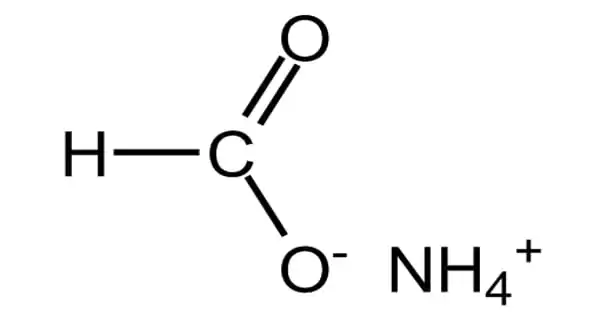
The ammonium salt of formic acid is ammonium formate, NH4HCO2. It is a white substance with a faint ammonia odor. It is a white, crystalline, hygroscopic solid. It is the formic acid ammonium salt. It serves as a barrier. It’s made from formic acid.
When heated, pure ammonium formate decomposes into formamide and water, and this is its principal application in industry. Formic acid can also be made by reacting ammonium formate with a dilute acid, and because ammonium formate is made from formic acid, it can be used to store formic acid.
Properties
- Melting point: 119-121 °C (lit.)
- Boiling point: 103.28°C (rough estimate)
- Density: 1.26 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- Flash point: 104℃
- Solubility H2O: 10 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
- Form: Solid
- Color: White
- Odor: Slight formic acid odour

Reductive amination
Acetone can be transformed into isopropylamine as follows:
CH3C(O)CH3 + 2 HCO2– +NH4 → (CH3)2CHNHCHO + 2 H2O + NH3 + CO
(CH3)2CHNHCHO + H2O → (CH3)2CHNH2 + HCO2H
The Henry reactions are the most prevalent ammonium acetate reactions. In an aqueous solution, it is a chemical substance known as spirit of Mindererus or ammonium acetate, a white, hygroscopic solid formed by the interaction of ammonia and acetic acid.
Uses
Formic acid’s ammonium salt is ammonium formate. When heated, pure ammonium formate decomposes into formamide and water, and this is its principal application in industry. It can also be employed in palladium to reduce the carbon content of functional groups. It is useful for the reductive amination of aldehydes and ketones. It is also used as a buffer in high performance liquid chromatography and can be utilized with liquid chromatography and mass spectroscopy.
Ammonium formate can also be utilized in the reduction of functional groups by palladium on carbon (Pd/C). Ammonium formate decomposes in the presence of Pd/C to hydrogen, carbon dioxide, and ammonia. This hydrogen gas is adsorbed on the palladium metal’s surface, where it can react with various functional groups. Alkenes, for example, can be converted to alkanes, formaldehyde to methanol, and nitro compounds to amines. Hydrogens can also replace activated single bonds to heteroatoms (hydrogenolysis).
Reactions
Ammonium formate removes water when heated, generating formamide. When heated further, it produces hydrogen cyanide (HCN) and water. The breakdown of formamide to carbon monoxide (CO) and ammonia is a byproduct of this process.