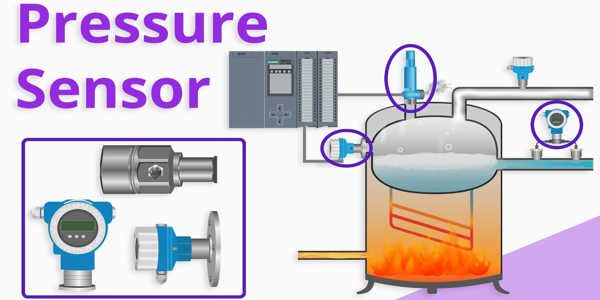
A pressure sensor is a device that measures the pressure of gases or liquids. Pressure is the force required to stop a fluid from expanding, and it is usually expressed in terms of force per unit area. Pressure sensors are used in a variety of industries, including the automotive, biomedical, aviation, and marine industries, to name a few. A pressure sensor is typically used as a transducer, generating a signal as a function of the applied pressure.
Pressure sensors are used in thousands of everyday applications for control and monitoring. Other variables such as fluid/gas flow, speed, water level, and altitude can also be measured indirectly using pressure sensors. Pressure sensors are also known as pressure transducers, pressure transmitters, pressure senders, pressure indicators, piezometers, and manometers.
A pressure sensor is a device that senses pressure and converts it into an electric signal where the amount depends upon the pressure applied. It is a device or instrument which is able to measure the pressure in gases or liquids.
Pressure sensors differ greatly in terms of technology, design, performance, application suitability, and cost. A conservative estimate would be that there are over 50 pressure sensor technologies and at least 300 companies worldwide.
There is also a type of pressure sensor that is designed to measure in a dynamic model in order to capture very fast changes in pressure. This type of sensor could be used to measure combustion pressure in an engine cylinder or in a gas turbine, for example. These sensors are typically made of piezoelectric materials such as quartz.
Types of pressure measurements
Pressure sensors are classified based on the pressure ranges they measure, the temperature ranges at which they operate, and, most importantly, the type of pressure they measure. Pressure sensors are given different names based on their function, but the same technology can be used under different names.
- Absolute pressure sensor
This sensor measures pressure in comparison to a perfect vacuum. Absolute pressure sensors are used in applications that require a constant reference, such as high-performance industrial applications such as vacuum pump monitoring, liquid pressure measurement, industrial packaging, industrial process control, and aviation inspection.
- Gauge pressure sensor
The pressure measured by this sensor is relative to the atmospheric pressure. A tire pressure gauge is an example of gauge pressure measurement; when it reads zero, the pressure being measured is equal to the ambient pressure. Most sensors for measuring up to 50 bar are made in this manner because atmospheric pressure fluctuations (weather) would otherwise be reflected as an error in the measurement result.
- Vacuum pressure sensor
This term can be perplexing. It can refer to a sensor that measures pressures below atmospheric pressure and displays the difference between that low pressure and atmospheric pressure, but it can also refer to a sensor that measures absolute pressure relative to a vacuum.
- Differential pressure sensor
This sensor detects the difference in pressure between two points, one on each side of the sensor. Differential pressure sensors are used to measure a variety of properties, including pressure drops across oil or air filters, fluid levels (by comparing the pressure above and below the liquid), and flow rates (by measuring the change in pressure across a restriction). Most pressure sensors are actually differential pressure sensors; for example, a gauge pressure sensor is simply a differential pressure sensor with one side open to the ambient atmosphere.
- Sealed pressure sensor
This sensor is similar to a gauge pressure sensor, but it measures pressure relative to a fixed pressure rather than the ambient atmospheric pressure (which varies according to the location and the weather).