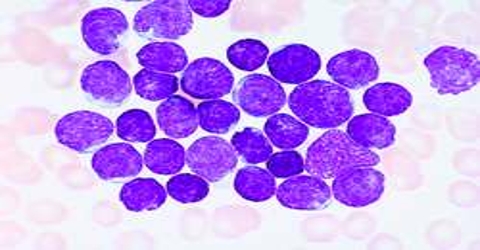
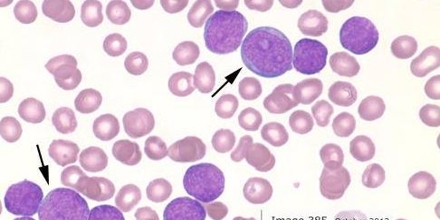
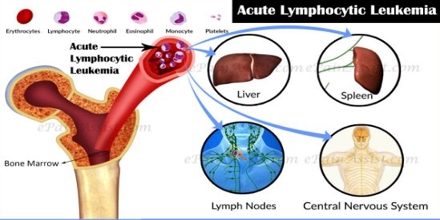
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) is a kind of cancer of the blood and bone marrow — the spongy tissue inside bones where blood cells are prepared. It caused by enhance in white blood cells called lymphocytes. It growth hastily and insistently and requires instant treatment. Both adults and children can be affected.
Causes
Acute lymphocytic leukemia occurs when a bone marrow cell grows errors in its DNA. The errors tell the cell to keep on growing and dividing, when a strong cell would usually stop dividing and ultimately die. When this happens, blood cell creation becomes irregular. The bone marrow produces undeveloped cells that grow into leukemic white blood cells called lymphoblasts. These irregular cells are not capable to occupation suitably, and they can build up and crowd out healthy cells.
General symptoms
Patients with ALL also often have several non-specific symptoms. These can include:
- Bleeding from the gums
- Bone pain
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness, fatigue or a general decrease in energy
Of course, these are not just symptoms of ALL and are more often caused by something other than leukemia.
Risk factors
Factors that may increase the risk of acute lymphocytic leukemia include:
Previous cancer treatment. Children and adults who’ve had assured types of chemotherapy and radiation therapy for other kinds of cancer may have an increased risk of developing acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Genetic disorders. Certain genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, are associated with an increased risk of acute lymphocytic leukemia.
Lymphocytic Leukemia Treatment
Treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia aims to bring your blood count back to regular. If this happens and your bone marrow looks normal under a microscope, your cancer is in reduction.
Chemotherapy is used to care for this type of leukemia. For the first treatment, you may have to be hospitalized for a few weeks. Later, you may be able to continue treatment as an outpatient.
Treatment is usually carried out in the following stages:
- induction – initially, treatment aims to kill the leukaemia cells in your bone marrow, restore the balance of cells in your blood and resolve any symptoms you may have
- consolidation – aims to kill any remaining leukaemia cells in your central nervous system
- maintenance – involves taking regular doses of chemotherapy tablets to prevent the leukaemia returning
In the event you have a low white blood cell count, you’ll most likely have to spend time in an isolation room to ensure protection from contagious diseases and other problems.
Conclusion
Acute lymphocytic leukemia is the mainly ordinary type of cancer in children, and treatments result in a good possibility for a cure. Acute lymphocytic leukemia can also arise in adults, though the possibility of a cure is wholly reduced.
There’s no confirmed cause of acute lymphocytic leukemia. However, you should avoid the risk factors for it, which include:
- radiation exposure
- chemical exposure
- exposure to viral infections
- cigarette smoking
- prolonged exposure to diesel fuel, gasoline, pesticides, and electromagnetic fields.