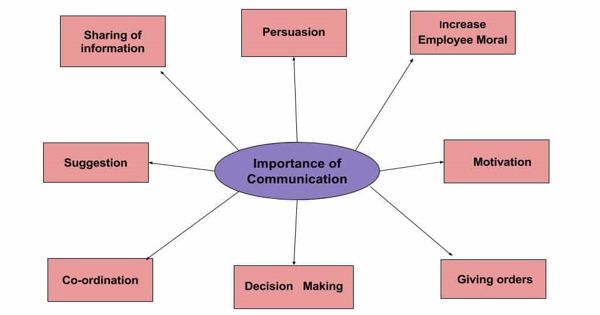
Communication is one of the most important tools in the process of management. Communication and management are closely related to each other. Effective Communication is significant for managers in the organizations so as to perform the basic functions of management, i.e., Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling. Communication is the lifeblood of management.
Having strong communication skills aids in all aspects of life – from professional life to personal life and everything that falls in between. Henry Mintzberg classified the role of managers into the following three (3) main groups where communication is essential:
- Interpersonal Roles
- Informational Roles
- Decisional Roles
(A) Interpersonal Roles: Management is the art of getting things done through others and this objective of management cannot be achieved unless there is the unity of purpose and harmony of effort.
It involves interacting with other people within and outside the organization such as:
- Figure Head: The manager is often asked to serve as figurehead i,e, attending ribbon-cutting ceremonies, or taking visitors to dinner and the like. Although these activities are typically ceremonial they involve communication.
- Leader: The manager acts as a leader i.e., he performs the job of hiring, firing, training, and motivating employees. Leadership can convince the subordinates stating how to do things and how to perform under pressure. Communication through an exchange of views and opinions plays a vital role in this regard.
- Liaison: Such a role involves serving as a co-coordinator or link between persons, groups, or organizations to make effective communication.
(B) Informational roles: Management is the art of getting things done through others and this objective of management cannot be achieved unless there is a unity of purpose and harmony of effort.
It involves the processing of information such as:
- Monitor: Such a role brings a manager to collect relevant information for decision making. For this purpose, the manager questions his subordinates and gets well informed as possible.
- Disseminator: The manager disseminates information to others in the workplace. The manager sends memos that involve new initiatives. Communication facilitates managers to disseminate the decisions.
- Spokesman: Sometimes the manager acts as a spokesman by relaying information to people outside the Organization. For example, the plant manager may represent the Organization before a chamber of commerce or a consumer group.
(C) Decisional roles: Communication is essential for decision-making and planning. It enables the management to secure information without which it may not be possible to take any decision.
- Entrepreneur: Sometimes a manager plays the role of an entrepreneur. He develops new ideas and sells his ideas and therefore exchanges views with others. Communication arises as a vital link between the entrepreneur (Manager) and others.
- Problem Handler: The manager on many occasions appears as a problem handler i,e, handling problems such as strike, blockage, power failure, etc. Here communication is the influencing factor.
- Resource Allocator: A manager takes rational decisions to utilize the limited resources on the basis of justification. This is possible when the manager is aware of the whole scenario of the Organization and communication is the only means here.
- Negotiator: A manager enters into negotiation with an agreement. The manager, for example, may settle the problem between two subordinates and negotiate with another department for additional support. Communication is a must for the manager to play these roles.
An effective and efficient communication system requires managerial proficiency in delivering and receiving messages. A manager must discover various barriers to communication, analyze the reasons for their occurrence and take preventive steps to avoid those barriers.
Information Source: