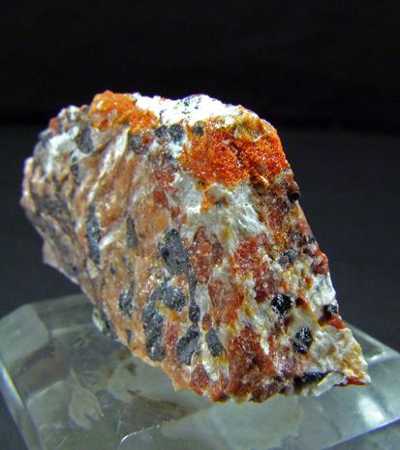
Adelite is a rare arsenic-containing mineral which occurs as colorless to grey or green elongated crystals, often in polycrystalline masses. The rare mineral adelite is a calcium, magnesium, arsenate with chemical formula CaMgAsO4OH. It forms a solid solution series with the vanadium-bearing mineral gottlobite. Various transition metals substitute for magnesium and lead replaces calcium leading to a variety of similar minerals in the adelite – duftite group.
Adelite forms variably colored (blue, green, yellow, and grey) crystals in the orthorhombic crystal system. The form is typically massive. It has a Mohs hardness rating of 5 and a specific gravity of 3.73 to 3.79.
It was first described in 1891 from Värmland, Sweden. Its name comes from the Greek word for indistinct. A basic arseniate of calcium and magnesium, of a grayish color, occurring in embedded grains and rarely in monoclinic crystals: found in Sweden.

Physical Properties
- Cleavage: Indistinct
- Color: Blue-gray, Green, Gray, Yellow, Light green.
- Density: 3.73 – 3.79, Average = 3.76
- Diaphaneity: Transparent
- Fracture: Conchoidal – Fractures developed in brittle materials characterized by smoothly curving surfaces, (e.g. quartz).
- Habit: Massive – Uniformly indistinguishable crystals forming large masses.
- Hardness: 5 – Apatite
- Luminescence: Non-fluorescent.
- Luster: Resinous
- Streak: white
Chemical Properties
- Formula: CaMg(AsO4)(OH)
- IMA Formula: CaMgAsO4 (OH)
- Elements listed: As, Ca, H, Mg, O – search for minerals with similar chemistry
- Common Impurities: Pb, Mn, Na, Cu, Ba
Information Source;