Rhodium Hexafluoride – an inorganic compound of rhodium and fluorine
Rhodium is a precious, transition metal that is hard and silvery in appearance. A hexafluoride is a chemical compound with the general formula QXnF6, QXnF6m-, or QXnF6m+. Rhodium hexafluoride, also rhodium(VI) fluoride, (RhF6) is the inorganic compound of rhodium and fluorine. A black volatile solid, it is a highly reactive material and a rare example of a rhodium(VI) compound. Precious metals are rare and valuable, and rhodium is one of the rarest elements on Earth. It is one of seventeen known binary hexafluoride. It is also known as a noble metal because it does not corrode or oxidize easily in the air.
Rhodium Hexafluoride is a black volatile solid, it is a highly reactive material and a rare example of a rhodium(VI) compound. Precious metals are rare and valuable, and rhodium is one of the rarest elements on Earth.
Synthesis, structure, properties
There is no biological role for rhodium. It is non-toxic in its pure form but can be toxic as a compound since most compounds are unstable. Rhodium hexafluoride is prepared by reaction of rhodium metal with an excess of elemental fluorine:
Rh + 3 F2 → RhF6
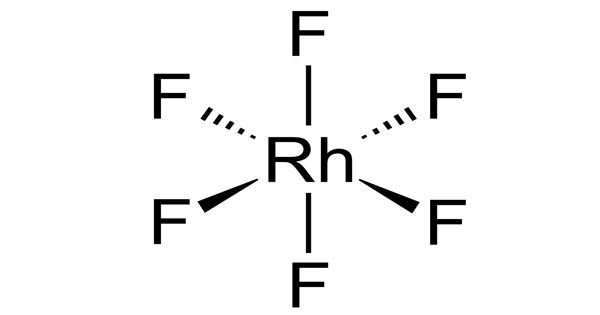
The RhF6 molecule has octahedral molecular geometry. Consistent with its d3 configuration, the six Rh–F bond lengths are equivalent, being 1.824 Å. The chemistries and physics of the molecular hexafluorides are well-developed. The hexafluorides of radioactive elements are insufficiently developed. It crystallizes in an orthorhombic space group Pnma with lattice parameters of a = 9.323 Å, b = 8.474 Å, and c = 4.910 Å. Molecular Weight is 216.8959 g/mol.
Like some other metal fluorides, RhF6 is highly oxidizing. It attacks even glass even in the absence of water. It can even react with elemental oxygen. One of the main uses of rhodium is in alloys with platinum and palladium. The addition of rhodium to alloys makes the metal harder and more resistant to corrosion.