Hormones are the chemical messengers of the endocrine system. Hormones are the signals which adjust the body’s internal working, together with the nervous system. Every multicellular organism has hormones. The cells which react to a given hormone have special receptors for that hormone. They affect growth and development, mood, sexual function, reproduction, and metabolism.
Many different kinds of cells can send a message. There are some kinds of cells whose main job is to make hormones. When many of these cells are together in one place, it is called a gland. Glands are groups of cells that make something and release it (put it outside the cell). Many glands make hormones. They are substances produced by your endocrine glands that have a tremendous effect on bodily processes.
The first discovery of a hormone was made in 1902. The hormone was secretin. The word ‘hormone’ was first used in 1905.
Actions
Hormones do many things. They are chemical messengers that are secreted directly into the blood, which carries them to organs and tissues of the body to exert their functions. They regulate metabolism. Metabolism is all of the chemical and energy reactions that happen in a living thing.
Hormones cause the growth and death of cells and of whole organisms. It also start and control sexual development. For example, the hormones estrogen and progesterone make girls go through puberty. Hormones help keep homeostasis in an organism. Homeostasis means to keep a constant state inside the body like temperature, amount of water and salts, and amount of sugar.
Types of hormones
There are four types of hormones in most vertebrates. They are grouped by the chemicals from which they are made.
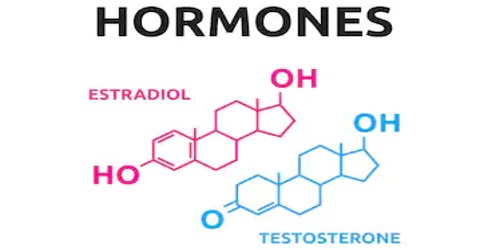
Steroid: these are made from cholesterol. Examples of steroid hormones include the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone as well as the stress hormone cortisol.
Eicosanoids: these are lipid hormones – hormones made from lipids, kinds of fats. These are mostly hormones that send messages near the cell that makes the hormones.
Amino acid-derived: Melatonin works on the brain, and thyroxine acts on almost all cells in the body. Many of these hormones are neurotransmitters, hormones that one nerve cell sends to another nerve cell.
Peptides, polypeptides, and proteins: small peptide hormones include TRH and vasopressin. Peptides composed of scores or hundreds of amino acids are referred to as proteins. Examples of protein hormones include insulin and growth hormone.
Information Source: