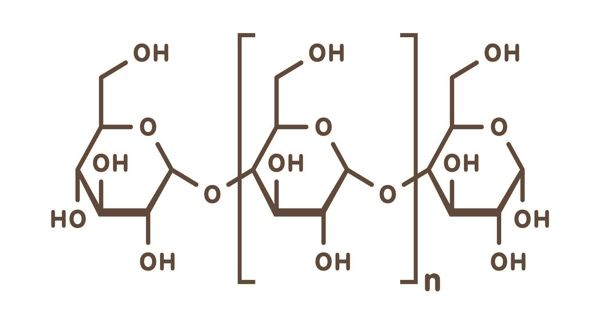
Polysaccharides are major classes of biomolecules. A polysaccharide is a complex carbohydrate. It is a large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. They are polymers made up of many monosaccharides. Monosaccharides are simple sugars, like glucose. They are very large, often branched, molecules. They are long chains of carbohydrate molecules, composed of several smaller monosaccharides. They tend to be amorphous, insoluble in water, and have no sweet taste.
A polysaccharide is a complex carbohydrate. It is a large molecule made of many smaller monosaccharides. The main functions of polysaccharides are structural support, energy storage, and cellular communication
When all the constituent monosaccharides are of the same type they are termed homopolysaccharides; when more than one type of monosaccharide is present they are termed heteropolysaccharides. Depending on which monosaccharides are connected, and which carbons in the monosaccharides connect, polysaccharides take on a variety of forms.
Depending on their structure, polysaccharides can have a wide variety of functions in nature. Some polysaccharides are used for storing energy, some for sending cellular messages, and others for providing support to cells and tissues. They are mostly used in foods to impart viscosity and induce gel formation.
Characteristics of Polysaccharides –
- They are not sweet in taste.
- Many are insoluble in water.
- They do not form crystals on desiccation.
- They are high molecular weight carbohydrates.
- They consist of hydrogen, carbon, and oxygen.
Examples of polysaccharides include storage polysaccharides such as starch and glycogen and structural polysaccharides such as cellulose and chitin. It used for energy storage will give easy access to the monosaccharides, while maintaining a compact structure. It also used for support is usually assembled as a long chain of monosaccharides, which acts as a fiber.
Polysaccharides are the largest component of biomass. It is estimated that more than 90% of the carbohydrate mass in nature is in the form of polysaccharides.
Functions
Many polysaccharides are used to store energy in organisms. While the enzymes that produce energy only work on the monosaccharides stored in a polysaccharide, polysaccharides typically fold together and can contain many monosaccharides in a dense area.
The polysaccharides serve as a structural organization in animals and plants. The main functions of polysaccharides are structural support, energy storage, and cellular communication. Other functions of polysaccharides include:
- They store energy in organisms.
- They allow for changes in the concentration gradient which influences the uptake of nutrients and water by the cells.
- They provide support to the cells. The cell wall of plants is made up of polysaccharide cellulose, which provides support to the cell wall of the plant.
Information Source: