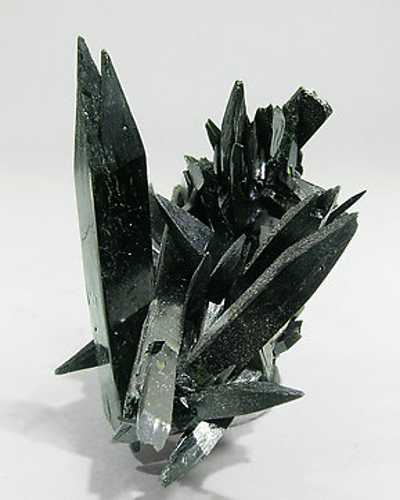
Aegirine is a member of the clinopyroxene group of inosilicates. Aegirine is the sodium endmember of the aegirine-augite series. Aegirine has the chemical formula NaFe3+[ Si2O6] in which the iron is present as Fe3+. In the aegirine-augite series, the sodium is variably replaced by calcium with iron (II) and magnesium replacing the iron(III) to balance the charge. Aluminium also substitutes for the iron (III). It is also known as acmite, which is a fibrous, green-colored variety.
It was first described in 1835 for an occurrence in Rundemyr, Buskerud, Norway. Aegirine was named after the Teutonic god of the sea. A synonym for the mineral is acmite in reference to the typically pointed crystals.
General Information
- Category: Silicate mineral, pyroxene
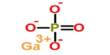
- Formula (repeating unit): NaFe3+[ Si2O6]
- Crystal system: Monoclinic

Identification
- Formula mass: 231.00 g/mol
- Color: Dark Green, Greenish Black
- Crystal habit: Prismatic crystals may be in sprays of acicular crystals, fibrous, in radial concretions
- Luster: Vitreous to slightly resinous
- Diaphaneity: Translucent to opaque
- Specific gravity: 3.50 – 3.60
Aegirine occurs as dark green monoclinic prismatic crystals. It has a glassy luster and perfect cleavage. The Mohs hardness varies from 5 to 6 and the specific gravity is 3.2 to 3.4.
Commonly occurs in alkalic igneous rocks, nepheline syenites, carbonatites, and pegmatites. Also in regionally metamorphosed schists, gneisses, and iron formations; in blueschist facies rocks, and from sodium metasomatism in granulites. It may occur as an authigenic mineral in shales and marls. It occurs in association with potassic feldspar, nepheline, riebeckite, arfvedsonite, aenigmatite, astrophyllite, catapleiite, eudialyte, serandite, and apophyllite.
Physical Properties of Aegirine
- Color: Green, Greenish black, Reddish brown, Black.
- Density: 3.5 – 3.54, Average = 3.52
- Diaphaneity: Subtransparent to translucent to opaque
- Fracture: Brittle – Generally displayed by glasses and most non-metallic minerals.
- Habit: Acicular – Occurs as needle-like crystals.
- Hardness: 6-6.5 – Orthoclase-Pyrite
- Luminescence: Non-fluorescent.
- Streak: yellowish gray
Chemical Properties
- Elements listed: Fe, Na, O, Si – search for minerals with similar chemistry
- Common Impurities: Al,Ti,V,Mn,Mg,Ca,K,Zr,Ce
Information Source: