Colpocephaly
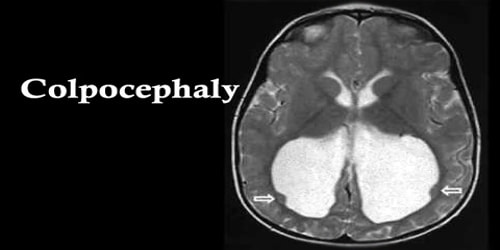
Definition: Colpocephaly is a congenital brain condition where underdeveloped white matter before birth results in abnormally large occipital horns (the rear portion of the lateral cavities of the brain). It is characterized by an abnormally small head, mental retardation, and movement disorders.
It is a nonspecific finding and is associated with multiple neurological syndromes, including agenesis of the corpus callosum, Chiari malformation, lissencephaly, and microcephaly. Although the exact cause of colpocephaly is not known yet, it is commonly believed to occur as a result of neuronal migration disorders during early brain development, intrauterine disturbances, perinatal injuries, and other central nervous system disorders.
Although the cause of colpocephaly is unknown, researchers believe that the disorder results from some kind of disturbance in the fetal environment that occurs between the second and sixth months of pregnancy. Colpocephaly may be diagnosed late in pregnancy when it is often misdiagnosed as hydrocephalus (excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain). It may be more accurately diagnosed after birth, when signs of mental retardation, microcephaly, and seizures are present.
Causes, Sign, and Symptom of Colpocephaly: There is no known definitive single mechanism that causes colpocephaly. However, researchers believe there are many possible causes of colpocephaly. It is a common symptom of other neurological disorders in newborns, can be caused as a result of shunt treatment of hydrocephalus, developmental disorders in premature infants, due to intrauterine disturbances during pregnancy, genetic disorders, underdevelopment or lack of white matter in the cerebrum, and exposure of the mother and the developing fetus to medications, infections, radiation, or toxic substances.
Often colpocephaly occurs as a result of hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus is the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the ventricles or in the subarachnoid space over the brain. The increased pressure due to this condition dilates occipital horns causing colpocephaly.
Colpocephaly is characterized by a small head circumference and in many cases, intellectual disability. Other signs and symptoms may include movement abnormalities, muscle spasms, and seizures. Poor vision, speech and language difficulties, deafness, and chorioretinitis have been described in individual cases. Cases of people with colpocephaly and normal neurological and motor development have also been described.
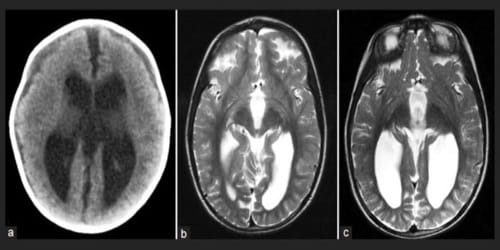
Diagnosis and Treatment of Colpocephaly: Diagnosing colpocephaly prenatally is difficult because in many cases signs start to appear after birth. Prenatal diagnosis is made by detecting enlargement of either or both occipital horns of the lateral ventricles. After birth, MR imaging can be done to look for cephalic abnormalities. This is the most commonly used method for diagnosing colpocephaly.
There is no definitive treatment for colpocephaly. Anticonvulsant medications are often prescribed to prevent seizures, and doctors rely on exercise therapies and orthopedic appliances to reduce shrinkage or shortening of muscles.
The prognosis for individuals with colpocephaly depends on the severity of the associated conditions and the degree of abnormal brain development. Some children benefit from special education.
Stem cell therapy is considered a very promising treatment for patients with colpocephaly. Oligodendroglial cells can be used which will increase the production of myelin and alleviate symptoms of colpocephaly.
Information Source: