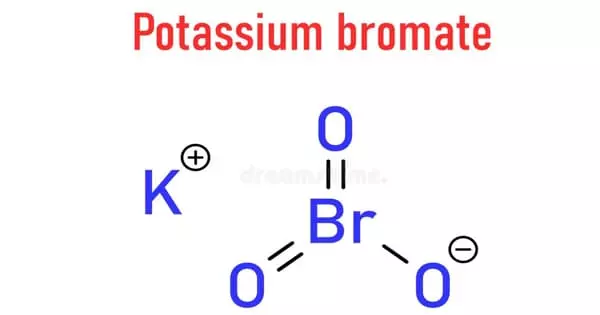
Potassium bromate (KBrO3) is potassium bromate that appears as white crystals or powder. It is a powerful oxidizing agent. It is commonly used as a flour improver in the United States. It strengthens the dough and allows for faster rising. It is an oxidizing agent used as a food additive, primarily in the bread-making process.
In nature, potassium bromate is carcinogenic; it has been linked to kidney, thyroid, and gastrointestinal cancer in animals. Such substances may also have the potential to harm human reproduction.
Properties
Potassium bromate is a white crystal, granules or powder, which is colorless, odorless, and tasteless. It is a white crystalline powder that is soluble in water. It is a potassium and bromate salt and an ionic compound. It is a Lewis acid/base generic complex and a strong oxidizing agent.
- Density: 3.27 g/cm³
- Molecular Weight/ Molar Mass: 167 g/mol
- Boiling Point: 370 °C
- Melting point: 350 °C
- Odour: Odourless
- Appearance: White crystalline powder

Preparation
Bromine can be converted into potassium bromate by passing it through a potassium hydroxide solution. However, the compound is primarily produced through large-scale industrial electrolytic processes.
When bromine is passed through a hot solution of potassium hydroxide, potassium bromate is formed. This first produces unstable potassium hypobromite, which rapidly degrades into bromide and bromate:
3BrO–(aq) → 2Br–(aq) + BrO-3(aq)
Bromate is produced by the electrolysis of potassium bromide solutions. Both processes are similar to those used in the manufacture of chlorates.
Bromine can be converted into potassium bromate by passing it through a hot solution of potassium hydroxide. Potassium bromide and water are also included in the products.
3Br2 + 6KOH = KBrO3 + 5KBr + 3H2O
Because potassium bromate is much less soluble than potassium bromide, it is easily separated from the potassium bromide present in both methods; when a solution containing potassium bromate and bromide is cooled to 0°C, nearly all bromate precipitates while nearly all bromide remains in solution.
Uses
Potassium bromate (KBrO3) is primarily used as a flour maturing agent and dough conditioner. It is widely regarded as one of the best dough conditioners available in the bakery industry. In 1990, scientific evidence emerged implicating bromate as a possible carcinogen. As a result of the potential risks, the United Nations Joint Food and Agricultural Organization and the World Health Organization decided to remove potassium bromide from the list of acceptable flour treatment additives.
- Used as a source of bromine. Standard potassium bromate can be used directly to prepare a standard solution that is stable indefinitely.
- Used as an antiseptic and astringent in toothpaste, mouthwashes and gargles as 3 to 5 percent solution.
- Potassium bromate is used primarily as a conditioner for flour and dough; some of its non-food uses include use as an oxidizing agent for analytic chemistry and as a brominating agent.
Health Hazard
Potassium bromate is a chemical that is moderately toxic. Ingestion results in nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, respiratory stimulation, a drop in body temperature, methemoglobinemia, and renal damage. It has been reported that it causes gum inflammation and bleeding when used in toothpaste.