The companies’ use of Big Data is becoming common these days to over-perform their peers. Both existing competitors and new entrants in most industries will use the strategies resulting from the analyzed data to compete, innovate, and capture value. In fact, Big Data is a term used to describe a gathering of data that is huge in volume but grows exponentially with time. In short such data is so large and sophisticated that none of the normal data management tools are able to store it or process it efficiently.
Since the 1990s the term “Big Data” has been in use, with some credit given to John Mashey for popularizing the term. Big data usually includes data sets with sizes that go beyond the ability of commonly used software tools to capture, curate, manage, and process data in a tolerable time span. It encourages the associations to make new development openings and completely new classifications of organizations that can consolidate and break down industry information. Enormous information requires a lot of procedures and advances with new types of combinations to uncover bits of knowledge from informational collections that are different, complex, and of huge scope.
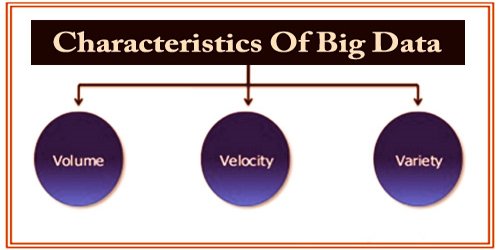
Big data can be described by the following characteristics:
Gartner analyst Doug Laney listed the 3 ‘V’s of Big Data – Variety, Velocity, and Volume. These characteristics, isolatedly, are enough to know what is big data.
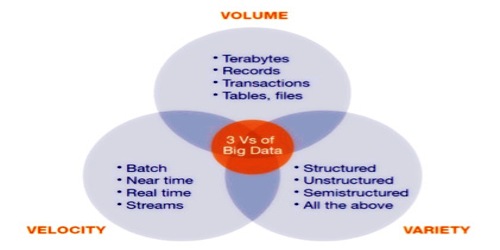
Volume – Volume is one of the big-data features. Organizations gather data from a variety of sources, including business transactions, social media, and sensor or machine to machine information. Data size plays a very important role in determining value from the data. It is also dependent on the volume of data whether or not a particular data can actually be considered as a Big Data. ‘Volume’ is therefore one characteristic that must be taken into account when dealing with ‘Big Data’.
Variety – Big Data variety refers to structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data which is collected from multiple sources. During earlier days, spreadsheets and databases were the only data sources that most of the applications considered. The Big Data advances developed with the prime goal to catch, store, and cycle the semi-organized and unstructured (assortment) information produced with rapid (speed), and colossal in size (volume). Afterward, these apparatuses and advances were investigated and used for dealing with organized information additionally yet best for capacity.
In analytics applications, data in the form of emails, photos, videos, monitoring devices, PDFs, audio, etc. are also being considered. This variety of unstructured data raises some storage, mining, and data analysis issues.
Velocity – The term ‘velocity’ refers to the rate at which data is generated. How quickly the data is generated and processed to meet the demands, determines the data’s real potential. The generation frequency and the frequency of handling, recording, and publishing are two types of velocity related to big data. Big Data Velocity manages the speed at which information streams in from sources like business measures, application logs, systems, and online media locales, sensors, Mobile gadgets, and so forth. The progression of information is huge and persistent.
‘Veracity’ is also the extended definition of big data which refers to the quality of data and the value of data. The quality of the data captured can vary considerably, affecting accurate analysis. Other significant features of Big Data are: exhaustive, fine-grained and unique lexical, Relational, Extensional, Scalability, Value, and Variability.
Information Sources: