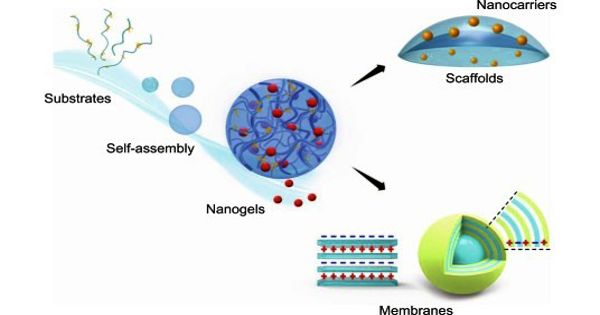
A nanogel is a nanoparticle composed of a hydrogel—a crosslinked hydrophilic polymer network. They are in nanosized range networks of physically or chemically entangled polymeric particles for offering uniform dispersion of the nanocarriers in the matrix gel and augmenting the contact time, which results in enhanced skin penetration of the bioactive. Nanogels are most often composed of synthetic polymers or biopolymers which are chemically or physically crosslinked. They are very promising carriers among other novel drug delivery vehicles for utilization in different therapeutics, diagnostics, macromolecules, and others.
Nanogels are a nanosized hydrogel. A hydrogel is a polymer-based gel that is constructed by crosslinking polymer chains together to form a macromolecular network.
Nanogels are usually in the tens to hundreds of nanometers in diameter. They are nanoparticles composed of a cross-linked hydrophilic polymer network. Like hydrogels, nanogels have a low density of macromolecules and their pores can be filled with small molecules or macromolecules, and their properties, such as swelling, degradation, and chemical functionality, can be controlled. They are swollen nanosized networks composed of amphiphilic or hydrophilic polyionic polymers, either natural or synthetic.
Applications
Potential applications of nanogels include drug delivery agents, contrast agents for medical imaging or 19F MRI tracers, nanoactuators, and sensors. They are established with great efficacy in the treatment of autoimmune disease, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, inflammatory disorders, and so many other disorders. They are very promising carriers among other novel drug delivery vehicles for utilization in different therapeutics, diagnostics, macromolecules, and others.
- Nanogels with cross-linked structures provide a versatile platform for the storage and release of proteins. It is a highly desirable method of loading and delivering active forms of proteins toward cells for remaining activity, enhancing stability, and avoiding potential immunogenicity of proteins.
- Nanogels composed of polyethyleneimine (PEI) has been used to deliver anti-cancer compounds into cells.
- Nanogels found a versatile application in cancer treatment. Multistimuli responsive nanogels are very effective in targeted therapy of cancer as compared to single responsive nanogels.
- Nanogels composed of dextran have been developed for imaging tumor-associated macrophages with radionuclides and targeting the bone.
Nanogels are nanoparticles composed of a hydrogel that is highly cross-linked physically or chemically with hydrophilic polymer chains. They are not to be confused with Nanogel aerogel, a lightweight thermal insulator, or with nanocomposite hydrogels (NC gels), which are nanomaterial-filled, hydrated, polymeric networks that exhibit higher elasticity and strength relative to traditionally made hydrogels. They are usually defined as aqueous dispersions of nanosized polymeric particles formed after physical or chemical cross-linking procedures.
Information Source: