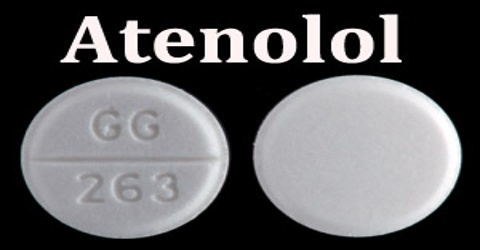
Atenolol
Definition
Atenolol is a synthetic isopropylamino-propanol derivative used as an antihypertensive, hypotensive and antiarrhythmic. Its acts as a peripheral, cardioselective beta blocker specific for beta-1 adrenergic receptors, without intrinsic sympathomimetic effects. It is a synthetic beta blocker, C14H22N2O and also used in the management of hypertension, angina pectoris, and cardiac arrhythmias and, topically, in the treatment of glaucoma.
Atenolol is effective at reducing blood pressure, but recent studies indicate that it does not reduce the morbidity or mortality caused by hypertension, and may even increase mortality in some subgroups. When people take this drug, they get better blood pressure numbers, but they still die of heart attacks and strokes, despite the lower blood pressure.
Atenolol has been given as an example of how slow healthcare providers are to change their prescribing practices in the face of medical evidence that indicates that a drug is ineffective.
Applications and Affects of Atenolol
Atenolol belongs to a class of medication known as beta blockers, which help control cardiovascular diseases by slowing down the heart and reducing its workload, thus lowering the blood pressure.
Atenolol is used alone or together with other medicines (such as hydrochlorothiazide) to treat high blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure adds to the workload of the heart and arteries. If it continues for a long time, the heart and arteries may not function properly. This can damage the blood vessels of the brain, heart, and kidneys, resulting in a stroke, heart failure, or kidney failure. High blood pressure may also increase the risk of heart attacks. It is also used to help prevent chest pain and to decrease the severity of heart attacks.
It is also used to treat heart rhythm disorders such as supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular irregular beats, and it’s sometimes prescribed for alcohol withdrawal, Graves’ disease, and prevention of migraines.
Common Side Effects of Atenolol:
- Constipation, indigestion
- Dizziness or faintness
- Dry mouth
- Impotence
- Cold extremities hands and feet
- Confusion
- Depression
- Insomnia, nightmares
- Edema
- Fatigue, lack of energy
Serious Side Effects of Atenolol:
- Low blood pressure
- Hallucinations
- Sensation of pins and needles
- Skin reactions, rash, hives, psoriasis
- Blurred vision
- Difficulty speaking, or hearing
- Unsteadiness
- Wheezing or noisy breathing
Certain medicines should not be used at or around the time of eating food or eating certain types of food since interactions may occur. Using alcohol or tobacco with certain medicines may also cause interactions to occur.
Reference: