Carbon Tetrachloride is a clear, colorless, volatile, and very stable chlorinated hydrocarbon. It is an organic compound with the chemical formula CCl4. It is a colorless liquid with a “sweet” smell that can be detected at low levels. It has practically no flammability at lower temperatures. Carbon tetrachloride was produced in large quantities to make refrigerants and propellants for aerosol cans, as a solvent for oils, fats, lacquers, varnishes, rubber waxes, and resins, and as a grain fumigant and a dry cleaning agent.
Carbon tetrachloride is a manufactured chemical and does not occur naturally in the environment. It was used in the production of refrigeration fluid and propellants for aerosol cans, as a pesticide, as a cleaning fluid and degreasing agent, in fire extinguishers, etc.
It is used as a solvent for oils and fats, as a refrigerant, and as a dry-cleaning agent. It was formerly widely used in fire extinguishers, as a precursor to refrigerants, and as a cleaning agent, but has since been phased out because of toxicity and safety concerns. Exposure to high concentrations of carbon tetrachloride (including vapor) can affect the central nervous system and degenerate the liver and kidneys. It is a very poisonous gas when heated in the presence of oxygen, and its use in fire extinguishers has been discontinued. Prolonged exposure can be fatal.
Properties
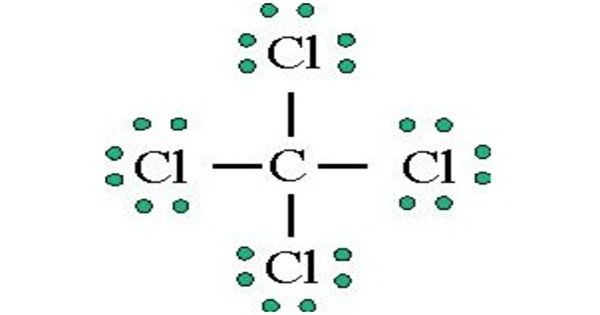
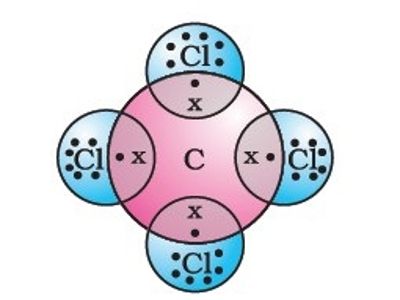
Carbon tetrachloride is a manufactured chemical that does not occur naturally. In the carbon tetrachloride molecule, four chlorine atoms are positioned symmetrically as corners in a tetrahedral configuration joined to a central carbon atom by single covalent bonds. Because of this symmetric geometry, CCl4 is non-polar. Methane gas has the same structure, making carbon tetrachloride a halomethane.
- Melting point: -23°C
- Boiling point: 76-77°C (lit.)
- Density: 1.594 g/mL at 25°C (lit.)
- Vapor density: 5.32 (vs air)
- Vapor pressure: 4.05 psi ( 20°C)
As a solvent, it is well suited to dissolving other non-polar compounds such as fats, and oils. It can also dissolve iodine.
Uses
In organic chemistry, carbon tetrachloride serves as a source of chlorine in the Appel reaction. It is not flammable and does not dissolve in water very easily. It was used in the production of refrigeration fluid and propellants for aerosol cans, as a pesticide, as a cleaning fluid and degreasing agent, in fire extinguishers, and in spot removers.
It is a precursor for chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) gases that have been used as aerosol propellants. One specialty use of carbon tetrachloride is in stamp collecting, to reveal watermarks on postage stamps without damaging them. A small amount of the liquid is placed on the back of a stamp, sitting in a black glass or obsidian tray. The letters or design of the watermark can then be seen clearly.
Information Source: