HR Operations Activities: A Study on Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh
In the beginning of the report there are description about Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh like how they started and which industry they are doing their business. In this report try to focus about their HR activities to know how a growing company manages their whole man power so that the total scenario about the organization can be understood.
An objective is made in a way so that the information regarding HR activities can be known. Most of the time the primary data was used and secondary data was used to know about the facts which are already been known or published. Interviewing some other people from HR department was another task which was done in order to know more information about their recruitment activities they do, selection process, and their performance appraisal system. The scope was doing this study was to find out the future prospect of Accenture whether they are really doing well or not or what would be their future planning in competition to the other competitors in market and what they would modify in their services to do more profit which is the ultimate goal.
But there were some limitations which create barrier for the study as all the information cannot be gathered and there were confidential information which Accenture couldn‘t provide. In the report it was discussed that how the IT industry is in Bangladesh and why Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh started their journey. Then their mission, vision and values are being stated in a way so that what they are all about can be understood.
The HR activity of Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh was described in a way so that every activity done by them can be understood. Recruitment and selection process, mobility, employee engagement and benefits available for the employees and so forth.
At last but not the least the analysis and recommendation portion of this report shows the findings of the report. A recommendation for HR department is made in way by which they can improve their work activities to achieve the position they want in the market. Conclusion part has been made to give a proper ending to this report.
Introduction
Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh is a multinational management consulting, technology services, and outsourcing company. Its incorporated headquarters are in Dublin, Republic of Ireland. It is the world’s largest consulting firm as measured by revenues and is a Fortune Global 500 company. As of 2013, the company reported net revenues of $28.6 billion with approximately 293,000 employees, serving clients in more than 200 cities in 56 countries.
Accenture has more employees in India than any other country; in the US, it has about 40,000 employees and 35,000 located in the Philippines. Accenture’s current clients include 91 of the Fortune Global 100 and more than three-quarters of the Fortune Global 500. Since September 1, 2009 the company has been incorporated in Ireland.
Accenture common equity is listed on the New York Stock Exchange, under the symbol ACN, and was added to the S&P 500 index on July 5, 2011. GPIT, an IT subsidiary of Grameenphone, sold 51 percent of its shares to US-based management and IT consultancy firm Accenture. The share transfer is a subject to board approval, says a notification to the Dhaka Stock Exchange. An extraordinary general meeting (EGM) is scheduled to take place on 01 August to obtain approval to transfer the shares to Accenture, says the notification. There is also a proposal to grant GP an option to sell its remaining GPIT shares to Accenture at a later date and also to grant Accenture an option to buy those remaining shares.
History
Continuous innovation and rapid transformation have been themes throughout Accenture’s history, which the company traces to the 1950s with the installation of the first computer system for commercial use in the United States at General Electric‘s Appliance Park facility.
The company built its reputation primarily as a technology consultant and systems integrator. By the late 1980s, Accenture began offering a new breed of business integration solutions to clients—solutions that aligned organizations’ technologies, processes and people with their strategies.
Throughout its history, Accenture has expanded its offerings and capitalized on evolving management trends and technologies to benefit its clients. The company pioneered systems integration and business integration; led the deployment of enterprise resource planning, customer relationship management and electronic services; and has established itself as a leader in today’s global marketplace.
Today Accenture is a global management consulting, technology services and outsourcing company, with more than 293,000 people serving clients in more than 56 countries. Combining unparalleled experience, comprehensive capabilities across all industries and business functions, and extensive research on the world‘s most successful companies, Accenture collaborates with clients to help them become high-performance businesses and governments. The company generated net revenues of US$28.6 billion for the fiscal year ended Aug. 31, 2013.
Accenture in Bangladesh
GPIT, an IT subsidiary of Grameenphone, sold 51 percent of its shares to US-based management and IT consultancy firm Accenture. The share transfer is a subject to board approval, says a notification to the Dhaka Stock Exchange. An extraordinary general meeting (EGM) is scheduled to take place on 01 August to obtain approval to transfer the shares to Accenture, says the notification. There is also a proposal to grant GP an option to sell its remaining GPIT shares to Accenture at a later date and also to grant Accenture an option to buy those remaining shares.
Grameenphone shareholders approved the 51 per cent share transfer of GPIT to Accenture Holdings BV at an Extra-ordinary General Meeting chaired by M Shahjahan, member of the board, on 1st August, 2013. The meeting was conducted by Hossain Sadat, company secretary of Grameenphone. At the meeting, the shareholders approved the transfer of 382,500 shares.
Accenture Strategy
Accenture Strategy operates at the intersection of business and technology. Because technology is transforming every organization, you need technology-enabled strategy to take advantage of the opportunities. Whether it’s business strategy, technology strategy or operations strategy, we drive value, shape new businesses and design operating models for the future. That‘s high performance, delivered.
Workforces
The four workforces serve clients in the areas of consulting, technology, and outsourcing, as well as the company itself. This is almost always an internal designation as it is common place for Accenture employees to work in blended teams for a variety of reasons.
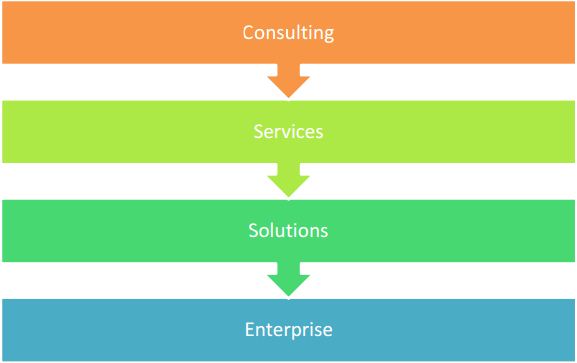
Consulting: Focus on management consulting, process design work and the application of technologies to business. Responsible for sales, delivery, and leadership of most of Accenture’s project-based work.
Services: Most focus on outsourcing engagements in the areas of business operations, IT, applications development and maintenance, help desk services, and HR. As part of some outsourcing deals, clients’ internal teams can be “re-badged” as Accenture employees aligned to this workforce. Sometimes they work on consulting projects or as internal Enterprise teams.
Solutions: The Accenture Technology Solutions subsidiary focuses on the specific technology skills needed to deliver projects or outsourcing arrangements. Comprises the majority of Accenture’s employees in delivery centers in developing countries like Brazil, India, and the Philippines.
Enterprise: Focus on managing and supporting all the activities across Accenture’s business, including legal, security, facilities, marketing, and client financial management.
Operating Groups
As most consulting firms, Accenture operates in a matrix structure. The first axis is dedicated to the operating groups, or industries of its clients. Broadly, the five Operating Groups are:
- Communications, Media & Technology
- Financial Services
- Products
- Resources
- Health & Public Services
The five Operating Groups comprises 19 industry subgroups that focus on industry evolution, business issues, and applicable technologies.
Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh
This project is on Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh, a multinational organization. In this project part the three most important parts is being discussed under the Operation department.
The working procedures and the type of work this department in involve with the sub departments are Employee relationship, Employee engagement and Mobility. The primary concern is to gather knowledge about the Organization itself but mostly the operation department.
Objective
General objective
The prime objective is to state the “Inside the operation department” of Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh
Primary objective
- To understand the inside-out of operation department.
- To understand their strategy to compete with other existing organization.
iii. How they track their important documents and what to write in different official papers.
- To know how Accenture deals with employees and maintain a strong PR.
- Track various employees who work in a foreign country.
- To understand how the insurance activities work underneath.
vii. The legal procedure to go for an agreement with partner countries.
viii. How they engage people and assure a strong employee engagement.
- Strategy for maintaining both locally and globally.
Methodology
To complete this project I used both Primary and Secondary methods in order to get prominent information which can full fill the objectives of my report. I took most of the information from the face to face communication with the employees. Some information is gathered from my own experience. On the secondary method I used Accenture‘s personal websites and other source of information‘s like online news and reports.
Accenture Global Operations Megatrends Study
Explore Supply Chain Success Factors in Emerging Markets study to learn how leading companies are adopting four practices to maximize their emerging market success. Ninety-five percent (95%) of the surveyed executives have experienced growth from emerging markets in the past three years, and cited China and India as one of their top three sources of the growth, followed by Southeast Asia and Eastern Europe.
The research also found that companies with high-performing supply chains were more likely to generate stronger growth than companies with average or low-performing supply chains. These leaders have employed a strategic mix of operational practices that has enabled them to achieve greater than 20 percent growth in their priority emerging markets. Explore the findings in detail and learn about the four supply chain practices than can help companies achieve strong growth in emerging markets.
Analysis of the Report
The operation department of Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh consists of three primary tasks.
- Employee Relationship
- Employee Engagement
- People Mobility
The Accenture Global Operations Megatrends research study is designed to explore key trends in the operations function. The research is focused on three areas of concern for supply chain leaders globally: emerging market growth, supply chain risk management and big data analytics. The intent of the research is to understand the specifics of what companies are executing and planning in these areas, and the effectiveness of those strategies.
The research involved a Web-based survey of 1,014 senior executives at large global companies headquartered in the respondents‘ locations. Fifty-six percent of respondents held C-level titles, including chief supply chain officer, chief procurement officer, chief sourcing officer, chief operations officer and chief operating officer. The remaining 44 percent were senior level supply chain, procurement or operations executives
Organizations Served
Human services agencies worldwide turn to Accenture for help on a variety of initiatives— from policy analysis and strategy to large-scale systems design, implementation and maintenance.
Eligibility Systems
Public service leaders must embrace four structural shifts—advancing toward personalized services, insight-driven operations, a public entrepreneurship mindset and a cross-agency commitment to mission productivity. By making these shifts, leaders can support flourishing societies, safe, secure nations and economic vitality for citizens—delivering public service for the future.
Education
Education institutions must deliver cost-effective and quality education for the 21st century student. Accenture helps education institutions modernize administrative processes and functions, becoming more agile while also improving the technology that underpins the organization.
Nonprofit
Nonprofit organizations today face unprecedented challenges—global economic conditions mean a steady decline in government support as demands for their services increase.
Accenture understands that nonprofits ultimately want to target donors more effectively and keep back-office expenses down using IT to drive transformation and realize lasting programmatic efficiency—so they can spend more effort and resources toward achieving their mission.
Employee Relationship
This department basically deals with all kinds of insurance facility for the permanent employees. During my internship I learned – how this department allocate and assure the insurance facilities and about the insurance plans as well. The rules and regulations are quite long and the procedures are quite important as well.
Basically this organization is highly promised with its individual employees to assist financially in their needs. It‘s a great way to ensure employee satisfaction.
- Official insurance partner: Delta insurance company, Bangladesh
- Financial support: The allocation of money for each is 2,000,00 taka only. It‘s for only the permanent employees. Most of the time when employees join they fill up all the prescribed paper where they submit their medical documents and other necessary papers. They also fill up the form where they mention the number of family members and their names as well.
- Who get the support: Definitely everyone will assume that the employee himself will get the financial security. But here it’s really comforting to see that, not only employee himself but the close ones or direct family members (Children, spouse and parents) get the same facility as well.
- Hospitals and Diagnosis: Organization has some listed hospitals where the employees are registered to get the medical facilities. Listed hospitals areApollo hospitals, Dhaka United hospital Lab aid Square hospital If in times of emergency employees can get help from non-listed hospital as well.
- Type of payment: Employees can get there payment in two types.
- Reimbursement: This method of payment is applicable only when the employee is having facility from the non-listed hospitals. In this case they pay first and then employees submit their cost/cash memo including all supporting documents to the organization. When this department checks or verifies the documents and sends the papers to the insurance company. Then employees can refund his/her payments.
- Direct: This is the regular procedure where company direct pay the necessary amount to the listed hospital at the time when employees are having medical support. Once the company will pay for employee or any of his/her family then after three month they can have the same amount money facilitated by the organization for the same medical treatment.
Besides, employee relationship also deals with AOR which stands for acceptance of resignation. When an employee wants to resign, then this particular department deals with all the official action necessary.
Employee Engagement
Employee engagement is a workplace approach designed to ensure that employees are committed to their organization‘s goals and values, motivated to contribute to organizational success, and are able at the same time to enhance their own sense of well-being.
There are differences between attitude, behavior and outcomes in terms of engagement. An employee might feel pride and loyalty (attitude); be a great advocate of their company to clients, or go the extra mile to finish a piece of work (behavior).
Outcomes may include lower accident rates, higher productivity, fewer conflicts, more innovation, lower numbers leaving and reduced sickness rates. But we believe all three – attitudes, behaviors and outcomes – are part of the engagement story. There is a virtuous circle when the pre-conditions of engagement are met when these three aspects of engagement trigger and reinforce one another.
Engaged organizations have strong and authentic values, with clear evidence of trust and fairness based on mutual respect, where two way promises and commitments – between employers and staff – are understood, and are fulfilled.
Although improved performance and productivity is at the heart of engagement, it cannot be achieved by a mechanistic approach which tries to extract discretionary effort by manipulating employees‘ commitment and emotions. Employees see through such attempts very quickly; they lead instead to cynicism and disillusionment.
By contrast, engaged employees freely and willingly give discretionary effort, not as an ‗add on‘, but as an integral part of their daily activity at work.
But is employee engagement something new, or simply old wine (long-standing management approaches) in new (fashionable management-speak) bottles? Is it just the latest management fad? We believe that while it does have clear overlaps with analytical antecedents such as commitment, ‗organizational citizenship behavior‘, job involvement and job satisfaction, there are also crucial differences.
In particular, engagement is two way: organizations must work to engage the employee, who in turn has a choice about the level of engagement to offer the employer. Each reinforces the other.
An engaged employee experiences a blend of job satisfaction, organizational commitment, job involvement and feelings of empowerment. It is a concept that is greater than the sum of its parts.
Despite there being some debate about the precise meaning of employee engagement there are three things we know about it: it is measurable; it can be correlated with performance; and it varies from poor to great. Most importantly employers can do a great deal to impact on people‘s level of engagement. That is what makes it so important, as a tool for business success.
By the name of this department it‘s almost clear what this department is all about. The main motto of this department is to break the ice between the coworkers.
After every certain period, employee engagement held a strategic meeting. This team organizes small games and corporate dancing and few other interesting activities in order to make employees comfortable to the environment. Few popular strategies for engagement are highly used in the global perspective. It‘s a way not to engage but to refresh individuals.
Generating Engagement
While it is possible to measure engagement itself through employee surveys, this does not assist in identifying areas for improvement within organizations. To manage employee engagement upwards, it is necessary to identify what drives engagement. Some points from research into drivers of engagement are presented below:
Employee perceptions of job importance – “…an employee’s attitude toward the job’s importance and the company had the greatest impact on loyalty and customer service than all other employee factors combined.”
Employee clarity of job expectations – “If expectations are not clear and basic materials and equipment are not provided, negative emotions such as boredom or resentment may result, and the employee may then become focused on surviving more than thinking about how he can help the organization succeed.”
Career advancement / improvement opportunities – “Plant supervisors and managers indicated that many plant improvements were being made outside the suggestion system, where employees initiated changes in order to reap the bonuses generated by the subsequent cost savings.”
Regular feedback and dialogue with superiors – “Feedback is the key to giving employees a sense of where they‘re going, but many organizations are remarkably bad at giving it. “‘What I really wanted to hear was ‘Thanks. You did a good job.’ But all my boss did was hand me a check.’
Quality of working relationships with peers, superiors, and subordinates – “…if employees’ relationship with their managers is fractured, then no amount of perks will persuade the employees to perform at top levels. Employee engagement is a direct reflection of how employees feel about their relationship with the boss.”
Perceptions of the ethos and values of the organization – “‘Inspiration and values’ is the most important of the six drivers in our Engaged Performance model. Inspirational leadership is the ultimate perk. In its absence, It is unlikely to engage employees.”
Effective internal employee communications – which convey a clear description of “what’s going on”. “‘
Reward to engage – look at employee benefits and acknowledge the role of incentives. “An incentive to reward good work is a tried and test way of boosting staff morale and enhancing engagement.”
Commitment theories are rather based on creating conditions, under which the employee will feel compelled to work for an organization, whereas engagement theories aim to bring about a situation in which the employee by free choice has an intrinsic desire to work in the best interests of the organization.
Recent research has focused on developing a better understanding of how variables such as quality of work relationships and values of the organization interact, and their link to important work outcomes. From the perspective of the employee, “outcomes” range from strong commitment to the isolation of oneself from the organization.
People Mobility
Accenture Mobility, part of Accenture Digital, plans, implements and manages mobility solutions for businesses and public organizations, including developing and implementing enterprise mobility strategies; incorporating applications and managed services; creating and delivering ecommerce solutions; and supplying credible, business ready Connected Product offerings.
Accenture Mobility services are based on deep industry insights and technical expertise that helps clients across all industries achieve growth, efficiency and manage a successful transformation as they adopt the tools of a digital business.
One of the most vital departments of Accenture CIS, This department is responsible with all kinds of “supporting” documents. Such as-
Invitation letters: in every month sometime probably in every fifteen days organization invites someone from outside the organization. Some are from different organization, some from out of the country. While doing that the person gets an invitation latter and by which he/she came to know the detail plan or at least the first step of the invitation. This department writes the necessary information and provide where needed.
Forwarding letters: Mobility also deals with forwarding letters. Every employee get this letter when they need to access to other organization for any official purpose. It‘s sort of evidence that one is working in Accenture, BD.
Introductory letters: In many times for meeting or training when employees visit beyond border then this department provide them introductory letter. It consists of all those supporting document(s) which is needed by the employee. It‘s a back support by the company for the employee in order to ease the foreign business tour.
Offer letter: It’s a general offer letter provided for the new comer. Mobility team also kept on tracing the employee‘s activity on what they do when they are in a foreign country on behalf of the company. Provide necessary official documents. This particular department is responsible to keep the work on process.
Conclusion
- Industry
- Infusing more talent into operating groups
- High-touch channel
- Enhance capacity to serve clients
- More quickly assemble integrated teams with specialized skills
- Move people from Management Consulting and Technology into the operating groups
- More responsive and relevant to client needs
- Strategy
- Expertise at the intersection of business, technology and operations
- Strategies enabled by technology.
- Highly-differentiated marketplace offering
- Accenture Technology
- Helping clients apply technology to innovate, grow and improve technology operations and performance
- With a continued focus on:
- Accenture Technology Labs
- Alliances with top technology providers
- Global delivery capability, which includes Global Delivery Network.
In short, Life in Accenture is all about ―Whole > Parts‖!
Finally I can say that throughout my internship, I gained lot of valuable knowledge by the Human Resources department. The company Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh lately came in the business with their own name and logo. I am highly obliged for being a part of this company, and understanding their services and policies, operational structure, strategies and the implementations of course of actions to achieve revenue. The HR Operations team of
Accenture contributes intensive effort to maintain the standards of the company. The reflection of the efforts could be seen from their employee‘s huge response and other services. The pace at which Accenture CIS Ltd. Bangladesh is currently accelerating, will undoubtedly lead the company to the peak of success soon. I will be concluding my affiliation report by stating that, being able to work with a company which is a brand enabled me to captivate a bundle of practical knowledge which will turn out to be a great support for my future plans.
Recommendation
For the customer, it‘s the invisible and omnipresent processes behind everything they do, every day –from first thing in the morning to last thing at night. Great service means things just. Great service like that is built around the customer, according to their needs and preferences. And that‘s where Accenture‘s Service Strategy and Operations Group come in.
Great service comes from using predictive analytics to see an issue and fix it before it becomes a problem. Leading businesses have mastered what it takes to deliver great service like this, round the clock – day in, day out.
But of course it‘s not easy to achieve. Customers have increasingly high expectations of service, but they‘re very often disappointed with what they receive and if they don‘t get what they want they won‘t come back.
Our global solutions and services encompass consulting, technology and outsourcing with a comprehensive range of offerings to address all dimensions of service strategy and operations.
Accenture is truly a full service provider: we can work with you to create your service strategy, help develop the required business capabilities, design and deploy the enabling technologies, and also offer managed services and BPO capabilities to support service execution.