when market interest rates rise. The idea of modified duration depicts how bond prices and interest rates change in different ways. Bond prices fall as interest rates rise, while bond prices rise when interest rates fall. To just ascertain the modified duration of the bond first, the financial backer requirements to work out another thing, which is the Macauley span. To work out the Macauley span, the financial backer requirements to sort out the thing is the circumstance of the income.
Formula and Calculation of Modified Duration:
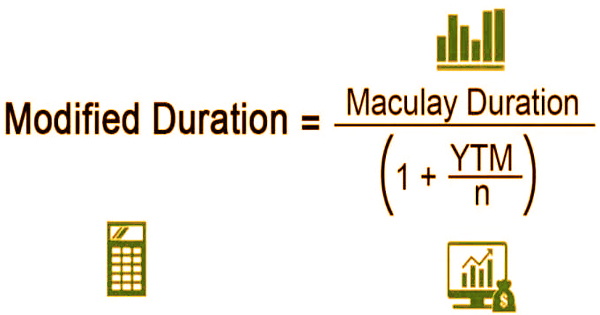
Modified Duration = Modified Duration / 1+ YTM/n
where:
Macauley Duration = weighted average term to maturity of the cash flows from a bond
YTM = yield to maturity
n = number of coupon periods per year
It’s crucial to understand the numerator component of the modified duration formula, the Macaulay duration, in order to calculate the bond’s modified duration. In general, the amount a bond price changes as a result of a change in yield (interest rate) is proportionate to the period to maturity. The weighted average period before a bondholder gets the bond’s cash flows is calculated using the Macaulay duration formula.
To compute modified duration, the Macaulay duration should initially be determined. It is the weighted normal of time until the incomes of a bond are gotten. In layman’s terms, the Macaulay span measures, in years, the measure of time needed for a financial backer to be reimbursed his underlying interest in a bond. It calculates the weighted average time till a bond pays off. Macaulay’s duration is modified such that it may be used to estimate price movement in response to a change in yield.
The percentage change in a bond’s price for a given change in yield is known as modified duration. The percentage change refers to the bond’s total price, including interest. The major benefit is that the investor must know the bond’s length since bond price volatility is directly proportional to bond prices. The more prominent the term of the bond, the more noteworthy is the value unpredictability. An altered term is an expansion of the Macaulay length, and to compute adjusted span, the Macaulay term should initially be determined.
The modified duration gives a decent estimation of a security’s affectability to changes in loan fees. The higher the Macaulay duration of security, the higher the subsequent adjusted term and instability to financing cost changes. The length of any investment instrument can aid in the management of future investment demands by allowing the investor to appropriately plan the future course of their investment. It’s also a gauge of the bond’s exposure to price changes and yield.
While modified duration is better than Macaulay’s duration, it has a few serious weaknesses:
It was thought that every rise or drop in yield would have the same effect on the bond price, which is not the case. It’s time to modify the convexity.
It calculates sensitivity using the yield to maturity rather than the whole structure of the yield curve. Modified duration is a poor substitute for the effective duration.
Because of the Macaulay Duration calculation, the modified duration calculation is complicated, and the user or investor additionally requires the yield and tenure inputs for the modified duration calculation. As a security’s development expands, span increments, and as a security’s coupon and loan cost builds, its length diminishes. Length is additionally not a total proportion of the danger containing in the bond cost and the bond span.
To create appropriate risk estimates, the investor cannot just rely on the duration measure. Because all other risk variables are equal, bonds with larger durations have greater price volatility than bonds with shorter durations. It is a highly significant statistic for portfolio managers, financial advisers, and customers to consider when picking investments. Macaulay duration calculates the bond’s weighted average duration, which isn’t always a reliable indicator of the bond’s risk.
Modified duration is a tool that offers an estimated assessment of how a bond price will vary given a small change in yield and is more often used than Macauley duration. Modified and Macaulay in spite of the fact that having impediments is to be sure an extremely accommodating idea, particularly for the portfolio administrators to quantify the unpredictability of the bond and the danger related with it, subsequently it can fill in as an exceptionally helpful instrument when the chief is building an arrangement of bonds and dealing with the danger related with it.
Information Sources: