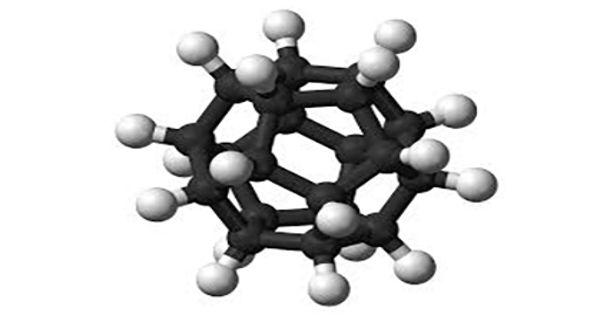
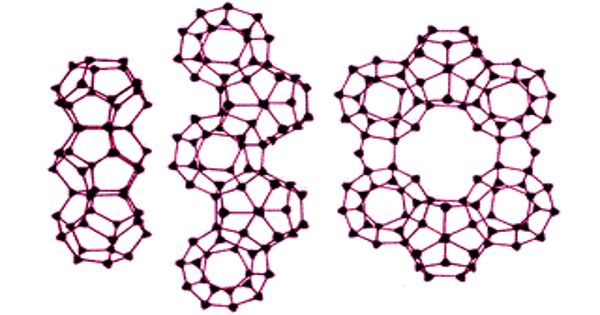
Dodecahedrane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons, CH, having the carbon atoms at the vertices of a regular dodecahedron. It is a chemical compound, a hydrocarbon with the formula C20H20, whose carbon atoms are arranged as the vertices (corners) of a regular dodecahedron. It is a chemical compound first synthesized by Leo Paquette of Ohio State University in 1982, primarily for the “aesthetically pleasing symmetry of the dodecahedral framework”. Each carbon is bound to three neighboring carbon atoms and to a hydrogen atom. This compound is one of the three possible Platonic hydrocarbons, the other two being cubane and tetrahedrane.
Dodecahedrane does not occur in nature and has no significant uses. It is one of the platonic hydrocarbons, the others being cubane and tetrahedrane, and does not occur in nature. It was synthesized by Leo Paquette in 1982, primarily for the “aesthetically pleasing symmetry of the dodecahedral framework”. In this molecule, each vertex is a carbon atom that bonds to three neighboring carbon atoms.
For many years, dodecahedrane was the simplest real carbon-based molecule with full icosahedral symmetry. Several Platonic hydrocarbons have been synthesized, including cubane and dodecahedrane. Buckminsterfullerene (C60), discovered in 1985, also has the same symmetry but has three times as many carbons and 50% more atoms overall.
Structure
The angle between the C-C bonds in each carbon atom is 108°, which is the angle between adjacent sides of a regular pentagon. Each carbon atom is bonded to a hydrogen atom as well. The molecule, like fullerene, has Ih symmetry, evidenced by its proton NMR spectrum in which all hydrogen atoms appear at a single chemical shift of 3.38 ppm. That value is quite close to the 109.5° central angle of a regular tetrahedron—the ideal angle between the bonds on an atom that has (sp3 hybridization. As a result, there is minimal angle strain. In dodecahedrane, a similar effect is observed for the C—H stretching modes, but no external mode peaks are observed. However, the molecule has significant levels of torsional strain as a result of the eclipsed conformation along each edge of the structure. The missing C-C bond is put in place by hydrogen pressurized dehydrogenation with palladium on carbon at 250°C to dodecahedrane 30.
Information Source: