Introduction
1.1 Origin of the Report:
Academic knowledge is not enough for business student, for the reason that there is a huge gap between theoretical aspect and practical situation. This is why internship program has been initiated mainly to bridge this gap. So it can be asserted that this report stems from the motto of gaining knowledge on practical business issues with the touch of knowledge acquired in the class room. Bangladesh is one of the poorest countries with a large unwaged population. As the opportunity to swell agricultural sector is limited, we have to predispose to expand industrial sector to triumph over our existing problems like joblessness, low economic augmentation and low living standard. Here industrial sector is very weak. To mull over the real situation government has instituted Bangladesh Shilpa Bank to stimulate industrialization. This bank offers term loan to different industries and entrepreneurs. The purpose of Bangladesh Shilpa Bank is not only to grant credit but also to develop the country in the course of industrialization by selecting correct venture and provides backing in different ways to execute successfully selected project.
1.2 Objectives of the Study:
The foremost purpose of this study is to identify and explore the Project Evaluation Practice by BSB. On my way to do this, I have tried to evaluate how BSB appraise the proposals of borrowers keeping the following points in mind. And these are
- To provide overall idea about the on hand project appraisal procedure
- Find out the ways that BSB uses in industrial development in Bangladesh.
- To study Bangladesh Shilpa Bank’s lending and implementation tactics like estimation of budget monitoring process, resource allocation etc.
- To indicate the limitations for problems of the lending and implementation procedure.
- To recommend necessary steps to overcome such limitations.
1.3 Methodology Required:
For preparing this report I had use some methodologies to collect proper and authentic data. Rules were followed to ease the data collection procedure. Accuracy of study depends on the information and data analysis.
Data have been collected from both primary and secondary sources . The sources of data are as follows.
Primary Data
- Face to face conversation with the head of the departments, respective officers of BSB.
- Relevant documents studies as provided by the officers concerned.
- Group discussion
- Discussion with my supervisor.
Secondary Sources of Data
- Annual Report of BSB,
- BSB order 1972,
- Project appraisal report,
- BSB General Regulation,
- Organizational charts,
- Journals and relevant books,
- BSB Website etc.
1.4 Constraints of the Report:
Actually, the truth is that, the limitations of this report are well tangible. They are as follows:
- Lack of experience: Honestly speaking , I agree that making a comprehensive study on project appraisal requires a clear idea regarding the total procedure of appraisal activities. As an intern I did not have enough access to share the real procedure of such activities.
- Time: It was one of the major limitations of this report. The subject matter of this report is so critical that despite of the time given, I have not been able to evaluate all the documents of BSB as it should be because of limited time submitting report.
- Inadequate discussion: As a new comer in the organization it is difficult to get a lot of time from the officials for discussion.
- Restricted Disclosures: Financial information is always confidential to any reporting entity. For the sake secrecy of all sort of information was not offered from the organization’s end.
Except those there are some other limitation as well –
- Lack of availability of data
- Up to date information is not available
- They are in govt. employee so have no eagerness to supply more because of extra hardness
1.5 Literature Review
Project evaluation practice of BSB is such an issue on which hundreds of studies have been done. So it is very difficult to bring something new on it. A project is a proposal for an investment to create, expand and/or develops certain facilities in order to increase the productions of goods and/or services in a community during a certain period of time. For the purpose of BSB, project means a scheme for capital investment to develop facilities to provide goods and services. BSB’s main function is to extend financial assistance to industrial project. It basically needs to be satisfied about the overall viability of a project to be financed. For this purpose, an objective assessment of the viability of the project is required to be examined by BSB from various points of view. Project appraisal consists of five different aspects of a project- Management and Organization, Technical, Market, Economic, and Financial.
A review of the promoters in respect of their integrity, experience and capabi1ities to implement and run the project is of prime importance before extending credit facilities to them. There are no set rules to find out if the borrowers or promoters are the men of integrity. It is to be done by direct and indirect investigation. The borrower’s experience .and capabilities can, on the other hand, be assessed in terms of his educational background, practical business experience, openness to new ideas, or good advice. By evaluating these it is possible to asses his adaptability in new and changing condition.
Directly related to the management is the form of organizational structure required to carry out and operate the project fruitfully. A very widespread consideration is the degree to which responsibility and authority are centralized or delegated.
The mechanical aspects of in industrial project are appraised to determine whether the project is sound with regard to every engineering and technological consideration, including product specification, process, size, internal balance, suitability and availability of physical facilities, designs and layouts of equipment and buildings etc.
For suitable marketing objective, it is necessary to look at depth into the – macro/micro demand/ supply situation for specific products in the market; Existing and expected competition in local and foreign markets; the market share, etc. While appraising industrial projects, the Bank is required to analyze these factors and to bring out the objective in quantitative terms-Product identification.
In economic appraisal, the project is looked at from the national or social point of view and the economic cash flow is constructed on the basis of “true or real prices”, commonly known as accounting or shadow prices. Economic appraisal should cover both quantifiable and non-quantifiable benefits (where applicable). Such benefits are Economic Rate of Return (ERR), Bruno Ration, Domestic Resource Cost, Contribution of Gross Domestic Product, and Employment Generation and Cost per employment.
The foremost rationale of financial appraisal is to assess if the proposed project is viable in term of its operation in the future years and its financial soundness. The financial analyst should have a clear idea as to what is intended to be achieved through the financial appraisal. The financial appraisal is directed to examine mainly the following two aspects: Fund requirement to bring the project in to existence and the probable sources from which the required funds will be mobilized; and Prospects of adequate revenue generation by the project when it goes into operation and the likely position of the concern with regard to its actual cash generation (liquidity) and its probable impact upon the financial condition (solvency).
Synopsis of BSB
2.1 Historical Background:
Industries play indispensable role in the economic enlargement of every country. This is why Industrialization has been used as as main mechanism of economic expansion in many developing countries. Government of Bangladesh instituted a development financial institution named Bangladesh Shilpa Bank on 31s December, 1972 under the presidential order no. 129 of 1972 with a mission of speeding the process of industrialization of the country by providing financial support and equity backing. It has been extending long and medium term loan facilities in local and foreign currencies to industrialize projects in the private and public sectors.
Institutional Overview of BSB
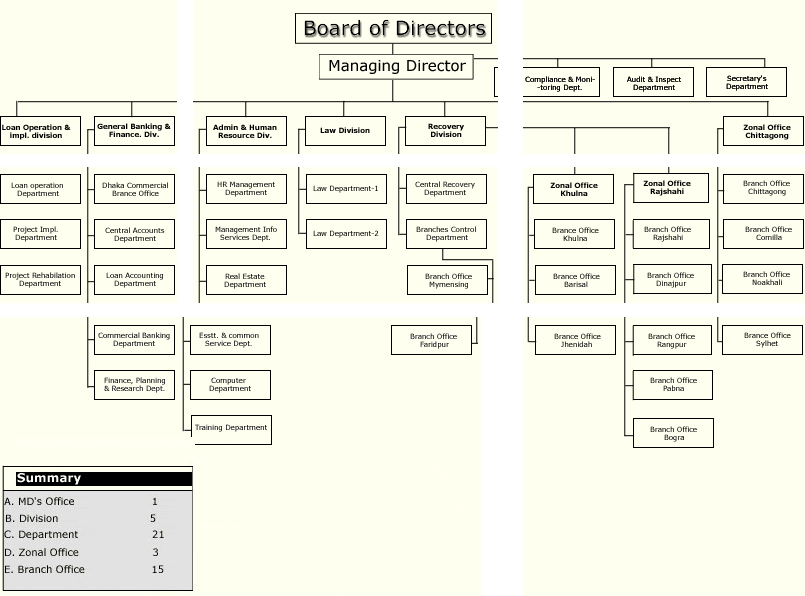
| Established | October 31,1972 | |
| Organization | Hear office | Dhaka |
| Division | 05 | |
| Department | 21 | |
| Zonal office | 03 | |
| Branch office | 15 | |
| Manpower | 769 |
2.2 Capital Structure and Sources of Fund:
Capital Structure of BSB
Capital Structure | Tk. (in Million) |
| Authorized | 2000 |
Paid – Up | 2000 |
Sources of Bank’s fund are the Government, Bangladesh Bank, Commercial Bank’s local / overseas financial institutions and supplies credit. At least fifty one percent of the authorized capital of Bangladesh Shilpa Bank must be subscribed by the government and remaining forty nine percent may be subscribed Bangladeshi nations or by financial institutions local or foreign. Presently, 100 percent ownership of the bank belongs to the government.
2.3 Ownership of BSB:
At least Bangladesh Government subscribes 51 percent of the Authorized capital of BSB and remaining 49 percent is subscribed by Bangladeshi nationals or by local or foreign Financial Institutions. Presently, 100 percent ownership of the Bank belongs to the Government.
2.4 Mission of BSB:
Bangladesh Shilpa Bank is the state owned Lending Department Financial Institution (DFI) of Bangladesh. The mission of BSB is accelerating the process of industrialization of the country by providing financial assistance and equity support.
2.5 Management of BSB:
The overall policy formulation and the general direction of Bank’s operation is taken in a Board of Directors appointed by the Government. This Board of Directors consists of 9(nine) members including the Chairman and the Managing Director. Non-Governments shareholders subscribing to the capital of the bank shall eventually elect 4 directors from amongst themselves. The Managing Directors is the chief executives of Bank. The General Managers assist the Managing Director in conducting the overall banking business.
2.6 Functions of BSB:
BSB extents term loan facilities in local and foreign currencies to industrial projects (both new and BMRE) in the and public sectors. Besides Bank also performs the following activities:
- Provides working capital loans to industrial projects.
- Provides equity support in the form of underwriting and bridge finance to public limited companies.
- Issues guarantees on behalf of borrowers for repayment of loan.
- Extends commercials banking services along with deposit mobilization.
- Purchases and sales shares / securities for BSB and on behalf of customers as member of Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE) ltd. and Chittagong Stock Exchange (CSE) ltd. for capital market development; and
- Conducts projects promotional activities along with preparation of various sub-sectoral study reports.
2.7 Other Activities
Advisory services:
The bank assists the interested entrepreneurs in selecting industrial projects having appropriate technology and potential market by providing advisory services and various information.
Training:
For upgrading the professional competence and skills of its employees, the bank is continually arranging training programs both at home and aboard. During FY-2002-03, 229 offices were provided in-house and local training. Besides, 40 offices wee sent aboard for the purposes.
Computerization:
To improve the working efficiency and provide better customer service, computerization of bank’s activities is on. In this regard, the bank has undertaken a far-figure action plan. Implementation of the first phase of network-based computerization is at the final stage.
2.8 Organizational Chart of BSB:
2.9: Significant Financial Indicators of BSB (in million taka)
| Indicators | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
| Total income | 771 | 772 | 714 | 690 | 824 |
| Total expenses | 350 | 941 | 343 | 338 | 361 |
| Net profit(loss) before tax | 421 | (220) | 335 | 497 | 326 |
| Total loan & advances | 6532 | 5269 | 6432 | 7010 | 6509 |
| Total borrowings | 7191 | 5911 | 5125 | 4538 | 3894 |
| Total deposits | 721 | 710 | 655 | 655 | 707 |
| Reserve fund & other reserves | 823 | 823 | 823 | 881 | 1110 |
| Paid- up capital | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 |
| Authorized capital | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 | 2000 |
| Provision for income tax | – | – | – | 497 | 77 |
| Payment to national exchequer | – | – | – | 10 | 10 |
Per cent | |||||
| Total income to total assets | 3.56 | 5.15 | 5.62 | 5.54 | 7.05 |
| Total expenses to total assets | 1.62 | 6.72 | 2.98 | 2.72 | 3.09 |
| Total expenses to total income | 45.40 | 130.33 | 48.03 | 44.98 | 43.65 |
| Total financial expenses to total income | 14.92 | 6.93 | 9.24 | 8.16 | 2.28 |
| Net profit to total income | 54.60 | (30.47) | 46.92 | 72.16 | 39.56 |
| Net profit to total equity | 17.02 | (9.76) | 12.94 | 16.45 | 9.69 |
| Administrative expenses to: | |||||
| Total assets | 0.94 | 1.56 | 1.94 | 2.26 | 2.61 |
| Total expenses | 58.00 | 23.27 | 69.96 | 83.25 | 84.51 |
| Total income | 26.33 | 30.33 | 35.01 | 40.78 | 37.01 |
ratio | |||||
| Debt- equity | 7:01 | 3:01 | 2.94:1 | 1.40:1 | 1.19:1 |
| Debt- service coverage | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
2.10: BSB at a Glance:
( number of projects)
Indicators | 2003-04 | 2004-05 | 2005-06 | 2006-07 | 2007-08 |
| Loans Applications Received | 51 | 83 | 96 | 51 | 47 |
| Term Loan Sanction | |||||
New | 21 | 34 | 45 | 37 | 12 |
BMRE | 3 | 1 | 2 | – | – |
Additional | 3 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 8 |
Total: | 27 | 38 | 52 | 39 | 20 |
| Working Capital Loan Sanctioned | 14 | 23 | 43 | 53 | 45 |
| Term Loan Disbursed | 5 | 3 | 9 | 15 | 3 |
| Started Commercial Operation | 4 | 7 | 25 | 8 | 27 |
| Rephrased / Rescheduled | 6 | 14 | 23 | 31 | 14 |
| Entered Into Loan Portfolio | 17 | 23 | 16 | 13 | 16 |
| Liquidated Loan Liabilities | 22 | 41 | 20 | 20 | 21 |
| Total Loan Portfolio | 308 | 166 | 164 | 179 | 177 |
| Write off ledger | – | 281 | 283 | 278 | 321 |
| Total No of Projects | 308 | 447 | 447 | 457 | 498 |
(Million Taka) | |||||
| Term Loan Sanctioned | 989 | 1009 | 1311 | 1006 | 918 |
| Term Loan Disbursed | 297 | 144 | 485 | 534 | 384 |
| Loan Recovered | 19 | 14 | 232 | 105 | 3 |
| Working Capital Loan Sanctioned | 26 | 21 | 32 | 196 | 33 |
| Working Capital Loan Disbursed | 1124 | 1391 | 1159 | 1065 | 981 |
| Rephrased / Rescheduled | 149 | 259 | 790 | 280 | 423 |
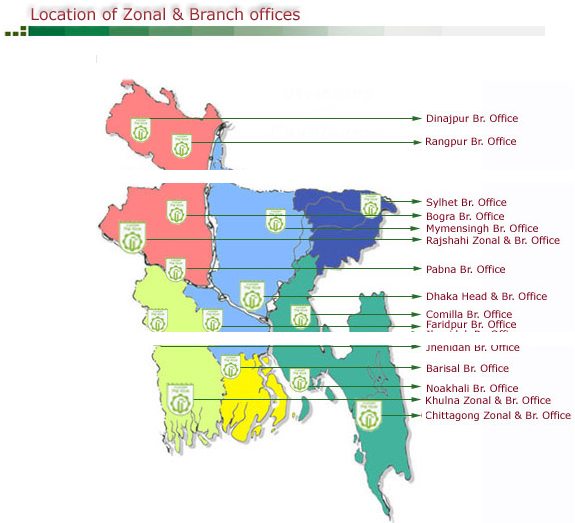
2.11: Zonal & Branch Offices of BSB (Location):
2.12:Prospects of BSB
Having a SWOT analysis is one of the most prolific techniques to bear out the prospects of an organization. The comparison of threats, opportunities, weaknesses and strengths is normally referred to as a SWOT analysis. It is popularly known as SWOT. The central purpose of the SWOT analysis is to identity strategies that align, fit, or match a company’s resources and capabilities to the demands of the environment in which the company operates. To put it another way, the purpose of the strategic alternatives generated by a SWOT analysis should be to build on company strength in order to exploit opportunities and counter threats and to correct company weakens. SWOT analysis explains in two broad ways on viewed of organizations environment. These are:
a): External Environment Analysis: It includes:
- Threats
- Opportunities and
b): Internal Environment Analysis: It includes:
- Weakness
- Strength
Throughout my period of internship program in BSB, I came across some aspects relating to the bank’s threats, opportunities, weaknesses and strengths which are more or less affects its performance. The points are summarized in the following table.
THREATS q Recovery systems are very weak q In some cases recovery policies are not practices properly q Introduction of certain harder banking rules and regulation q Third party consideration (Bangladesh Bank, Ministry of Finance etc. regulates the overall internal activities of the bank and bank must be bound to follow the rules f Bangladesh Bank.)
| WEAKNESS q Employee relation is bad in some cases q Normally in BSB mid and low level personnel are les qualified and experienced. q Bureaucracy official process hampered the daily internal workflow q The prime weakness I found lack of motivation of workers, originating from interpersonal clash, work environment, low salary structure q Absence of team work because of interpersonal clash q Management
|
OPPORTUNITIES q Gear –up recovery through setting up of pragmatic recovery targets q Expansion of new area of investment q Clearing loan ledger with exit facilities q All about efforts for deposit mobilization q Undertake need-based training program including computer training to all officers & develop a computerized data-base system and q Full computerization of bank’s activities
| STRENGTHS q As a prime DFI, it has a large number of qualified & experienced professionals. q Structural set-up & business location is strategic. q BSB’s assets position is quite satisfactory and q BSB has requisite strength and opportunity to sustain the challenge of the market economy
|
Functional Department of BSB and Their Activities:
3.1:Departments
Bangladesh Shilpa Bank has eight well-designed departments. The operational activities of Bangladesh Shilpa Bank have been operated by these departments in different ways. Every department has its own policies, procedure, and strategy to lending, and implementing credit. Each of the department depends on each other for sanctioning loan for propose industries. Loan Operation Department is the first step of loan sanction procedure and it is the most important department of Bangladesh Shilpa Bank:-
- Loan Operation Department
- Documentation and Machineries Procurement Department
- Project Implementation Department
- Project Rehabilitation Department
- Human Resource Management Department
- Law Department
- Loan Accounting Department
- Central Recovery Department.
3.2: Loan Operation Department :
Bangladesh Shilpa Bank grants loan on the basis of certain criteria. Any entrepreneur who wants to borrow money, from Bangladesh Shilpa Bank must fulfill at first Bank Standard Questionnaire Form (BSQF) in terms of TK. 1000.00. These processes are as follows:
- At first an application form is supplied to the entrepreneur for taka 1,000.00 only.
- After filling up the application form it is submitted by the entrepreneur;
- A project appraisal letter is supplied by the entrepreneur;
- After analyzing the project appraisal, the board decides whether the loan should be sanctioned or not;
- If the loan is sanctioned it is forwarded to the project implementation department.
3.3: Project Implementation Department:
When the loan operation department forwards the documents to the Project implementation department (PID), it performs the following activities:
- Undertaking necessary action initiatives after granting loan in favor of the project.
- Taking necessary action to make the factory lay-out.
- Making necessary adjustment in case of change of the project place, change of board of directors and change or extension of product mix etc.
- Making necessary attempt to give the loan a stage after the loan granting.
- To ensure that necessary capital has been supplied by the entrepreneur to ensure its proper utilization.
- To give necessary assistance in the case of Bridge loan from any financial institution.
- Taking necessary initiatives to construct the lay- out of the project according to construction cycle.
- Monitoring the machinery of the project, inspection and taking any kind of advice regarding to any machine related problem from machinery department.
- Verification of new material process of project ensuring the cash capital according to the loan terms and condition and providing necessary assistance in this matter.
- Inspection and monitoring experimental production extension of loan period.
- Making the final construction report (FCR) and transferring it to central recovery department (CRD) and concerned department/authorities.
- Determination of the construction period of the project preparing loan repayment schedule and taking after necessary action regarding this.
- Monitoring and inspecting the project to see whether the project is implementing according to time schedule and taking necessary initiatives to solve any kind of problem arising out therefore, and providing necessary advice to the entrepreneur.
- Receiving insurance letter against the predetermined risk of the implementation project assets and ensuring its deposit to bank.
- Inspection of the utility of the principles regarding the project implementation and presiding up to date principles.
3.4: Documentation and Machinery Procurement Department:
After sanctioning loan by Loan Operation Department, it issues a letter to documentation department, parties and after concerned departments. The documentation department issues a letter to the parties to produce necessary documents. Those documents are:
- Memorandum of Association and Articles of Association.
- The land upon which the project will be established, document of this land must be produced.
- Receipts of rent.
- Documentation fee.
- Mouja Map.
- The documents that reveal that the land were not sold within preceding two years.
Then a form is filled up. These documents are sent to lawyer. It every thing is good enough it is transferred to project implementation department.
In the documentation process the borrower are required to submit a copy of memorandum of association and articles of association. It is returned after the confirmation that it has been submitted according to the rules the borrower company must submit after the authorization by direction of registration of Joint Stock Company and firm. The following activities are performed during the time of documentation process:
- The Borrower Company must submit necessary documents.
- Verification of documents by documentation and machinery dept. and law dept.
- Preparation of all documents of the borrower company director.
3.5: Central Recovery department
Project implementation department makes a repayment schedule and gives it to the borrower. Normally the interval is 6 months. This department inspects the project after every 6 months to see whether there is any leakage. If the borrower fails to repay the loan as the application of the borrower it is rescheduled. Sometimes a portion of interest is exempted. If the borrower fails to repay the loan than it is transferred to law department to take legal action on the application of the borrower. Sometimes the project is transferred to project Rehabilitation Department to restore the project.
Principles of classification of loan and provision:
For the purpose of classification all loans and advances are divided into 4. These are:
- Continuous loan: The loan which can be granted and recovered without any repayment schedule but have an expiry date and maximum limit are called continuous loan.
- Demand loan: The loan which must be repaid as the bank calls it is demand loan.
- Term loan: The loan which must be repaid as the bank calls it is term loan.
- Short-term agricultural and micro-credit: The loan which is paid in less term and condition is known as short-term agricultural and micro-credit loan.
Objective criteria:
If any continuers loan is not repaid within the expiry date then it is called irregular loan. The classification of loan are as follows:
6 months > continuous loan > 3 months = sub topped
12 months > continuous loan > 6 months = doubtful
Continuous loan > 12 months = bad
If any installment of any term loan is not repaid within specific date it is treated installment default.
Maintenance of provision:
- On the basis of the equity of the loan the following precession are maintained:
- Substandard 20%
- Doubtful 50%
- Bad debt 100%
- On all debt other than bad debt 5%
- On bad debt 100%
- On short term agricultural and micro-credit the following provision to be kept:
3.6: Loan Accounting Department:
Loan Accounting Department is the department which centrally maintains all loan amounts of the bank. There are 4 sections which perform the activities of the department:
- Not due section
- Amount due section / over due section
- Replacement section
- General and policy section.
1. Not due is the installment not yet due for payment in schedule time fixed by the project
Department /Branch officer.
2. The payment of installment and interest in not paid /cleared in time is overdue.
The functions of this department are:
- accurately list of balance preparation
- advice sending to borrower
- Quarter / half year by interest charge.
3. When the overdue is rephrased or waived then the replacement section will do the needful activities.
4. General and policy section do the following:
a. To prepare the monthly Trial balance
b. Monthly recovery statement
c. Monthly disbursement schedule
d. To make entry all the transaction as per daily statement received from the branch officer.
e. All list of balances of not due send to the Head Office and staff as specific guidelines
of the authorities.
f. To prepare distribution of work among the officers and staff as specific guidelines of the authorities.
3.7: Law Department:
If the Bangladesh Shilpa Bank fails to recover its loan in the normal way, it must undertake alternative actions and file case in the court. The cases which Bangladesh Shilpa Bank files are:
- Recovery Case Section 33
- Financial Loan Case Section 5(a)
- Certificate case Section 35
- Bankruptcy Case Section 9(1)
- Case if Check is not cashed Section 198
(Petition case)
- Case if machinery of projects are
transferred from the project Section 37
3.8: Human Resources Management Department:
Bangladesh Shilpa Bank has total 725 personnel. It is divided into two categories. These are:
- Job-wise distribution
- Profession-wise distribution
Training & Development of Human Resource:
Bank has a Training Department for upgrading the professional competence and skills of its officers and Staff. Below are the main functions of Training Department: –
To prepare & implement Annual Training Program.
To impart training of the Officers/Staff regarding business & operations of the Bank.
To adopt measures to hold in-house training and make arrangements to send Bank’s officers to overseas training programs.
To establish liaison with domestic & overseas organizations relating to training.
To send Officers to local training institutions for improving professional skills; and
To organize Seminar/Workshop/Symposium on key economic/banking issues.
Types of Training:
There are as many as 3 (three) types of training as under: –
- In-house.
- Local and
- Overseas.
Logistic support:
Training Department has the following logistic support: –
- Training Hall with Air-condition facility accommodating about 25 (twenty five) participants.
- Multi-media Projector.
- Flip Chart.
- Mini Computer Lab and
- In-house Resource Persons.