Meaning of Recruitment
Recruitment means to estimate the available vacancies and to make suitable arrangements for their selection and appointment. Recruitment is understood as the process of searching for and obtaining applicants for the jobs, from among whom the right people can be selected.
A formal definition states, “It is the process of finding and attracting capable applicants for the employment. The process begins when new recruits are sought and ends when their applicants are submitted. The result is a pool of applicants from which new employees are selected”. In this, the available vacancies are given wide publicity and suitable candidates are encouraged to submit applications so as to have a pool of eligible candidates for scientific selection.
In recruitment, information is collected from interested candidates. For this different source such as newspaper advertisement, employment exchanges, internal promotion, etc. are used.
In the recruitment, a pool of eligible and interested candidates is created for selection of most suitable candidates. Recruitment represents the first contact that a company makes with potential employees.
According to Edwin B. Flippo, “Recruitment is the process of searching the candidates for employment and stimulating them to apply for jobs in the organization”. Recruitment is the activity that links the employers and the job seekers. A few definitions of recruitment are:
- A process of finding and attracting capable applicants for employment. The process begins when new recruits are sought and ends when their applications are submitted. The result is a pool of applications from which new employees are selected.
- It is the process to discover sources of manpower to meet the requirement of staffing schedule and to employ effective measures for attracting that manpower in adequate numbers to facilitate effective selection of an efficient working force.
Recruitment is a continuous process whereby the firm attempts to develop a pool of qualified applicants for the future human resources needs even though specific vacancies do not exist. Usually, the recruitment process starts when a manger initiates an employee requisition for a specific vacancy or an anticipated vacancy.
Sources of Recruitment
Every organization has the option of choosing the candidates for its recruitment processes from two kinds of sources: internal and external sources. The sources within the organization itself (like transfer of employees from one department to other, promotions) to fill a position are known as the internal sources of recruitment. Recruitment candidates from all the other sources (like outsourcing agencies etc.) are known as the external sources of recruitment.
Figure: Sources of Recruitment
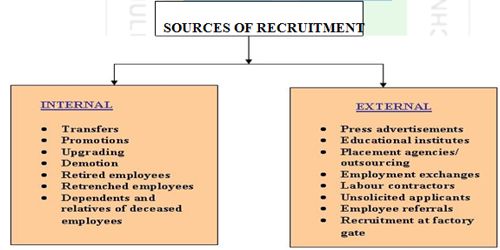
Internal Recruitment
Internal recruitment seeks applicants for positions from within the company. The various internal sources include:
- Promotions and Transfers: Promotion is an effective means using job posting and personnel records. Job posting requires notifying vacant positions by posting notices, circulating publications or announcing at staff meetings and inviting employees to apply. Personnel records help discover employees who are doing jobs below their educational qualifications or skill levels. Promotions has many advantages like it is good public relations, builds morale, encourages competent individuals who are ambitious, improves the probability of good selection since information on the individual’s performance is readily available, is cheaper than going outside to recruit, those chosen internally are familiar with the organization thus reducing the orientation time and energy and also acts as a training device for developing middle-level and top-level managers. However, promotions restrict the field of selection preventing fresh blood & ideas from entering the organization. It also leads to inbreeding in the organization. Transfers are also important in providing employees with a broad-based view of the organization, necessary for future promotions.
- Employee referrals: Employees can develop good prospects for their families and friends by acquainting them with the advantages of a job with the company, furnishing them with introduction and encouraging them to apply. This is a very effective means as many qualified people can be reached at a very low cost to the company. The other advantages are that the employees would bring only those referrals that they feel would be able to fit in the organization based on their own experience. The organization can be assured of the reliability and the character of the referrals. In this way, the organization can also fulfill social obligations and create goodwill.
- Former Employees: These include retired employees who are willing to work on a part-time basis, individuals who left work and are willing to come back for higher compensations. Even retrenched employees are taken up once again. The advantage here is that the people are already known to the organization and there is no need to find out their past performance and character. Also, there is no need of an orientation program for them, since they are familiar with the organization.
- Dependents of deceased employees: Usually, banks follow this policy. If an employee dies, his / her spouse or son or daughter is recruited in their place. This is usually an effective way to fulfill social obligation and create goodwill.
- Recalls: When management faces a problem, which can be solved only by a manager who has proceeded on long leave, it may de decided to recall that persons after the problem is solved, his leave may be extended.
- Retirements: At times, management may not find suitable candidates in place of the one who had retired, after meritorious service. Under the circumstances, management may decide to call retired managers with new extension.
- Internal notification (advertisement): Sometimes, management issues an internal notification for the benefit of existing employees. Most employees know from their own experience about the requirement of the job and what sort of person the company is looking for. Often employees have friends or acquaintances who meet these requirements. Suitable persons are appointed at the vacant posts.
External Recruitment
External recruitment seeks applicants for positions from sources outside the company. They have outnumbered the internal methods. The various external sources include:
- Professional or Trade Associations: Many associations provide placement service to its members. It consists of compiling job seeker’s lists and providing access to members during regional or national conventions. Also, the publications of these associations carry classified advertisements from employers interested in recruiting their members. These are particularly useful for attracting highly educated, experienced or skilled personnel. Also, the recruiters can zero on in specific job seekers, especially for hard-to-fill technical posts.
- Advertisements: It is a popular method of seeking recruits, as many recruiters prefer advertisements because of their wide reach. Want ads describe the job benefits, identify the employer and tell those interested how to apply. Newspaper is the most common medium but for highly specialized recruits, advertisements may be placed in professional or business journals. Advertisements must contain proper information like the job content, working conditions, location of job, compensation including fringe benefits, job specifications, growth aspects, etc. The advertisement has to sell the idea that the company and job are perfect for the candidate. Recruitment advertisements can also serve as corporate advertisements to build company image. It also cost effective.
- Employment Exchanges: Employment Exchanges have been set up all over the country in deference to the provision of the Employment Exchanges (Compulsory Notification of Vacancies) Act, 1959. The Act applies to all industrial establishments having 25 workers or more each. The Act requires all the industrial establishments to notify the vacancies before they are filled. The major functions of the exchanges are to increase the pool of possible applicants and to do the preliminary screening. Thus, employment exchanges act as a link between the employers and the prospective employees. These offices are particularly useful to in recruiting blue-collar, white collar and technical workers.
- Campus Recruitments: Colleges, universities, research laboratories, sports fields and institutes are fertile ground for recruiters, particularly the institutes. Campus Recruitment is going global with companies like HLL, Citibank, HCL-HP, ANZ Grind lays, L&T, Motorola and Reliance looking for global markets. Some companies recruit a given number of candidates from these institutes every year. Campus recruitment is so much sought after that each college; university department or institute will have a placement officer to handle recruitment functions. However, it is often an expensive process, even if recruiting process produces job offers and acceptances eventually. A majority leave the organization within the first five years of their employment. Yet, it is a major source of recruitment for prestigious companies.
- Walk-ins, Write-ins and Talk-ins: The most common and least expensive approach for candidates is direct applications, in which job seekers submit unsolicited application letters or resumes. Direct applications can also provide a pool of potential employees to meet future needs. From employees’ viewpoint, walk-ins are preferable as they are free from the hassles associated with other methods of recruitment. While direct applications are particularly effective in filling entry-level and unskilled vacancies, some organizations compile pools of potential employees from direct applications for skilled positions. Write-ins are those who send written enquiries. These jobseekers are asked to complete application forms for further processing. Talk-ins involves the job aspirants meeting the recruiter (on an appropriated date) for detailed talks. No application is required to be submitted to the recruiter.
- Contractors: They are used to recruit casual workers. The names of the workers are not entered in the company records and, to this extent; difficulties experienced in maintaining permanent workers are avoided.
- Consultants: They are in the profession for recruiting and selecting managerial and executive personnel. They are useful as they have nationwide contacts and lend professionalism to the hiring process. They also keep prospective employer and employee anonymous. However, the cost can be a deterrent factor.
- Head Hunters: They are useful in specialized and skilled candidate working in a particular company. An agent is sent to represent the recruiting company and offer is made to the candidate. This is a useful source when both the companies involved are in the same field, and the employee is reluctant to take the offer since he fears, that his company is testing his loyalty.
- Radio, Television and Internet: Radio and television are used to reach certain types of job applicants such as skilled workers. Radio and television are used but sparingly, and that too, by government departments only. Companies in the private sector are hesitant to use the media because of high costs and also because they fear that such advertising will make the companies look desperate and damage their conservative image. However, there is nothing inherently desperate about using radio and television. It depends upon what is said and how it is delivered. Internet is becoming a popular option for recruitment today. There are specialized sites like naukri.com. Also, websites of companies have a separate section wherein; aspirants can submit their resumes and applications. This provides a wider reach.
- Competitors: This method is popularly known as “poaching” or “raiding” which involves identifying the right people in rival companies, offering them better terms and luring them away. For instance, several executives of HMT left to join Titan Watch Company. There are legal and ethical issues involved in raiding rival firms for potential candidates. From the legal point of view, an employee is expected to join a new organization only after obtaining a ‘no objection certificate’ from his/ her present employer. Violating this requirement shall bind the employee to pay a few months’ salary to his/ her present employer as a punishment. However, there are many ethical issues attached to it.
- Mergers and Acquisitions: When organizations combine, they have a pool of employees, out of whom some may not be necessary any longer. As a result, the new organization has, in effect, a pool of qualified job applicants. As a result, new jobs may be created. Both new and old jobs may be readily staffed by drawing the best-qualified applicants from this employee pool. This method facilitates the immediate implementation of an organization’s strategic plan. It enables an organization to pursue a business plan, However, the need to displace employees and to integrate a large number of them rather quickly into a new organization means that the personnel-planning and selection process becomes critical more than ever.
Information Source: